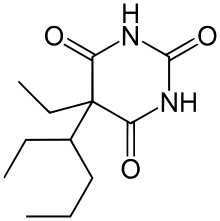
Tetrabarbital
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | None |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 76-23-3 |
| PubChem (CID) | 101534 |
| ChemSpider | 91745 |
| UNII | 3K441526FO |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.861 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H20N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 240.299 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Tetrabarbital (INN; Butysal, Butysedal, Tetramal) is a barbiturate derivative used as a hypnotic.[1][2]
See also
References
- ↑ C. R Ganellin; D. J Triggle; F.. Macdonald (1997). Dictionary of pharmacological agents. CRC Press. p. 842. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. Retrieved 28 November 2011.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2004). "The use of stems in the selection of International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for pharmaceutical substance" (PDF).
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/20/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.