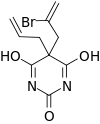
Brallobarbital
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | Brallobarbital |
| CAS Number |
561-86-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 68416 |
| ChemSpider |
61699 |
| UNII |
D0N7A2M3MU |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL2106093 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.387 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H11BrN2O3 |
| Molar mass | 287.110 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Brallobarbital is a barbiturate developed in the 1920s.[1] It has sedative and hypnotic properties, and was used for the treatment of insomnia. Brallobarbital was primarily sold as part of a combination product called Vesparax, composed of 150 mg secobarbital, 50 mg brallobarbital and 50 mg hydroxyzine.[2] The long half-life of this combination of drugs tended to cause a hangover effect the next day,[3] and Vesparax fell into disuse once newer drugs with lesser side effects had been developed.[4]
References
- ↑ US Patent 1869666
- ↑ Lhermann J. Clinical application of a new very active hypnotic associating sodium secobarbital, calcium brallobarbital and hydroxyzine (UC-8130). Gazette Medicale de France. 1964 Mar 10;71:961-2. (French)
- ↑ Yih TD, Rossum JM. Peculiar pharmacokinetics of brallobarbital as a source of complications in Vesparax intoxication. Xenobiotica. 1976 Jun;6(6):355-62.
- ↑ Fischbach R. Efficacy and safety of midazolam and vesparax in treatment of sleep disorders. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 1983;16 Suppl 1:167S-171S.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.