Optic chiasm
| Optic chiasma | |
|---|---|
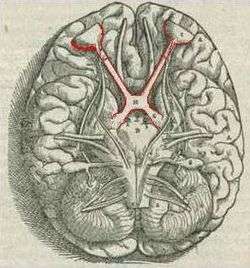 Brain viewed from below; the front of the brain is above. Visual pathway with optic chiasm (X shape) is shown in red (1543 image from Andreas Vesalius' Fabrica) | |
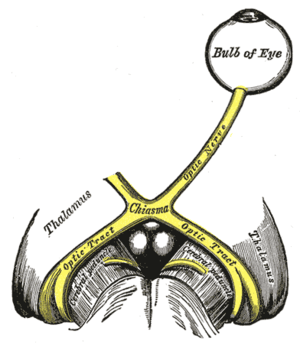 Optic nerves, chiasm, and optic tracts | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | chiasma opticum |
| MeSH | A08.800.800.120.680.600 |
| NeuroLex ID | Optic chiasm |
| TA | A14.1.08.403 |
| FMA | 62045 |
The optic chiasm or optic chiasma (pronunciation: /ɒptɪk kaɪæzəm/; Greek χίασμα, "crossing", from the Greek χιάζω 'to mark with an X', after the Greek letter 'Χ', chi) is the part of the brain where the optic nerves (CN II) partially cross. The optic chiasm is located at the bottom of the brain immediately below the hypothalamus.[1] The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrates, although in cyclostomes (lampreys and hagfishes) it is located within the brain.[2] [3]
Pathways
The optic nerve fibres on the nasal sides of each retina cross over to the opposite side of the brain via the optic nerve at the optic chiasm (decussation of medial fibers). The temporal hemiretina, on the other hand, stays on the same side. The inferonasal retina are related to anterior portion of the optic chiasm whereas superonasal retinal fibers are related to the posterior portion of the optic chiasm.
The crossing over of optic nerve fibres at the optic chiasm allows the visual cortex to receive the same hemispheric visual field from both eyes. Superimposing and processing these monocular visual signals allow the visual cortex to generate binocular and stereoscopic vision. For example, the right visual cortex receives the nasal visual field from the left eye, and the temporal visual field from the right eye, which results in the right visual cortex producing a binocular image of the left hemispheric visual field. The net result of optic nerve crossing over at the optic chiasm is for the right cerebral hemisphere to sense and process left hemispheric vision, and for the left cerebral hemisphere to sense and process right hemispheric vision.[4]
This decussation (crossing) is an adaptive feature of frontally oriented eyes, found mostly in predatory animals requiring precise visual depth perception. (Prey animals, with laterally positioned eyes, have little binocular vision, so there is a more complete crossover of visual signals.) Beyond the optic chiasm, with crossed and uncrossed fibers, the optic nerves become optic tracts. The signals are passed on to the lateral geniculate body, in turn giving them to the occipital cortex (the outer matter of the rear brain).[5]
Optic chiasm in cats
In Siamese cats with certain genotypes of the albino gene, this wiring is disrupted, with more of the nerve-crossing than is normal, as a number of scholars have reported.[6] To compensate for lack of crossing in their brains, they cross their eyes (strabismus).[7]
This is also seen in albino tigers, as Guillery & Kaas report.[8]
Additional images
 Mesal aspect of a brain sectioned in the median sagittal plane.
Mesal aspect of a brain sectioned in the median sagittal plane. Median sagittal section of brain.
Median sagittal section of brain. Scheme showing central connections of the optic nerves and optic tracts.
Scheme showing central connections of the optic nerves and optic tracts. Base of brain.
Base of brain. Coronal section of brain through anterior commissure.
Coronal section of brain through anterior commissure. The fornix and corpus callosum from below.
The fornix and corpus callosum from below. Diagram showing the positions of the three principal subarachnoid cisternæ.
Diagram showing the positions of the three principal subarachnoid cisternæ. The hypophysis cerebri in position. Shown in sagittal section.
The hypophysis cerebri in position. Shown in sagittal section. Median sagittal through the hypophysis of an adult monkey. Semidiagrammatic.
Median sagittal through the hypophysis of an adult monkey. Semidiagrammatic.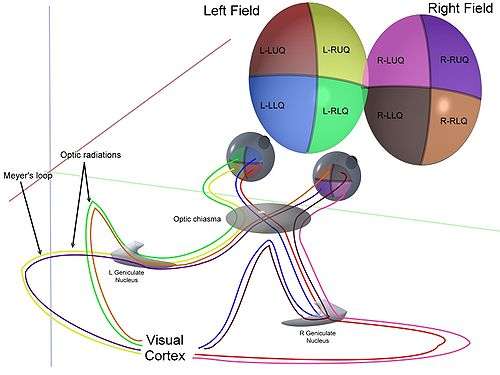 3D schematic representation of optic tracts
3D schematic representation of optic tracts- Human brainstem anterior view
- Optic chiasm
- Optic chiasma
- Cerebrum. Deep dissection. Inferior dissection.
- Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection
- Spinal cord. Brachial plexus. Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection.
- Cerebral peduncle, optic chiasm, cerebral aqueduct. Inferior view. Deep dissection.
- Cerebral peduncle, optic chiasm, cerebral aqueduct. Inferior view. Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum. Optic and olfactory nerves.Inferior view. Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum.Inferior view. Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum. Inferior view.Deep dissection
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Optic chiasm. |
References
- ↑ Colman, Andrew M. (2006). Oxford Dictionary of Psychology (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 530. ISBN 0-19-861035-1.
- ↑ Bainbridge, David (30 June 2009). Beyond the Zonules of Zinn: A Fantastic Journey Through Your Brain. Harvard University Press. p. 162. ISBN 978-0-674-02042-9. Retrieved 22 November 2015.
- ↑ de Lussanet, Marc H.E.; Osse, Jan W.M. (2012). "An ancestral axial twist explains the contralateral forebrain and the optic chiasm in vertebrates". Animal Biology. 62 (2): 193–216. arXiv:1003.1872
 . doi:10.1163/157075611X617102. ISSN 1570-7555.
. doi:10.1163/157075611X617102. ISSN 1570-7555. - ↑ Purves, Dale; Augustine, George; Fitzpatrick, David; Hall, William; LaMantia, Anthony-Samuel; White, Leonard (2012). Neuroscience. Sinauer Associates. p. 261. ISBN 978-0-87893-695-3.
- ↑ "eye, human." Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD 2009
- ↑ "Abnormal retinotopic organization of the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the tyrosinase-negative albino cat.". Retrieved 2014-05-09.
- ↑ Guillery, RW; Kaas, JH (June 1973). "Genetic abnormality of the visual pathways in a "white" tiger". Science. 180 (4092): 1287–9. Bibcode:1973Sci...180.1287G. doi:10.1126/science.180.4092.1287. PMID 4707916.
- ↑ Guillery RW (May 1974). "Visual pathways in albinos". Sci. Am. 230 (5): 44–54. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0574-44. PMID 4822986.
- Jeffery G (October 2001). "Architecture of the optic chiasm and the mechanisms that sculpt its development". Physiol. Rev. 81 (4): 1393–414. PMID 11581492.
External links
- Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-1 at Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, Elsevier