Yamagata, Yamagata
| Yamagata 山形市 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Special city | |||
|
Downtown Yamagata, on the Yamagataekimae Ōdōri (Prefectural Road 16) | |||
| |||
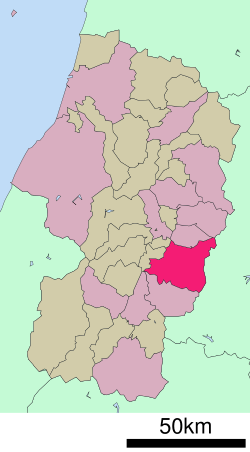 Location of Yamagata in Yamagata Prefecture | |||
 Yamagata
| |||
| Coordinates: 38°15′19.5″N 140°20′22.6″E / 38.255417°N 140.339611°ECoordinates: 38°15′19.5″N 140°20′22.6″E / 38.255417°N 140.339611°E | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Tōhoku | ||
| Prefecture | Yamagata Prefecture | ||
| Government | |||
| • -Mayor | Takahiro Satō | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 381.30 km2 (147.22 sq mi) | ||
| Population (October 2015) | |||
| • Total | 252,632 | ||
| • Density | 663/km2 (1,720/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | Japan Standard Time (UTC+9) | ||
| - Tree | Japanese Rowan | ||
| - Flower | Safflower | ||
| Phone number | 023-641-1212 | ||
| Address | 2-3-25 Hatagomachi, Yamagata-shi, Yamagata-ken 990-8540 | ||
| Website | Official website | ||

Yamagata (山形市 Yamagata-shi) is the capital city of Yamagata Prefecture located in the Tōhoku region of northern Japan.
As of October 2015, the city had an estimated population of 252,632 and a population density of 663 persons per km². The total area was 381.3 square kilometres (147 sq mi).
Geography
Yamagata is located in mountainous southeast Yamagata Prefecture. The Mogami River passes through the city, which includes Mount Zaō within its borders.
Neighboring municipalities
- Yamagata Prefecture
- Miyagi Prefecture
Climate
Yamagata City falls within the northern extremity of the humid subtropical climate transitioning into humid continental in the north. This climate zone is characterized by hot, humid summers with daytime temperatures commonly higher than 30 °C (86 °F) and moderately long, cold and very snowy winters. Yamagata city is part of the heavy snow area of Japan (Gosetsu chitai, 豪雪地帯) with snowfall most days throughout the winter season.
Yamagata City is located in a wide central valley that can heat up quickly in spring and summer and is often grey and humid, while to the east in Miyagi Prefecture on the Pacific coast it is usually clearer and more temperate.
| Climate data for Yamagata, Yamagata (1981-2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 3.1 (37.6) |
4.0 (39.2) |
8.4 (47.1) |
16.2 (61.2) |
22.0 (71.6) |
25.4 (77.7) |
28.4 (83.1) |
30.4 (86.7) |
25.2 (77.4) |
19.0 (66.2) |
12.2 (54) |
6.4 (43.5) |
16.72 (62.11) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −0.4 (31.3) |
0.1 (32.2) |
3.5 (38.3) |
10.1 (50.2) |
15.7 (60.3) |
19.8 (67.6) |
23.3 (73.9) |
24.9 (76.8) |
20.1 (68.2) |
13.6 (56.5) |
7.4 (45.3) |
2.6 (36.7) |
11.73 (53.11) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −3.4 (25.9) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
4.5 (40.1) |
10.1 (50.2) |
15.2 (59.4) |
19.4 (66.9) |
20.7 (69.3) |
16.2 (61.2) |
9.2 (48.6) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
7.53 (45.58) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 83.0 (3.268) |
62.7 (2.469) |
68.6 (2.701) |
68.4 (2.693) |
75.4 (2.969) |
110.5 (4.35) |
157.0 (6.181) |
150.8 (5.937) |
127.2 (5.008) |
92.4 (3.638) |
84.5 (3.327) |
82.7 (3.256) |
1,163.2 (45.797) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 148 (58.3) |
125 (49.2) |
57 (22.4) |
3 (1.2) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
10 (3.9) |
77 (30.3) |
420 (165.3) |
| Average snowy days | 26.6 | 22.2 | 16.5 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.2 | 18.5 | 90.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 81 | 77 | 69 | 62 | 65 | 72 | 77 | 75 | 77 | 77 | 78 | 80 | 74.2 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 84.8 | 98.9 | 140.3 | 176.1 | 191.5 | 158.8 | 143.7 | 178.4 | 128.7 | 132.1 | 99.2 | 80.7 | 1,613.2 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
- Yamagata registered the highest temperature ever recorded in Japan (40.8 °C or 105.4 °F on July 25, 1933) until the record was broken by two cities (40.9 °C or 105.6 °F in Kumagaya, Saitama and Tajimi, Gifu) on August 16, 2007[1]
History
The area of present-day Yamagata was part of Dewa Province. During the Edo period, it was the center of Yamagata Domain under the Tokugawa shogunate. The modern city of Yamagata was founded on April 1, 1889 as the capital of Yamagata Prefecture. The city attained Special city status on April 1, 2001.
Education
- Yamagata University, including Kojirakawa Campus (Faculty of Literature & Social Science, the Faculty of Science and the Faculty of Education, Art & Science) and Iida Campus (Faculty of Medicine, School of Nursing and University Hospital).
- Yamagata Prefectural University of Health Sciences
- Tohoku University of Art & Design
- Tohoku Bunkyo College
- Yamagata has 36 elementary schools, 15 middle schools, 14 high schools and three special education schools.
Transportation
Railway
- JR East - Yamagata Shinkansen
- JR East - Ōu Main Line
- Zaō - Yamagata - Kita-Yamagata - Uzen-Chitose - Minami-Dewa - Urushiyama]
- JR East - Senzan Line
- JR East - Aterazawa Line
Highway
- Tōhoku Chūō Expressway: Yamagata-chūō, Yamagata-Kaminoyama interchanges
- Yamagata Expressway: Yamagata-Zaō, Yamagata-kita, Sekizawa interchanges
- National Route 13
- National Route 48
- National Route 112
- National Route 112
- National Route 286
- National Route 348
- National Route 458
Culture
Local events
- Hanagasa festival (花笠祭り Hanagasa Matsuri) - one of Tōhoku's major summer festivals, is held in the city every August 5, 6 and 7. Yamagata also hosts the bi-annual Yamagata International Documentary Film Festival. An autumn tradition is Imoni-kai (taro potato party). Taro potatoes, thin-sliced meat, and vegetables are cooked in a large pot at picnic spots. The banks of the Mamigasaki River are popular. Once a year, on the first Sunday in September, the city government serves thousands of bowls from its giant iron pot, which is serviced by a building crane. In 2009, 30,000 servings were prepared and served, and still a crowd waited in line.[2]
Local attractions
- Yama-dera (Ryushaku-ji) lies within the city limits, 15 minutes by train from the center.
- Kajo Park, located in the city center of town northwest of the train station, is the extensive grounds of castle keep of feudal warlord Mogami Yoshiaki. While most of the park is athletic fields and public function buildings, the rebuilt walls, eastern main gate, and surrounding moat of the former castle are impressive. The Mogami Yoshiaki Historical Museum nearby features items from the Edo period, and information on these exhibits and the history of the castle town. It also contains a small public museum with displays of natural and social history.
- Yamagata Museum of Art.
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Yamagata is twinned with the following towns and cities.[3]
- Domestic
-
 Izu Ōshima (since 1978)[3]
Izu Ōshima (since 1978)[3] -
 Kami, Miyagi (since 1989)[3]
Kami, Miyagi (since 1989)[3]
- International
-
 Kitzbühel, Tyrol, Austria (since 1963)[3][4]
Kitzbühel, Tyrol, Austria (since 1963)[3][4] -
 Swan Hill, Victoria, Australia (since 1980)[3]
Swan Hill, Victoria, Australia (since 1980)[3] -
 Jilin City, Jilin, China (since 1983)[3]
Jilin City, Jilin, China (since 1983)[3] -
 Ulan-Ude, Buryatia, Russia (since 1991)[3]
Ulan-Ude, Buryatia, Russia (since 1991)[3] -
 Boulder, Colorado, United States (since 1994)[3][5]
Boulder, Colorado, United States (since 1994)[3][5] -
 Khorramabad, Iran (since 2009)[6]
Khorramabad, Iran (since 2009)[6]
Notable people from Yamagata
- Yoshiharu Abe, musician
- Joji Kato, speed skater
- Yuko Oga, basketball player
- Shozo Sasahara, wrestler
- Chihiro Suzuki, voice actor
- Miyuki Takahashi, volleyball player
- Eriko Watanabe, actress
References
- ↑ 河北新報 (Kahoku Shimpō newspaper) page 1; August 17, 2007.
- ↑ Yamagata Shinbun Newspaper, Sept.7, 2009
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 山形市の友好姉妹都市 [Yamagata City Twin Cities] (in Japanese). Japan: Yamagata City. Retrieved 12 October 2011.
- ↑ "Partnerstädte". Stadtgemeinde Kitzbühel (in German). Retrieved 2008-08-04.
- ↑ "Boulder Sister City Program". City of Boulder, Colorado. Retrieved September 9, 2011.
- ↑ لرستان و یاماگاتای ژاپن خواهرخوانده شدند [Kayhan newspaper] (in Persian). iran.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yamagata, Yamagata. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Yamagata. |
- Official website (Japanese)


