Solar eclipse of November 13, 2012
| Solar eclipse of November 13, 2012 | |
|---|---|
|
Totality as seen from Mount Carbine, Queensland | |
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | -0.3719 |
| Magnitude | 1.05 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 242 sec (4 m 2 s) |
| Coordinates | 40°00′S 161°18′W / 40°S 161.3°W |
| Max. width of band | 179 km (111 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| (P1) Partial begin | 19:37:58 |
| (U1) Total begin | 20:35:08 |
| Greatest eclipse | 22:12:55 |
| (U4) Total end | 23:48:24 |
| (P4) Partial end | 0:45:34 |
| References | |
| Saros | 133 (45 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9536 |
A total solar eclipse took place on 13–15 November 2012 (UTC). Because it crossed the International Date Line it began in local time on November 14 west of the date line over northern Australia, and ended in local time on November 13 east of the date line near the west coast of South America. Its greatest magnitude was 1.0500, occurring only 12 hours before perigee, with greatest eclipse totality lasting just over four minutes. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
Visibility
For this eclipse, totality was visible from northern Australia to about 4° north of the Chilean Juan Fernández Islands in the southern Pacific Ocean where totality ended. The most populous city to experience totality was Cairns, which had 2 minutes of totality an hour after daybreak (06:39 AEST, 20:39 UTC) with the sun at an altitude of 14°.[1] Norfolk Island, a small Pacific island east of Australia, experienced a partial eclipse with a maximum of 98% of the sun obscured at 09:37 NFT and an altitude of 42°.
New Zealand experienced a partial eclipse. Auckland had 87.0% of the sun obscured, whereas Wellington, Christchurch and Dunedin respectively had 76.4%, 68.9% and 61.5% of the sun obscured. Maximum eclipse over New Zealand occurred around 10:30 NZDT (21:30 UTC), with Auckland at 10:28, Wellington at 10:34, Christchurch at 10:35 and Dunedin at 10:36.[2][3]
Most of Chile and parts of Argentina saw a partial eclipse at sunset. In some places over half the sun was obscured. In Chile, Valdivia in Los Ríos saw 63% obscured, Quellón in Los Lagos saw 54% obscured. Chilean coastal locations were ideally situated to observe an eclipsing sunset over the Pacific Ocean. Points further north, up to about La Serena, saw the eclipse begin as the sun was setting.
West of the International Date Line the eclipse took place on the morning of November 14. The maximum eclipse totality, of duration 4 min 2 sec, occurred east of the International Date Line on November 13, approximately 2000 km east of New Zealand, and 9600 km west of Chile.
On the morning of November 14, skies in Auckland were cloudy, obscuring much of the eclipse, which peaked at 10:28 NZDT.[4] Cloud also obscured the moment of totality at Cairns, disappointing many tourists that had flocked to the area. Eclipse chasers along the northern beaches up through to Port Douglas generally got a clear view however. Morning November 15 from South Pole
Photo gallery
 Screen capture of NASA video as seen from northern Australia
Screen capture of NASA video as seen from northern Australia Video of total eclipse in Australia
Video of total eclipse in Australia Totality from East Arnhem Region at 22:05:48 UTC
Totality from East Arnhem Region at 22:05:48 UTC- Totality with Diamond ring effect from Ellis Beach, Queensland
 Tauranga, New Zealand at 22:15 UTC
Tauranga, New Zealand at 22:15 UTC Tauranga, New Zealand at 22:15 UTC
Tauranga, New Zealand at 22:15 UTC Tauranga, New Zealand at 22:15 UTC
Tauranga, New Zealand at 22:15 UTC Auckland, New Zealand, time lapse images
Auckland, New Zealand, time lapse images Ubirr, Kakadu National Park at 22:20:05 UTC
Ubirr, Kakadu National Park at 22:20:05 UTC
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 2011-2014
Each member in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit. Note: Partial solar eclipses on January 4, 2011, and July 1, 2011, occur in the previous semester series.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2011–14 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||
| Saros | Map | Saros | Map | |
| 118 | June 1, 2011 Partial |
123 | November 25, 2011 Partial | |
128 Middlegate, Nevada |
May 20, 2012 Annular |
133 Ellis Beach, Queensland |
November 13, 2012 Total | |
| 138 Churchills Head, Australia |
May 10, 2013 Annular |
143 Partial from Accra, Ghana |
November 3, 2013 Hybrid | |
| 148 | April 29, 2014 Annular |
153 Partial from Minneapolis |
October 23, 2014 Partial | |
Saros 133
Solar Saros 133, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, contains 72 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on July 13, 1219. It contains annular eclipses from November 20, 1435, through January 13, 1526, with a hybrid eclipse on January 24, 1544. It has total eclipses from February 3, 1562, through June 21, 2373. The series ends at member 72 as a partial eclipse on September 5, 2499. The longest duration of totality was 6 minutes, 50 seconds on August 7, 1850.[5] The total eclipses of this saros series are getting shorter and farther south with each iteration.
| Series members 30-49 occur between 1742 and 2100 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
| June 3, 1742 | June 13, 1760 |  June 24, 1778 |
| 33 | 34 | 35 |
| July 4, 1796 | July 17, 1814 | July 27, 1832 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 |
| August 7, 1850 |  August 18, 1868 |
 August 29, 1886 |
| 39 | 40 | 41 |
 September 9, 1904 |
 September 21, 1922 |
 October 1, 1940 |
| 42 | 43 | 44 |
 October 12, 1958 |
 October 23, 1976 |
 November 3, 1994 |
| 45 | 46 | 47 |
 November 13, 2012 |
 November 25, 2030 |
 December 5, 2048 |
| 48 | 49 | 50 |
 December 17, 2066 |
 December 27, 2084 |
January 8, 2103 |
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Inex series members between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
 January 14, 1926 (Saros 130) |
 December 25, 1954 (Saros 131) |
 December 4, 1983 (Saros 132) |
 November 13, 2012 (Saros 133) |
 October 25, 2041 (Saros 134) |
 October 4, 2070 (Saros 135) |
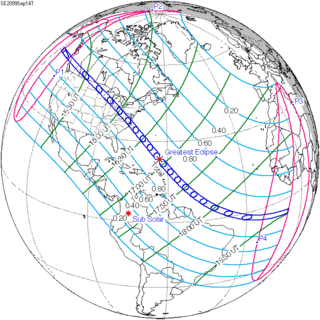 September 14, 2099 (Saros 136) |
||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 21 eclipse events between June 21, 1982, and June 21, 2058 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| June 21 | April 8-9 | January 26 | November 13-14 | September 1-2 |
| 117 | 119 | 121 | 123 | 125 |
 June 21, 1982 |
 April 9, 1986 |
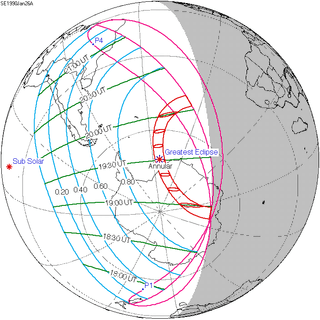 January 26, 1990 |
 November 13, 1993 |
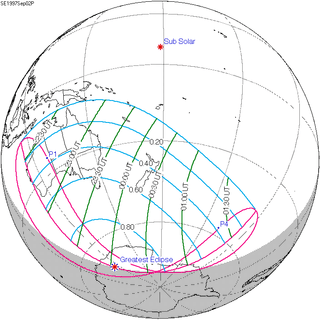 September 2, 1997 |
| 127 | 129 | 131 | 133 | 135 |
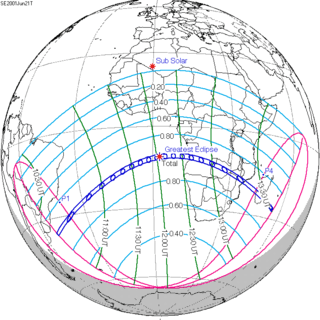 June 21, 2001 |
 April 8, 2005 |
 January 26, 2009 |
 November 13, 2012 |
 September 1, 2016 |
| 137 | 139 | 141 | 143 | 145 |
 June 21, 2020 |
 April 8, 2024 |
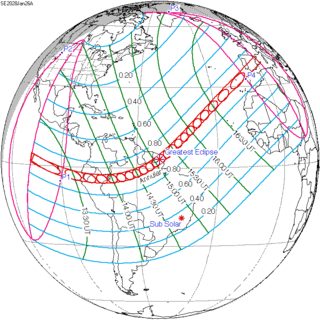 January 26, 2028 |
 November 14, 2031 |
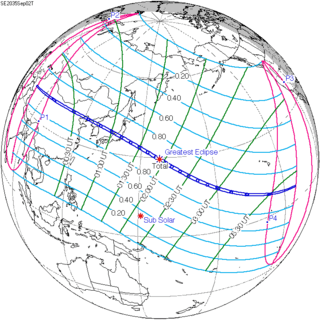 September 2, 2035 |
| 147 | 149 | 151 | 153 | 155 |
 June 21, 2039 |
 April 9, 2043 |
 January 26, 2047 |
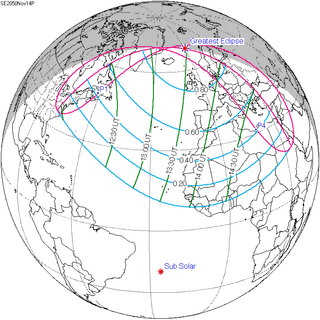 November 14, 2050 |
 September 2, 2054 |
| 157 | ||||
 June 21, 2058 | ||||
References
- ↑ "Eclipse Calculator – Solar Eclipses in Cairns, Queensland, Australia". Time and Date AS. Retrieved 13 November 2012.
- ↑ "Future solar eclipses in New Zealand". Royal Astronomical Society of New Zealand. Retrieved 6 November 2012.
- ↑ Total Solar Eclipse of 2012 November 14 in Australia Xavier M. Jubier
- ↑ "New Zealanders treated to solar eclipse". 3 News NZ. 14 November 2012.
- ↑ http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEsaros/SEsaros133.html
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Solar eclipse of 2012 November 13. |
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- www.eclipser.ca: Jay Anderson 2012 November 13 Total Solar Eclipse
- timeanddate.com Nov 13 - Nov 14, 2012 Total Solar Eclipse — Animated eclipse viewer
- NASA video of eclipse, shot in northern Australia
