Thiacloprid
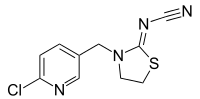 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
{(2Z)-3-[(6-Chloropyridin-3-yl)methyl]-1,3-thiazolidin-2-ylidene}cyanamide | |
| Other names
[3-[(6-Chloro-3-pyridinyl)methyl]-2-thiazolidinylidene]cyanamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 111988-49-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:39176 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL451432 |
| ChemSpider | 103099 |
| DrugBank | DB08620 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.129.728 |
| KEGG | C18512 |
| PubChem | 115224 |
| UNII | DSV3A944A4 |
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C10H9ClN4S | |
| Molar mass | 252.72 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellowish crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.46 g·cm−3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | 136 °C (277 °F; 409 K) |
| 185 mg/L at 20°C[2] | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Thiacloprid is an insecticide of the neonicotinoid class. Its mechanism of action is similar to other neonicotinoids and involves disruption of the insect's nervous system by stimulating nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Thiacloprid was developed by Bayer CropScience for use on agricultural crops to control of a variety of sucking and chewing insects, primarily aphids and whiteflies.[1][3]
References
- 1 2 Thiacloprid Pesticide Fact Sheet, United States Environmental Protection Agency
- ↑ "Thiacloprid". Bayer CropScience Crop Compendium. Bayer CropScience. Retrieved 30 November 2011.
- ↑ Schuld, Michael; Schmuck, Richard (2000). Ecotoxicology. 9 (3): 197. doi:10.1023/A:1008994705074. Missing or empty
|title=(help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/16/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.