Myelitis
| Myelitis | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | neurology |
| ICD-10 | G04-G05 |
| ICD-9-CM | 323 |
| DiseasesDB | 29461 |
| MeSH | D009187 |

Myelitis involves the infection or the inflammation of the white matter or gray matter of the spinal cord which is a part of the central nervous system that acts as a bridge between the brain and the rest of the body. During an inflammatory response in the spinal cord, the myelin and axon may be damaged causing symptoms such as paralysis and sensory loss. Myelitis is classified to several categories depending on the area or the cause of the lesion; however, people often refer to any inflammatory attack on the spinal cord as transverse myelitis.
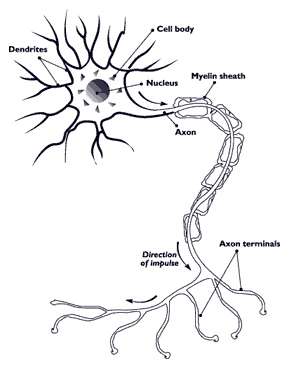
Types of Myelitis
Myelitis lesions usually occur in a narrow region but can be spread and affect many areas.
- Poliomyelitis:[1] disease caused by viral infection in the gray matter with symptoms of muscle paralysis or weakness
- Leukomyelitis: lesions in the white matter
- Transverse Myelitis: caused by axonal demyelination encompassing both sides of the spinal cord
- Meningococcal Myelitis (or meningomyelitis): lesions occurring in the region of meninges and the spinal cord
Symptoms
Depending on the cause of the disease, such clinical conditions manifest different speed in progression of symptoms in a matter of hours to days. Most myelitis manifests fast progression in muscle weakness or paralysis starting with the legs and then arms with varying degrees of severity. Sometimes the dysfunction of arms or legs cause instability of posture and difficulty in walking or any movement. Also symptoms generally include paresthesia which is a sensation of tickling, tingling, burning, pricking, or numbness of a person's skin with no apparent long-term physical effect. Adult patients often report pain in the back, extremities, or abdomen.[2] Patients also present increased urinary urgency, bowel or bladder dysfunctions such as bladder incontinence, difficulty or inability to void, and incomplete evacuation of bowel or constipation. Others also report fever, respiratory problems and intractable vomiting.[3]
Cause
Myelitis occurs due to various reasons such as infections. Direct infection by viruses, bacteria, mold, or parasites such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), human T cell lymphotropic virus types I and II (HTLV-I/II), syphilis, lyme disease, and tuberculosis can cause the myelitis but it can also be caused due to non-infectious or inflammatory pathway. Myelitis often follows after the infections or after vaccination. These phenomena can be explained by a theory of autoimmune attack which states that the autoimmune bodies attack its spinal cord in response to immune reaction.
Mechanism of Myelitis
The theory of autoimmune attack claims that a person with neuroimmunologic disorders have genetic predisposition to auto-immune disorder, and the environmental factors would trigger the disease. The specific genetics in myelitis is not completely understood. It is believed that the immune system response could be to viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infection; however, it is not known why the immune system attacks itself. Especially, for immune system to cause inflammatory response anywhere in the central nervous system, the cells from immune system must pass through the blood brain barrier. In the case of myelitis, not only is the immune system dysfunctional, but the dysfunction also crosses this protective blood brain barrier to affect the spinal cord.[4]
Infectious Myelitis[5]
- Viral Myelitis
Most viral myelitis is acute, but the retrovirus (HIV, HTLV) can cause chronic myelitis. Poliomyelitis, or gray matter myelitis, is usually caused by infection of anterior horn of the spinal cord by the enteroviruses (polioviruses, enteroviruses (EV) 70 and 71, echoviruses, coxsackieviruses A and B) and the flaviviruses (West Nile, Japanese encephalitis, tick-borne encephalitis). On the other hand, transverse myelitis or leukomyelitis, or white matter myelitis, are often caused by the herpesviruses and influenza virus. It can be due to direct viral invasion or via immune mediated mechanisms.
- Bacterial Myelitis
Bacterial myelitis includes Mycoplasma Pneumoniae, which is a common agent for respiratory tract. Studies have shown respiratory tract infections within 4–39 days prior to the onset of transverse myelitis. Or, tuberculosis, syphilis, and brucellosis are also known to cause myelitis in immune-compromised individuals. Myelitis is a rare manifestation of bacterial infection.
- Fungal Myelitis
Fungi have been reported to cause spinal cord disease either by forming abscesses inside the bone or by granuloma. In general there are two groups of fungi that may infect the CNS and cause myelitis - Primary and Secondary pathogens. Primary pathogens include following: Cryptococcus neoformans, Coccidiodes immitis, Blastomyces dermatitides, Hystoplasma capsulatum; Secondary pathogens are opportunistic agens that primarily infect immunocompromised hosts such as candida species, aspergillus species, and zygomycetes.
- Parasitic Myelitis
Parasitic species infect human hosts through larvae that penetrate the skin. Then they enter the lymphatic and circulatory system, and migrate to liver and lung. Some reach the spinal cord. Parasitic infections have been reported with Schistosoma species, Toxocara canis, Echinococcus species, Taenia solium, Trichinella spiralis, and Plasmodium species.
Diseases Associated With Myelitis
Conditions associated with myelitis include:
- Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: autoimmune demyelination of the brain causing severe neurological signs and symptoms
- Multiple sclerosis: demyelination of the brain and spinal cord
- Neuromyelitis optica or Devic's disease: immune attack on optic nerve and spinal cord
- Sjögren's syndrome: destruction of the exocrine system of the body
- Systemic lupus erythematosus: a systemic autoimmune disease featuring a wide variety of neurological signs and symptoms
- Sarcoidosis:[6] chronic inflammatory cells form as nodules in multiple organs
- Atopy: an immune disorder of children manifesting as eczema or other allergic conditions.[7] It can include atopic myelitis, which causes weakness.[8]
Diagnosis
Myelitis has an extensive differential diagnosis. The type of onset (acute versus subacute/chronic) along with associated symptoms such as the presence of pain, constitutional symptoms that encompass fever, malaise, weight loss or a cutaneous rash may help identify the cause of myelitis. In order to establish a diagnosis of myelitis, one has to localize the spinal cord level, and exclude cerebral and neuromuscular diseases. Also a detailed medical history, a careful neurologic examination, and imaging studies using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are needed. In respect to the etiology of the process, further work-up would help identify the cause and guide treatment. Full spine MRI is warranted, especially with acute onset myelitis, to evaluate for structural lesions that may require surgical intervention, or disseminated disease.[9] Adding gadolinium further increases diagnostic sensitivity. A brain MRI may be needed to identify the extent of central nervous system (CNS) involvement. Lumbar puncture is important for the diagnosis of acute myelitis when a tumoral process, inflammatory or infectious etiology are suspected, or the MRI is normal or non-specific. Complementary blood tests are also of value in establishing a firm diagnosis. Rarely, a biopsy of a mass lesion may become necessary when the etiology is uncertain. However, in 15–30% of patients with subacute or chronic myelitis, a clear etiology is never uncovered and their condition is considered idiopathic.[5]
Treatment
Since each case is different, the following are possible treatments that patients might receive in the management of myelitis.
- Intravenous Steroids
High-dose intravenous methyl-prednisolone for 3–5 days is considered as a standard of care for patients suspected to have acute myelitis, unless there are compelling reasons otherwise. The decision to offer continued steroids or add a new treatment is often based on the clinical course and MRI appearance at the end of 5 days of steroids.[10]
- Plasma Exchange (PLEX)[11]
Patients with moderate to aggressive forms of disease who don’t show much improvement after being treated with intravenous and oral steroids will be treated with PLEX. Retrospective studies of patients with TM treated with IV steroids followed by PLEX showed a positive outcome. It also has been shown to be effective with other autoimmune or inflammatory central nervous system disorders. Particular benefit has been shown with patients who are in the acute or subacute stage of the myelitis showing active inflammation on MRI. However, because of the risks implied by the lumbar puncture procedure, this intervention is determined by the treating physician on a case-by-case basis.[10]
- Immunosuppressants/Immunomodulatory Agents
Myelitis with no definite cause seldom recurs, but for others, myelitis may be a manifestation of other diseases that are mentioned above. In these cases, ongoing treatment with medications that modulate or suppress the immune system may be necessary. Sometimes there is no specific treatment. Either way, aggressive rehabilitation and long-term symptom management are an integral part of the healthcare plan.
Prospective Research Direction
Central Nervous System Nerve Regeneration would be able to repair or regenerate the damage caused to the spinal cord. It would restore functions lost due to the disease.[12]
- Engineering Endogenous Repair
Currently, there exists a hydrogel based scaffold which acts as a channel to deliver nerve growth-enhancing substrates while providing structural support. These factors would promote nerve repairs to the target area. Hydrogels' macroporous properties would enable attachment of cells and enhance ion and nutrient exchange. In addition, hydrogels' biodegradability or bioresolvability would prevent the need for surgical removal of the hydrogel after drug delivery. It means that it would be dissolved naturally by the body's enzymatic reaction.
- Biochemical Repair
Neurotropic Factor Therapy and Gene Therapy Neurotropic growth factors regulate growth, survival, and plasticity of the axon. They benefit nerve regeneration after injury to the nervous system. They are a potent initiator of sensory axon growth and are up-regulated at the lesion site. The continuous delivery of neurotropic growth factor (NGF) would increase the nerve regeneration in the spinal cord. However, the excessive dosing of NGF often leads to undesired plasticity and sprouting of uninjured sensory nerves. Gene therapy would be able to increase the NGF efficacy by the controlled and sustained delivery in a site-specific manner.
- Stem Cell Based Therapies
The possibility for nerve regeneration after injury to the spinal cord was considered to be limited because of the absence of major neurogenesis. However, Joseph Altman showed that cell division does occur in the brain which allowed potential for stem cell therapy for nerve regeneration.[13][14] The stem cell-based therapies are used in order to replace cells lost and injured due to inflammation, to modulate the immune system, and to enhance regeneration and remyelination of axons.[15] Neural stem cells (NSC) have the potential to integrate with the spinal cord because in the recent past investigations have demonstrated their potential for differentiation into multiple cell types that are crucial to the spinal cord. Studies show that NSCs that were transplanted into a demyelinating spinal cord lesion were found to regenerate oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells, and completely remyelinated axons.[16]
See also
- Encephalomyelitis
- Myalgic encephalomyelitis aka Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Transverse myelitis
References
- ↑ Kelly, H. (2006). Evidence for a causal association between oral polio vaccine and transverse myelitis: A case history and review of the Literature. Journal Of Paediatrics And Child Health, 42(4), 155-159.
- ↑ Thomas, M., & Thomas, J. (1997). Acute transverse myelitis. The Journal Of The Louisiana State Medical Society: Official Organ Of The Louisiana State Medical Society, 149(2), 75-77.
- ↑ Wasay, M., Arif, H., Khealani, B., & Ahsan, H. (2006). Neuroimaging of tuberculous myelitis: analysis of ten cases and review of literature. Journal Of Neuroimaging: Official Journal Of The American Society Of Neuroimaging, 16(3), 197-205.
- ↑ http://myelitis.org
- 1 2 Mihai, C., & Jubelt, B. (2012). Infectious myelitis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep, 12(6), 633-641. doi: 10.1007/s11910-012-0306-3
- ↑ Baum, J., Solomon, M., & Alba, A. (1981). Sarcoidosis as a cause of transverse myelitis: case report. Paraplegia, 19(3), 167-169.
- ↑ Stenius, B., Wide, L., Seymour, W.M., Holford-Strevens, V. and Pepys, J. (1971) Clinical significance of specific IgE to common allergens. I. Relationship of specific IgE against Dermatophagoides spp. and grass pollen to skin and nasal tests and history. Clin. Allergy, 1: 37–55
- ↑ Yoon, J. H., Joo, I. S., Li, W. Y., & Sohn, S. Y. (2009). Clinical and laboratory characteristics of atopic myelitis: Korean experience. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 285(1-2), 154-158. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2009.06.033
- ↑ Kitley, J., Leite, M., George, J., & Palace, J. (2012). The differential diagnosis of longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Multiple Sclerosis (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England), 18(3), 271-285.
- 1 2 http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/neurology_neurosurgery/specialty_areas/transverse_myelitis/about-tm/treatment.html
- ↑ Scott, T., Frohman, E., De Seze, J., Gronseth, G., & Weinshenker, B. (2011). Evidence-based guideline: clinical evaluation and treatment of transverse myelitis: report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology, 77(24), 2128-2134.
- ↑ Karumbaiah, L., Bellamkonda, R. . Neural Tissue Engineering.
- ↑ Altman J, Das GD (1965) Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol 124(3):319-335
- ↑ Reynolds BA, Weiss S (1992) Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells from the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science 255(5052):1707-1710
- ↑ Rowland JW, Hawryluk GW, Kwon B, Fehlings MG (2008) Current status of acute spinal cord injury pathophysiology and emerging therapies: promise on the horizon. Neurosurg Focus 25(5):E2
- ↑ Keirstead HS, Ben-Hur T, Rogister B, O'Leary MT, Dubois-Dalcq M, Blakemore WF (1999) Polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule-positive CNS precursors generate both oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells to remyelination the CNS after transplantation. J Neurosci 19(17):7529-7536