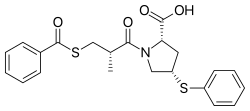
Zofenopril
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | C09AA15 (WHO) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
81872-10-8 |
| PubChem (CID) | 92400 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 6462 |
| ChemSpider |
83422 |
| UNII |
290ZY759PI |
| KEGG |
D08688 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:78539 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL331378 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H23NO4S2 |
| Molar mass | 429.552 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Zofenopril (INN) is a medication that protects the heart and helps reduce high blood pressure. It is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor.[1]
In small studies, zofenopril appeared significantly more effective in reducing hypertension than two older antihypertensive drugs, atenolol and enalapril, and was associated with fewer adverse effects.[2][3]
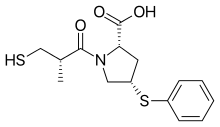
Zofenoprilat — the active metabolite of zofenopril
References
- ↑ Ambrosioni E (2007). "Defining the role of zofenopril in the management of hypertension and ischemic heart disorders". Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 7 (1): 17–24. doi:10.2165/00129784-200707010-00002. PMID 17355163.
- ↑ Nilsson P (October 2007). "Antihypertensive efficacy of zofenopril compared with atenolol in patients with mild to moderate hypertension". Blood Press Suppl. 2: 25–30. PMID 18046976.
- ↑ Mallion JM (October 2007). "An evaluation of the initial and long-term antihypertensive efficacy of zofenopril compared with enalapril in mild to moderate hypertension". Blood Press Suppl. 2: 13–8. PMID 18046974.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.