Ubenimex
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoic acid | |
| Other names
Bestatin; N-[(2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyryl]-L-leucine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 58970-76-6 65391-42-6 (HCl) | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL29292 |
| ChemSpider | 65145 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.055.917 |
| PubChem | 72172 |
| UNII | I0J33N5627 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H24N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 308.38 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 245 °C (473 °F; 518 K) (decomposes) |
| Hazards | |
| S-phrases | S22 S24/25 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Ubenimex (INN), also known more commonly as bestatin, is a competitive, reversible protease inhibitor. It is an inhibitor of arginyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase B),[2] leukotriene A4 hydrolase (a zinc metalloprotease that displays both epoxide hydrolase and aminopeptidase activities),[3] alanyl aminopeptidase (aminopeptidase M/N),[4] leucyl/cystinyl aminopeptidase (oxytocinase/vasopressinase),[5][6] and membrane dipeptidase (leukotriene D4 hydrolase). It is being studied for use in the treatment of acute myelocytic leukemia.[7] It is derived from Streptomyces olivoreticuli.[8] Ubenimex has been found to inhibit the enzymatic degradation of oxytocin, vasopressin, enkephalins, and various other peptides and compounds.
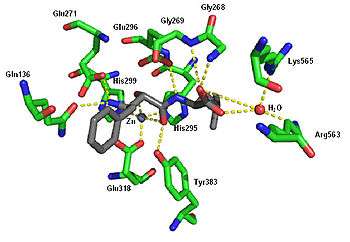
Crystal structure of ubenimex in the binding pocket of leukotriene A4 hydrolase. Rendered from PDB 1HS6.
See also
References
- ↑ N-((2S,3R)-3-Amino-2-hydroxy-4-phenylbutyryl)-L-leucine at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Umezawa,H.; Aoyagi,T.; Suda,H.; Hamada,M.; Takeuchi,T. (1976). "Bestatin, an inhibitor of aminopeptidase B, produced by actinomycetes." (29): 97–99.
- ↑ Muskardin,D.T.; Voelkel,N.F.; Fitzpatrick,F.A. (1994). "Modulation of pulmonary leukotriene formation and perfusion pressure by Bestatin, an inhibitor of leukotriene A4 hydrolase." (48): 131–137.
- ↑ K Sekine; H Fujii; F Abe (1999). "Induction of apoptosis by Bestatin (ubenimex) in human leukemic cell lines". 13 (5): 729–734.
- ↑ Nakanishi Y, Nomura S, Okada M, Ito T, Katsumata Y, Kikkawa F, Hattori A, Tsujimoto M, Mizutani S (2000). "Immunoaffinity purification and characterization of native placental leucine aminopeptidase/oxytocinase from human placenta". Placenta. 21 (7): 628–34. doi:10.1053/plac.2000.0564. PMID 10985965.
- ↑ Naruki M, Mizutani S, Goto K, Tsujimoto M, Nakazato H, Itakura A, Mizuno K, Kurauchi O, Kikkawa F, Tomoda Y (1996). "Oxytocin is hydrolyzed by an enzyme in human placenta that is identical to the oxytocinase of pregnancy serum". Peptides. 17 (2): 257–61. doi:10.1016/0196-9781(95)02124-8. PMID 8801531.
- ↑ Hirayama, Y; Sakamaki, S; Takayanagi, N; Tsuji, Y; Sagawa, T; Chiba, H; Matsunaga, T; Niitsu, Y (2003). "Chemotherapy with ubenimex corresponding to patient age and organ disorder for 18 cases of acute myelogeneous leukemia in elderly patients--effects, complications and long-term survival". Gan to kagaku ryoho. Cancer & chemotherapy. 30 (8): 1113–8. PMID 12938265.
- ↑ Bauvois, B; Dauzonne, D (January 2006). "Aminopeptidase-N/CD13 (EC 3.4.11.2) inhibitors: Chemistry, biological evaluations, and therapeutic prospects". Medicinal Research Reviews. 26 (1): 88–130. doi:10.1002/med.20044. PMID 16216010.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.