Mambai
| Mambai | |
|---|---|
| Region | East Timor |
Native speakers | 130,000 (2010 census)[1] |
|
Austronesian
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 |
mgm |
| Glottolog |
mamb1306[2] |
|
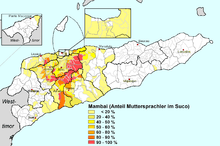
Distribution of Mambai mother-tongue speakers in East Timor | |
.jpg)
Typical Mambai house in Northern Ainaro.
The Mambai (also Mambae, Manbae) are the second largest ethnic group in East Timor. Their language is also called Mambai (or Mambae, Manbae).
People
The Mambai number about 80,000[3] from the interior of Dili District to the south coast of the territory, especially in the districts of Ainaro and Manufahi. Circular houses with conical roofs are typical dwellings,[4] and the Mambai cultivate maize, rice, and root vegetables.[3]
Ethnically Mambai politicians include Francisco Xavier do Amaral,[5] Manuel Tilman,[6] Lúcia Lobato,[7] and Fernando de Araújo.[7]
References
- ↑ Mambai at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Mambae". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- 1 2 Clifford Sather and James J. Fox (eds), Origins, Ancestry and Alliance: Explorations in Austronesian Ethnography, ANU E Press, 2006, Chapter 7.
- ↑ Tony Wheeler, East Timor, Lonely Planet, 2004, p. 93.
- ↑ Asian survey, University of California Press, 2003, Volume 43, Issues 4-6, p. 754
- ↑ International Crisis Group, Asia Briefing N°65, 13 June 2007
- 1 2 East Timor Legal Information Site, 2007
Further reading
People
- Elizabeth Gilbert Traube, Ritual exchange among the Mambai of East Timor: gifts of life and death, Harvard University Press, 1977.
- Elizabeth Gilbert Traube, Cosmology and Social Life: ritual exchange among the Mambai of East Timor, University of Chicago Press, 1986.
Language
- Geoffrey Hull, Celestino de Araújo, and Benjamim de Araújo e Corte-Real, Mambai Language Manual: Ainaro dialect, Sebastião Aparício da Silva Project, 2001.
- Alexandra Y. Aikhenvald and Robert M. W. Dixon (eds), Grammars in contact: a cross-linguistic typology, Oxford University Press, 2006, Chapter 6.
External links
- John 8,1-11 in Mambai
- Kaipuleohone's materials include Robert Blust's written notes on Mambai
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/4/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.