Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve
| Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve | |
|---|---|
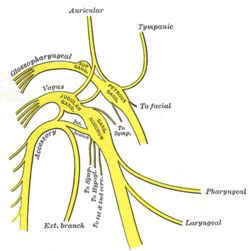 Plan of upper portions of glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. (Pharyngeal visible at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| From | vagus nerve |
| To | pharyngeal plexus |
| Innervates | pharynx |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ramus pharyngeus nervi vagi |
| TA | A14.2.01.158 |
| FMA | 6234 |
The pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve, the principal motor nerve of the pharynx, arises from the upper part of the ganglion nodosum, and consists principally of filaments from the cranial portion of the accessory nerve.
It passes across the internal carotid artery to the upper border of the Constrictor pharyngis medius, where it divides into numerous filaments, which join with branches from the glossopharyngeal, sympathetic, and external laryngeal to form the pharyngeal plexus.
From the plexus, branches are distributed to the muscles and mucous membrane of the pharynx (except the stylopharyngeus, which is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)) and the muscles of the soft palate, except the Tensor veli palatini, which is supplied by the nerve to tensor veli palatini, a branch of the nerve to medial pterygoid (which itself is a branch of the mandibular nerve - CNV/2). A minute filament descends and joins the hypoglossal nerve as it winds around the occipital artery.
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (X)