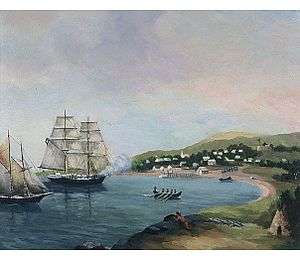Raid on Lunenburg, Nova Scotia (1782)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Raid on Lunenburg (also known as the Sack of Lunenburg) occurred during the American Revolution when the US privateer, Captain Noah Stoddard of Fairhaven, Massachusetts, and four other privateer vessels attacked the British settlement at Lunenburg, Nova Scotia on 1 July 1782.[5] [6] [7] Lunenburg was defended by militia leaders Colonel John Creighton and Major Dettlieb Christopher Jessen. In Nova Scotia, the assault on Lunenburg was the most spectacular raid of the war.[8] On the morning of 1 July Stoddard led approximately 170 US privateers in four heavily armed vessels and overpowered Lunenburg’s defence, capturing the blockhouses and burning the house of Jessen. The privateers then looted the settlement and kept the militia at bay with the threat of destroying the entire town. The American privateers plundered the town and took three prisoners, including Creighton, who were later released from Boston without a ransom having been paid.[8][9]
Historical context

During the American Revolution, Nova Scotia was invaded regularly by American Revolutionary forces by land and sea. Throughout the war, American privateers devastated the maritime economy by raiding many of the coastal communities. There were constant attacks by privateers,[10] such as the numerous raids on Liverpool (October 1776, March 1777, September 1777, May 1778, September 1780) and on Annapolis Royal (1781).[11] There was also a naval engagement with a French fleet at Spanish River, Cape Breton Island (1781).[12]
On 17 November 1775, Washington's Marblehead Regiment aboard the Hancock and Franklin made an unopposed landing at Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island. Three days later, they expedited to Nova Scotia and raided Canso. In 1779, American privateers returned to Canso and destroyed the fisheries, which were worth ₤50,000 a year to Britain.[13]
The 84th Regiment had been defending Nova Scotia, attacking an American privateer ship off of Lunenburg, Nova Scotia (1775). The 84th was led by Captain John MacDonald. They boarded the warship when some of its crew were ashore seeking plunder. They captured the crew and sailed her into Halifax.[14] There were also Patriot attacks on Nova Scotia by land, such as the Battle of Fort Cumberland and the Siege of Saint John (1777). There was the constant threat that American Patriots would attack Halifax by land.
Stoddard's vessel the Scammell was commissioned in April 1782 and made the plan in Boston to raid Lunenburg.[15] Soon after, he rescued the 60 American prisoners on board the H.M.S. Blonde which was wrecked on Seal Island, Nova Scotia. Stoddard allowed the British crew to return to Halifax in the HMS Observer (which was involved in the Naval battle off Halifax en route).[16] [17] On June 30, the day before the raid on Lunenburg, Stoddard and others were involved in gathering intelligence at Chester, Nova Scotia for the raid.
Raid on Lunenburg
During the early morning of 1 July 1782, five American privateers, who had left Boston under the command of Captain Noah Stoddard, began to raid Lunenburg. Captain Stoddard’s ship was the schooner Scammel, which had sixteen guns and sixty men.[8][18] Stoddard organized both a land and sea assault of the town. The vessels first landed at Red Head, two miles outside of the town and soldiers began to march toward the town. The vessels then moved toward a frontal assault on the town.
The Lunenburg militia was led by Colonel John Creighton and Major D. C. Jessen. Colonel Creighton and five other militia men occupied the eastern blockhouse and began firing at the approaching land assault. Several of Captain Stoddard’s privateers were wounded. The landed fleet of privateers then rounded East Point. The vessels landed and quickly took control of the western blockhouse and established themselves at Blockhouse Hill (See image above). Captain Creighton and others in the blockhouse were cannonaded into silence and the blockhouse burned.[19] Colonel Creighton surrendered and was taken prisoner along with two other men aboard Captain Stoddard’s vessel Scammel.[20]
Resistance was also offered by Major D. C. Jessen. He was initially held up in his home, which the privateers fired full of bullets. He escaped and his house was looted. Major Jessen assembled with a militia behind the hill overlooking the town. A militia from La Have under the command of Major Joseph Pernette also advanced toward Lunenburg to join Major Jessen. Captain Stoddard sent a message to Jensen and Pernette that if they advanced on the town, all the homes would be burned. To ensure his threat was not idle, Captain Stoddard burned down Major Jessen’s home.[21]
Captain Stoddard’s privateers looted the town and destroyed what remained. The Reverend Johann Gottlob Schmeisser tried to intervene and was bound by the privateers and placed in the middle of town.[22]
Relief came when Lt. Governor Hamond dispatched from Halifax three ships under the command of Captain Douglass of the HMS Chatham (1758), one of which had 200 Hessians soldiers aboard. [23]Captain Stoddard began the retreat. Despite not having received a ransom, Captain Stoddard released Colonel Creighton and the other prisoners after they arrived in Boston.[21]
Sylvia, an African slave working for Creighton, was a significant part of Lunenburg's resistance to the raid. [24] She assisted in supplying munitions to Creighton at the blockhouse and sheltered his son.[25] And after being released from being captured by Stoddard, she also protected the home and possessions of Major Jessen.[21] [26]
Fiction
- Jan Andrews The Dancing Sun: A Celebration of Canadian Children, 1981;
- Joyce Barkhouse. "The Heroine of Lunenburg", with illustrations by Peter Ferguson
See also
References
- ↑ Author of The Holy Communion: A Relic of the Past and an Instructor of the Present : Being a Sermon Written in the Year A.D. 1797
- ↑ p.338
- ↑ Capt. John Tibbets' (1748-1786) father's house
- ↑ casualties taken from Boston Gazette, July 15, August 5, 1782 ; Massachusetts Spy, August 8, 1782
- ↑ Eastman, pp. 61–63
- ↑ Captain Noah Stoddard, died in New Bedford, January 29, 1850, aged 95 ; a soldier of the Revolution.
- ↑ p.7
- 1 2 3 Gwyn, p. 75
- ↑ DesBraisay, p. 68
- ↑ Benjamin Franklin also engaged France in the war, which meant that many of the privateers were also from France.
- ↑ Roger Marsters (2004). Bold Privateers: Terror, Plunder and Profit on Canada's Atlantic Coast", pp. 87–89 ISBN 0887806449
- ↑ Thomas B. Akins. (1895) History of Halifax. Dartmouth: Brook House Press, p. 82
- ↑ Lieutenant Governor Sir Richard Hughes stated in a dispatch to Lord Germaine that "rebel cruisers" made the attack.
- ↑ Craig, C. (1989). The Young Emigrants: Craigs of the Magaguadavic, p. 53
- ↑ The Boston Gazette, and the Country Journal, Monday, July 15, 1782; The Massachusetts Spy: Or, American Oracle of Liberty [Worcester], Thursday, July 25, 1782; The Continental Journal [Boston], Thursday, July 18, 1782. Joseph Pernette to Franklin, letter, dated at La Have, July 3, 1782, reprinted in DesBrisay, Mather Byles, History of the County of Lunenburg, Toronto: Wesley Briggs, 1895, 65-67.
- ↑ Sacking of Lunenburg. Saga of the Seas, Archibald MacMechan, 1923
- ↑ Thomas Head Raddall. Adventures of H.M.S. Blonde in Nova Scotia, 1778-1782. Collections of the Nova Scotia Historical Society. 1966.
- ↑ MacMechan, p. 59
- ↑ Gwyn, p. 25
- ↑ MacMechan, pp. 62–63
- 1 2 3 MacMechan, p. 68
- ↑ MacMechan, p. 67
- ↑ Scammell
- ↑ http://www.ryerson.ca/equity/BHAC/history.html
- ↑ MacMechan refers to Sylvia as a servant. It is unclear whether her status was that of an Indentured servant or a slave.
- ↑ Sylvia Hamilton. A Survey of Early Black Women In Nova Scotia. In We're Rooted Here and They Can't Pull Us Up.
Bibliography
- DesBrisay, Mather Byles (1895). History of the county of Lunenburg.
- Eastman, Ralph M. "Captain Noah Stoddard" in Some Famous Privateers of New England. 1928. pp. 61–63
- Gwyn, Julian. Frigates and Foremasts: The North American Squadron in Nova Scotia Waters, 1745–1815, University of British Columbia Press. 2003 ISBN 0774809116.
- MacMechan, Archibald (1923), “The Sack of Lunenburg” in Sagas of the Sea. The Temple Press, pp. 57–72.
- Invasion of Lunenburg in Acadie and the Acadians
Primary documents
- The Boston Gazette, and the Country Journal, Monday, July 15, 1782;
- The Massachusetts Spy: Or, American Oracle of Liberty [Worcester], Thursday, July 25, 1782;
- The Continental Journal [Boston], Thursday, July 18, 1782.
- Joseph Pernette to Franklin, letter, dated at La Have, July 3, 1782, reprinted in DesBrisay, Mather Byles, History of the County of Lunenburg, Toronto: Wesley Briggs, 1895, 65-67.
Further reading
- Howe, Octavius Thorndike. Beverly Privateers in the Revolution, 1922, p. 361.
- Bell, Winthrop Pickard. (1961). The "Foreign Protestants" and the Settlement of Nova Scotia.
- Privateering and piracy : the effects of New England raiding upon Nova Scotia during the American Revolution, 1775-1783. By John Dewar Faibisy
External links
- Sack of Lunenburg Plaque
- Sacking of Lunenburg – Primary Sources
- Beck, J. Murray (1983). "Creighton, John (1721-1807)". In Halpenny, Francess G. Dictionary of Canadian Biography. V (1801–1820) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press.
- Sack of Lunenburg – American War of Independence at Sea
- MA Scammel