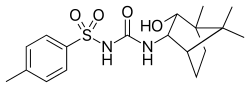
Glibornuride
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-(3-hydroxy-4,7,7-trimethyl-2-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptanyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylurea | |
| Identifiers | |
| 26944-48-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 16735831 |
| DrugBank | DB08962 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.043.735 |
| EC Number | 248-124-6 |
| KEGG | D02427 |
| MeSH | C073323 |
| PubChem | 33649 |
| UNII | VP83E7434R |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H26N2O4S | |
| Molar mass | 366.48 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| A10BB04 (WHO) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Glibornuride (INN) is an anti-diabetic drug from the group of sulfonylureas.[1] It is manufactured by MEDA Pharma and sold in Switzerland under the brand name Glutril.[2]
Synthesis

Glibornuride synthesis:[3] See also: U.S. Patent 3,770,761; eidem, U.S. Patent 3,654,357 (to Hoffmann-La Roche).
Gliburnide is an endo-endo derivative made from camphor-3-carboxamode by borohydride reduction (exo approach), followed by Hofmann rearrangement to carbamate, followed by displacement with sodium tosylamide.
References
- ↑ Haupt E, Köberich W, Beyer J, Schöffling K (December 1971). "Pharmacodynamic aspects of tolbutamide, glibenclamide, glibornuride and glisoxepide. I. Dose response relations and repeated administration in diabetic subjects". Diabetologia. 7 (6): 449–54. doi:10.1007/bf01212061. PMID 5004178.
- ↑ "Glutril — Drugs.com". Drugs.com. Retrieved 12 July 2016.
- ↑ Bretschneider, H.; Hohenlohe-Oehringen, K.; Graßmayr, K. (1969). "Arylsulfonylureido- und Arylsulfonylamidoacyl-derivate von Oxy- und Oxo-cycloalkanen als potentielle Antidiabetica". Monatshefte für Chemie. 100 (6): 2133. doi:10.1007/BF01151769.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.