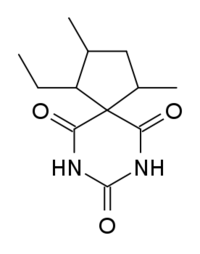
Spirobarbital
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | 5-spiro-(2'-ethyl-3'-5'-dimethyl-cyclopentyl)barbituric acid |
| CAS Number |
12262-77-0 |
| UNII |
LR477QH2IL |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H18N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 238.282 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| (verify) | |
Spirobarbital is a barbiturate derivative developed by Eli Lilly in the 1940s.[1] It has hypnotic and sedative effects, and has a moderate potential for abuse.[2]
References
- ↑ US Patent 2561688
- ↑ Isbell H, Chrusciel TS. Dependence Liability of Non-Narcotic Drugs. Bulletin of the World Health Organisation 1970; 43: Supplement.
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/11/2014. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.