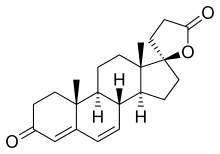
Canrenone
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Contaren, Luvion, Phanurane, Spiroletan |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | C03DA03 (WHO) |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Biological half-life | 10–35 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | RP-11614, SC-9376 |
| CAS Number |
976-71-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 13789 |
| ChemSpider |
13192 |
| UNII |
78O20X9J0U |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1463345 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H28O3 |
| Molar mass | 340.456 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Canrenone (INN, USAN) (brand names Contaren, Luvion, Phanurane, Spiroletan), also known as aldadiene,[1] is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid and weak antiandrogen and progestogen[2][3] of the spirolactone group related to spironolactone which is or has been used as a diuretic in Europe, including in Italy and Belgium.[4][5][6]
Canrenone is an active metabolite of spironolactone, canrenoic acid, and potassium canrenoate, and is believed to be partially or largely responsible for their effects (depending on the drug in question).[7]
Canrenone is more potent as an antimineralocorticoid relative to spironolactone, but is considerably less potent and effective as an antiandrogen.[8][9] Similarly to spironolactone, canrenone inhibits steroidogenic enzymes such as 11β-hydroxylase, cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme, 17α-hydroxylase, and 21-hydroxylase, but once again, is comparatively less potent in doing so.[10]
Canrenone has been found to be effective in the treatment of hirsutism in women.[11]
See also
References
- ↑ Jürg Müller (6 December 2012). Regulation of Aldosterone Biosynthesis: Physiological and Clinical Aspects. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 164–. ISBN 978-3-642-83120-1.
- ↑ Losert, W; Casals-Stenzel, J; Buse, M (1985). "Progestogens with antimineralocorticoid activity". Arzneimittelforschung. 35 (2): 459–71. PMID 4039568.
- ↑ Fernandez, MD; Carter, GD; Palmer, TN (1983). "The interaction of canrenone with oestrogen and progesterone receptors in human uterine cytosol". Br J Clin Pharmacol. 15 (1): 95–101. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01470.x. PMC 1427833
 . PMID 6849751.
. PMID 6849751. - ↑ Hill, R.A.; Makin, H.L.J.; Kirk, D.N.; Murphy, G.M. (23 May 1991). Dictionary of Steroids. CRC Press. pp. 656–. ISBN 978-0-412-27060-4.
- ↑ Romanelli, RG; Gentilini, P (May 2004). "Cross reactivity due to positive canrenone interference". Gut. 53 (5): 772–3. PMC 1774040
 . PMID 15082604.
. PMID 15082604. - ↑ Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 167–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ↑ Clark, Michelle A.; Harvey, Richard A.; Finkel, Richard; Rey, Jose A.; Whalen, Karen (15 December 2011). Pharmacology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 286–. ISBN 978-1-4511-1314-3.
- ↑ Coelingh Benni, H.J.T.; Vemer, H.M. (15 December 1990). Chronic Hyperandrogenic Anovulation. CRC Press. pp. 152–. ISBN 978-1-85070-322-8.
- ↑ Seldin, Donald W.; Giebisch, Gerhard H. (23 September 1997). Diuretic Agents: Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology. Academic Press. pp. 630–. ISBN 978-0-08-053046-8.
- ↑ Colby HD (1981). "Chemical suppression of steroidogenesis". Environ. Health Perspect. 38: 119–27. doi:10.1289/ehp.8138119. PMC 1568425
 . PMID 6786868.
. PMID 6786868. - ↑ Sobbrio, GA; Granata, A; Panacea, A; Trimarchi, F (1989). "Effectiveness of short term canrenone treatment in idiopathic hirsutism". Minerva Endocrinol. 14 (2): 105–8. PMID 2761494.
| Sulfonamides (and etacrynic acid) |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium-sparing (at CD) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Osmotic diuretics (PT, DL) | |||||||||||||||
| Vasopressin receptor inhibitors (DCT and CD) | |||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Mineralocorticoids |
|
|---|---|
| Antimineralocorticoids | |
| Synthesis modifiers | |
See also: Androgens and antiandrogens • Estrogens and antiestrogens • Progestogens and antiprogestogens • Glucocorticoids and antiglucocorticoids | |
| AR |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPRC6A |
| ||||||||||
See also: Estrogenics • Glucocorticoidics • Mineralocorticoidics • Progestogenics • Steroid hormone metabolism modulators • List of androgens/anabolic steroids | |||||||||||
| MR |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
See also: Androgenics • Estrogenics • Glucocorticoidics • Progestogenics • Steroid hormone metabolism modulators | |||||||
| PR |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mPRs (PAQRs) |
| ||||||||||
See also: Androgenics • Estrogenics • Glucocorticoidics • Mineralocorticoidics • Steroid hormone metabolism modulators | |||||||||||
| HMGCR | |
|---|---|
| FPS | |
| 24-DHCR24 |
|
| 20,22-Desmolase (P450scc) |
|
| 17α-Hydroxylase, 17,20-Lyase |
|
| 3α-HSD | |
| 3β-HSD | |
| 11β-HSD |
|
| 21-Hydroxylase |
|
| 11β-Hydroxylase |
|
| 18-Hydroxylase |
|
| 17β-HSD |
|
| 5α-Reductase |
|
| Aromatase |
|
| SST/EST |
|
| STS |
|
| 27-Hydroxylase | |
| Others |
|
See also: Androgenics • Estrogenics • Glucocorticoidics • Mineralocorticoidics • Progestogenics | |