Optic tract
| Optic tract | |
|---|---|
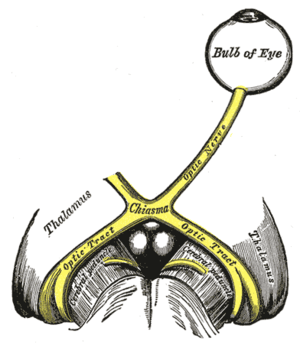 The left optic nerve and the optic tracts. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Visual system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tractus opticus |
| TA | A14.1.08.404 |
| FMA | 62046 |
The optic tract (from the Latin tractus opticus) is a part of the visual system in the brain. It is a continuation of the optic nerve that relays information from the optic chiasm to the ipsilateral lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus.[1]
It is composed of two individual tracts, the left optic tract and the right optic tract, each of which conveys visual information exclusive to its respective contralateral half of the visual field. Each of these tracts is derived from a combination of temporal and nasal retinal fibers from each eye that corresponds to one half of the visual field. In more specific terms, the optic tract contains fibers from the ipsilateral temporal hemiretina and contralateral nasal hemiretina.
Visual System
The optic tract carries retinal information relating to the whole visual field. Specifically, the left optic tract corresponds to the right visual field, while the right optic tract corresponds to the left visual field. To form the right visual field, temporal retinal fibers from the left eye and nasal retinal fibers from the right eye form the left optic tract, and to form the left visual field, temporal retinal fibers from the right eye and nasal retinal fibers from the left eye form the right optic tract.[2]
| Optic Tract | Visual Field | Temporal Retinal Fibers | Nasal Retinal Fibers |
| Left | Right | Left | Right |
| Right | Left | Right | Left |
Autonomics
Several autonomic ocular motor responses are consensual. The optic tract is primarily responsible relaying visual information to the LGN, but it is also peripherally responsible for transducing these bilateral autonomic reflexes, including the pupillary light reflex and pupillary dark reflex.[3]
Pupillary Light Reflex
The pupillary light reflex is an autonomic reflex that controls pupil diameter to accommodate for increases in illumination as perceived by the retina. Higher light intensity causes pupil constriction, and the increase of light stimulation of one eye will cause pupillary constriction of both eyes. The neural circuitry of the pupillary light reflex includes the optic tract which joins the optic nerve to the brachium of the superior colliculus.[4]
Pupillary Dark Reflex
Similarly to the pupillary light reflex, the pupillary dark reflex is an autonomic reflex that controls pupil diameter to accommodate for decreases in illumination as perceived by the retina. Lower light intensity causes pupil dilation, and the decrease of light stimulation of one eye will cause pupillary dilation of both eyes. Similarly, the neural circuitry of the pupillary dark reflex includes the optic tract which joins the optic nerve to the hypothalamus.[5]
Damage and Pathologies
Lesions
Lesions in the optic tract correspond to visual field loss on the left or right half of the vertical midline, also known as homonymous hemianopsia. A lesion in the left optic tract will cause right-sided homonymous hemianopsia, while a lesion in the right optic tract will cause left-sided homonymous hemianopsia. Stroke, congenital defects, tumors, infection, and surgery are all possible causes of optic tract damage. Peripheral prism expanders and vision restitution therapy are often employed in patients with visual field loss resultant of permanent optic tract damage.[6]
Split-Brain
In certain split-brain patients who have undergone a corpus callosotomy to treat severe epilepsy, the information from one optic tract does not get transmitted to both hemispheres. For instance, a split-brain patient shown an image in the left visual field will be unable to vocally name what has been seen as the speech-control center is in the left hemisphere of the brain.
Pupillary Reflexes
Pupillary reflexes, particularly the pupillary light reflex, are a powerful diagnostic tool often employed in clinical and emergency medical practice. A lack of equal consensual pupillary constriction to a light stimulus can be indicative of optic nerve damage, brainstem death, or optic tract damage in between.
Additional images
.jpg) Diagram of hippocampus
Diagram of hippocampus Schematic diagram of the primate lateral geniculate nucleus.
Schematic diagram of the primate lateral geniculate nucleus. Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Ventral view.
Superficial dissection of brain-stem. Ventral view. Coronal section of brain through intermediate mass of third ventricle.
Coronal section of brain through intermediate mass of third ventricle. Hind- and mid-brains; postero-lateral view.
Hind- and mid-brains; postero-lateral view. Scheme showing central connections of the optic nerves and optic tracts.
Scheme showing central connections of the optic nerves and optic tracts. Base of brain.
Base of brain. Section of brain showing upper surface of temporal lobe.
Section of brain showing upper surface of temporal lobe. Dissection showing the course of the cerebrospinal fibers.
Dissection showing the course of the cerebrospinal fibers.- Human brainstem anterior view
 Optic tract and optic nerve
Optic tract and optic nerve- Optic tract
- Cerebrum. Deep dissection. Inferior dissection.
- Cerebral peduncle, optic chasm, cerebral aqueduct. Inferior view. Deep dissection.
- Cerebral peduncle, optic chasm, cerebral aqueduct. Inferior view. Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum.Inferior view.Deep dissection.
- Cerebrum. Inferior view.Deep dissection
- Cerebrum. Inferior view.Deep dissection
References
- ↑ Optic tract. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved from: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/430336/optic-tract (accessed Nov 1, 2013).
- ↑ Chudler E. (2011). Visual Pathway. Neuroscience for Kids. Retrieved from: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/vispath.html (accessed July 28, 2014).
- ↑ Dragoi V. (1997). Chapter 7: Ocular Motor System. Neuroscience Online. Retrieved from: http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter15.html (accessed Nov 2, 2013).
- ↑ Optic nerve. Science Daily. Retrieved from: http://www.sciencedaily.com/articles/o/optic_nerve.htm (accessed Nov 2, 2013).
- ↑ Kolb H, Fernandez E, and Nelson R. (2007). Gross Anatomy of the Eye. The Organization of the Retina and Visual System.
- ↑ Optic tract. Healthline Body Maps. Retrieved from: http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/optic-tract#3/12 (accessed Nov 1, 2013).
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Optic tract. |