Prüm Convention
| Convention on the stepping up of cross-border cooperation, particularly in combating terrorism, cross-border crime and illegal migration | |
|---|---|
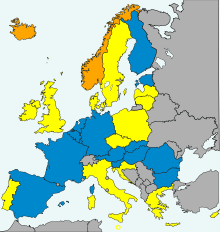 Parties to the Prüm Convention and Prüm Decision participants Other Prüm Decision participants Other EU member states non-EU member states which have signed an agreement to participate | |
| Type | Intergovernmental agreement |
| Signed | 27 May 2005 |
| Location | Prüm, Germany |
| Effective | 1 November 2006 |
| Condition | 2 ratifications |
| Parties | 14 |
| Depositary | Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Federal Republic of Germany |
| Languages | German, Spanish, French and Dutch (original) |
|
| |
The Prüm Convention (sometimes known as Schengen III Agreement)[1] is a treaty which was signed on 27 May 2005 by Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and Spain in the town of Prüm in Germany, and which is open to all members of the European Union, 14 of which are currently parties.
The treaty was based on an initiative by the then German Minister Otto Schily from mid-2003.[2] Core elements of the convention were picked up by EU Council Decision 2008/615/JHA on 23 June 2008 on the stepping up of cross-border cooperation, particularly in combating terrorism and cross-border crime.[3]
The full name of the treaty is Convention between the Kingdom of Belgium, the Federal Republic of Germany, the Kingdom of Spain, the French Republic, the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, the Kingdom of the Netherlands and the Republic of Austria on the stepping up of cross-border cooperation, particularly in combating terrorism, cross-border crime and illegal migration.
Contents of the Convention
The Convention was adopted so as to enable the signatories to exchange data regarding DNA, fingerprints and vehicle registration of concerned persons and to cooperate against terrorism. It also contains provisions for the deployment of armed sky marshals on flights between signatory states, joint police patrols, entry of (armed) police forces into the territory of another state for the prevention of immediate danger (hot pursuit), and cooperation in case of mass events or disasters. Furthermore, a police officer responsible for an operation in a state may, in principle, decide to what degree the police forces of the other states that were taking part in the operation could use their weapons or exercise other powers.
Relation to the European Union
The Convention was adopted outside of the European Union framework (and its mechanism of Enhanced co-operation), but asserts that it is open for accession by any Member state of the European Union and that:
provisions of this Convention shall only apply in so far as they are compatible with European Union law ... [EU law] should take precedence in applying the relevant provisions of this Convention— Convention on the stepping up of cross-border cooperation, particularly in combating terrorism, cross-border crime and illegal migration, Article 47
Additionally the text of the Convention and its annexes were circulated on 7 July 2005 between the delegations to the Council of the European Union.
Some of the Convention provisions, falling under the former third pillar of the EU, were later subsumed into the police and judicial cooperation provisions of European Union law by a 2008 Council Decision,[3][4] commonly referred to as the Prüm Decision. It provides for Law Enforcement Cooperation in criminal matters primarily related to exchange of Fingerprint, DNA (both on a hit no-hit basis) and Vehicle owner registration (direct access via the EUCARIS system) data. The data exchange provisions are to be implemented in 2012. The remaining provisions of the Convention falling under the former third pillar are not yet adopted into EU law.
Parties to the convention
The states which have ratified the convention are:
| Contracting party[5][6][7] | Date of signature[5] | Date of deposit of instrument of ratification or accession[5] | Entry into force[5] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | 27 May 2005 | 21 June 2006 | 1 November 2006 |
| Belgium | 27 May 2005 | 5 February 2007 | 6 May 2007 |
| Bulgaria | - | 25 May 2009 | 23 August 2009 |
| Estonia | - | 23 September 2008 | 22 December 2008 |
| Finland | - | 19 March 2007 | 17 June 2007 |
| France | 27 May 2005 | 2 October 2007 | 31 December 2007 |
| Germany | 27 May 2005 | 25 August 2006 | 23 November 2006 |
| Hungary | - | 16 October 2007 | 14 January 2008 |
| Luxembourg | 27 May 2005 | 8 February 2007 | 9 May 2007 |
| Netherlands | 27 May 2005 | 20 February 2008 | 20 May 2008 |
| Romania | - | 3 December 2008 | 3 March 2009 |
| Slovakia | - | 27 February 2009 | 28 May 2009 |
| Slovenia | - | 10 May 2007 | 8 August 2007 |
| Spain | 27 May 2005 | 3 August 2006 | 1 November 2006 |
Greece, Italy, Portugal and Sweden, have notified the Council of the European Union of their desire to accede to the Prüm Convention.[8]
While the Decisions were originally applicable to all EU member states, the United Kingdom subsequently exercised their right to opt-out from them effective 1 December 2014.[9] However, the UK committed to assess their future participation and make a decision by 31 December 2015 on whether to rejoin the Decisions.[10] On 22 January 2016 the UK notified the EU of its desire to resume participating in the Prum Decisions, which was approved by the Commission on 20 May 2016.[11]
Norway and Iceland signed a treaty with the EU in 2009 to apply certain provisions of the Decisions.[12] Neither state has ratified the agreement as of 2015.[13] Switzerland and Liechtenstein have requested that a similar agreement be concluded with them.[14] The Council of the European Union authorized the launch of negotiations in June 2016.[15]
Notes
- ↑ Christopher Walsch (July 2009). "Europeanization and Democracy: Negotiating the Prüm Treaty and the Schengen III Agreement". Croatian Political Science Review. 45 (5). Retrieved 29 August 2010.
- ↑ The Treaty of Prüm: A Replay of Schengen?
- 1 2 OJ L 210, 6 August 2008, p. 1
- ↑ Decision 2008/616/2008 implementing 2008/615/2008
- 1 2 3 4 "Convention between the Kingdom of Belgium, the Federal Republic of Germany, the Kingdom of Spain, the French Republic, the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, the Kingdom of the Netherlands and the Republic of Austria concerning the intensification of cross-border cooperation, particularly in the fight against terrorism, cross-border crime and illegal migration" (PDF). German Foreign Office. 2012-01-30. Retrieved 2012-04-14.
"Vertrag zwischen dem Königreich Belgien, der Bundesrepublik Deutschland, dem Königreich Spanien, der Französischen Republik, dem Großherzogtum Luxemburg, dem Königreich der Niederlande und der Republik Österreich über die Vertiefung der grenzüberschreitenden Zusammenarbeit, insbesondere zur Bekämpfung des Terrorismus, der grenz-überschreitenden Kriminalität und der illegalen Migration" (PDF) (in German). German Foreign Office. 2011-09-26. Retrieved 2014-05-03. - ↑ "Treaty between the Kingdom of Belgium, the Federal Republic of Germany, the Kingdom of Spain, The French Republic, the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, the Kingdom of the Netherlands and the Republic of Austria concerning the intensification of cross-border cooperation, particularly in the fight against terrorism, cross-border crime and illegal migration". UN Treaty database. 2009-09-04. Retrieved 2012-04-14.
- ↑ "Convention between the Kingdom of Belgium, the Federal Republic of Germany, the Kingdom of Spain, the French Republic, the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, the Kingdom of the Netherlands and the Republic of Austria on the stepping up of cross-border cooperation, particularly in combating terrorism, cross-border crime and illegal migration". Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs. 2012-04-14. Retrieved 2012-04-14.
- ↑ "2807th Council Meeting: Justice and Home Affairs" (PDF). Council of the European Union. 2007-06-13. Retrieved 2012-04-14.
- ↑ Barker, Alex (2014-11-12). "Police to share DNA database with Europe's forces". Financial Times. Retrieved 2014-11-20.
- ↑ "Council Decision of 27 November 2014 determining certain consequential and transitional arrangements concerning the cessation of the participation of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in certain acts of the Union in the field of police cooperation and judicial cooperation in criminal matters adopted before the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon". Official Journal of the European Union. L 343/11. 2014-11-27. Retrieved 2014-11-28.
- ↑ "Commission Decision (EU) 2016/809 of 20 May 2016 on the notification by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland of its wish to participate in certain acts of the Union in the field of police cooperation adopted before the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon and which are not part of the Schengen acquis". Official Journal of the European Union. L 132/105. 2016-05-21. Retrieved 2016-07-04.
- ↑ "Summary of Treaty". European Commission. 2010-09-13. Retrieved 2012-04-14.
- ↑ "Agreement details". Council of the European Union. Retrieved 2012-04-14.
- ↑ "Coopération Prüm: le Conseil fédéral délivre un mandat de négociation". Federal Department of Foreign Affairs of Switzerland. 2015-03-13. Retrieved 2015-03-17.
- ↑ "OUTCOME OF THE COUNCIL MEETING - 3473rd Council meeting - Justice and Home Affairs". Council of the European Union. 2016-06-10. Retrieved 2016-07-04.
See also
External links
- Official depositary page
- Text of the Prüm Convention
- The Prüm Process: Playing or abusing the system?
- The Prüm Regime: Situated Dis/Empowerment in Transnational DNA Profile Exchange, see:
