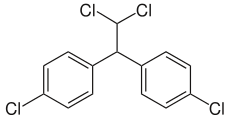
Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
1-chloro-4-[2,2-dichloro-1-(4- chlorophenyl)ethyl]benzene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 72-54-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Abbreviations | DDD |
| 4-05-00-01884 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:27841 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL196590 |
| ChemSpider | 6057 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.712 |
| EC Number | 200-783-0 |
| KEGG | C06636 |
| MeSH | DDD |
| PubChem | 6294 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H10Cl4 | |
| Molar mass | 320.04 |
| Appearance | Colorless and crystalline |
| Density | 1.476 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 109.5 °C (229.1 °F; 382.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 350 °C (662 °F; 623 K) |
| 0.09 mg/L | |
| log P | 6.02 (octanol-water) |
| Vapor pressure | 1.35×10−6 mm Hg |
| Henry's law constant (kH) |
6.6×10−6 atm ∙ m3/mol |
| Atmospheric OH rate constant |
4.34×10−12 cm3/molecule ∙ s |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
DDE, DDT, mitotane, perthane |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane (DDD) is an organochlorine insecticide that is slightly irritating to the skin.[1] DDD is a metabolite of DDT.[2] DDD is colorless and crystalline;[3] it is closely related chemically and is similar in properties to DDT, but it is considered to be less toxic to animals than DDT.[4] The molecular formula for DDD is (ClC6H4)2CHCHCl2 or C14H10Cl4, whereas the formula for DDT is (ClC6H4)2CHCCl3 or C14H9Cl5.
DDD is in the “Group B2” classification, meaning that it is a probable human carcinogen. This is based on an increased incidence of lung tumors in male and female mice, liver tumors in male mice, and thyroid tumors in male rats. Further basis is that DDD is so similar to and is a metabolite of DDT, another probable human carcinogen.[2]
DDD is no longer registered for agricultural use in the United States, but the general population continues to be exposed to it due to its long persistence time. The primary source of exposure is oral ingestion of food.[5]
1946 is the date of the earliest recorded use in English of the abbreviation “DDD” to stand for dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane, as far as could be determined.[3]

Mitotane
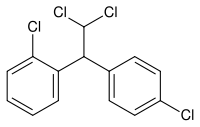
Interestingly enough, if one of the p-chlorines in DDD is switched to ortho-position, then we get a useful chemotherapeutic agent, mitotane. This is an example of a positional isomer.
Table of names
The following are synonyms for DDD:
| Systematic Names | Superlist Names | Other Names |
|---|---|---|
| Benzene, 1,1'-(2,2- dichloroethylidene) bis(4-chloro- (9CI) |
4,4'-DDD | 1,1'-(2,2-Dichloroethylidene)bis (4-chlorobenzene) |
| Ethane, 1,1- dichloro-2,2-bis(p- chlorophenyl)- |
Benzene, 1,1'-(2,2- dichloroethylidene)bis(4-chloro- |
1,1-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-2,2- dichloroethane |
| TDE | DDD | 1,1-Bis(p-chlorophenyl)-2,2- dichloroethane |
| p,p'-TDE | DDD, p,p'- | 1,1-Dichloor-2,2-bis(4-chloor fenyl)-ethaan (Dutch) |
| Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane | 1,1-Dichlor-2,2-bis(4-chlor- phenyl)-aethan (German) | |
| RCRA waste number U060 | 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis(4- chlorophenyl)-ethane (French) | |
| TDE | 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis(4- chlorophenyl)ethane | |
| Tetrachlorodiphenylethane | 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis(p- chlorophenyl)ethane | |
| p,p'-TDE | 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis (parachlorophenyl)ethane | |
| 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-di(4- chlorophenyl)ethane | ||
| 1,1-Dicloro-2,2-bis(4-cloro-fenil)- etano (Italian) | ||
| 2,2-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)-1,1- dichloroethane | ||
| 2,2-Bis(p-chlorophenyl)-1,1- dichloroethane | ||
| 4,4' DDD | ||
| 4,4-DDD | ||
| 4,4'- Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane | ||
| 4-05-00-01884 (Beilstein Handbook Reference) | ||
| AI3-04225 | ||
| Benzene, 1,1'-(2,2- dichloroethylidene)bis[4-chloro- | ||
| BRN 1914072 | ||
| CCRIS 573 | ||
| Caswell No. 307 | ||
| DDD analogue | ||
| DDD in whole water sample | ||
| Dichlorodiphenyl dichloroethane | ||
| Dichlorodiphenyldichlorethane | ||
| Dilene | ||
| EINECS 200-783-0 | ||
| ENT 4,225 | ||
| EPA Pesticide Chemical Code 029101 | ||
| Ethane, 1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(p- chlorophenyl)- | ||
| HEPT | ||
| HSDB 285 | ||
| ME-1700 | ||
| Me-700 | ||
| NCI-C00475 | ||
| NSC 8941 | ||
| OMS 1078 | ||
| para-para DDD | ||
| para,para'-DDD | ||
| para,para'- Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane | ||
| p,p-DDD | ||
| p,p'-DDD | ||
| p,p'-Dichlorodiphenyl-2,2-dichloroethylene | ||
| p,p'-Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane | ||
| Rhothane | ||
| Rhothane D-3 | ||
| Rothane | ||
| Rothane WP-50 |
References
- “Chemicals: Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane.” The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database. MDI Biological Laboratory, 11 Apr. 2007 <http://ctd.mdibl.org/detail.go?type=chem&acc=D003632>.
- “Data From SRC PhysProp Database.” SRC PhysProp Database. Syracuse Research Corporation. 11 Apr. 2007 <http://esc.syrres.com/interkow/webprop.exe?CAS=72-54-8>.
- “DDD.” Hazardous Substances Data Bank. United States National Library of Medicine. 25 Apr. 2007 <http://toxmap.nlm.nih.gov/toxmap/main/chemPage.jsp?chem=4,4-DICHLORODIPHENYLDICHLOROETHANE then click “Env. Fate / Exposure”>.
- “DDD—RN: 72-54-8.” ChemIDplus Lite Record. 9 Sept. 2004. United States National Library of Medicine Specialized Information Services. 11 Apr. 2007 <http://chem2.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/direct.jsp?regno=72-54-8>.
- Guralnik, David B., Editor in Chief. “DDD.” Webster’s New World Dictionary of the American Language. Second College Edition. New York, NY: Prentice Hall Press, 1986. ISBN 0-671-41809-2 (indexed), ISBN 0-671-41807-6 (plain edge), ISBN 0-671-41811-4 (pbk.), and ISBN 0-671-47035-3 (LeatherKraft).
- Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. “DDD.” Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary. 9th ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., 1985. ISBN 0-87779-508-8, ISBN 0-87779-509-6 (indexed), and ISBN 0-87779-510-X (deluxe).
- “p,p'-DDD.” Substance Registry System. 1 Feb. 2006. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 11 Apr. 2007 <http://iaspub.epa.gov/srs/srs_proc_qry.navigate?P_SUB_ID=4937>.
- “p,p'-Dichlorodiphenyl dichloroethane (DDD) (CASRN 72-54-8).” Integrated Risk Information System. 25 Jan. 2007. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 23 Apr. 2007 <http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst/0347.htm>.
Notes
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th ed, p482
- 1 2 “p,p'-Dichlorodiphenyl dichloroethane (DDD) (CASRN 72-54-8).” Integrated Risk Information System. 25 Jan. 2007. United States Environmental Protection Agency. 23 Apr. 2007 <http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst/0347.htm>.
- 1 2 Mish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. “DDD.” Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary. 9th ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., 1985.
- ↑ Guralnik, David B., Editor in Chief. “DDD.” Webster’s New World Dictionary of the American Language. Second College Edition. New York, NY: Prentice Hall Press, 1986.
- ↑ “DDD.” Hazardous Substances Data Bank. United States National Library of Medicine. 25 Apr. 2007 <http://toxmap.nlm.nih.gov/toxmap/main/chemPage.jsp?chem=4,4-DICHLORODIPHENYLDICHLOROETHANE then click “Env. Fate / Exposure”>.
External links
- TOXMAP Chemical Page for DDD
- MSDS for rhothane (DDD) provided by the Physical and Theoretical Chemistry Laboratory of the University of Oxford