Lithium sulfide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Lithium hydrosulfide | |
| Preferred IUPAC name
Lithium sulfide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 12136-58-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 8466196 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.013 |
| EC Number | 235-228-1 |
| PubChem | 10290727 |
| RTECS number | OJ6439500 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Li2S | |
| Molar mass | 45.95 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.66 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 938 °C (1,720 °F; 1,211 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,372 °C (2,502 °F; 1,645 K) |
| very soluble | |
| Solubility | very soluble in ethanol |
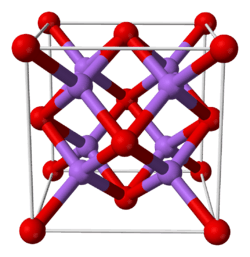
| Structure | |
| Antifluorite (cubic), cF12 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Tetrahedral (Li+); cubic (S2−) | |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S |
63 J/mol K |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
-9.401 kJ/g or -447 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) |
240 mg/kg (oral, rat)[1] |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions |
Lithium oxide |
| Other cations |
Sodium sulfide Potassium sulfide |
| Related compounds |
Lithium hydrosulfide |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Lithium sulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula Li2S. It crystallizes in the antifluorite motif, described as the salt (Li+)2S2−. It forms a solid yellow-white deliquescent powder. In air, it easily hydrolyses to release hydrogen sulfide (rotten egg odor).[2]
Preparation
Lithium sulfide is prepared by treating lithium with sulfur.[3] This reaction is conveniently conducted in anhydrous ammonia.[4]
- 2 Li + S → Li2S
The THF-soluble triethylborane adduct of lithium sulfide can be generated using superhydride.[5]
Reactions and applications
Lithium sulfide has been considered for use in lithium-sulfur batteries.[6]
References
- ↑ http://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/rn/12136-58-2
- ↑ Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
- ↑ "Webelements – Lithium Sulfide". Retrieved 2005-09-16.
- ↑ Rankin, D. W. H. (1974). "Digermanyl Sulfide". Inorg. Synth. 15: 182–84. doi:10.1002/9780470132463.ch40. ISBN 978-0-470-13246-3.
- ↑ Gladysz, J. A.; Wong, V. K. and Jick, B. G., "Reduction of S-S Bonds with LiBHEt3", Tetrahedron, 1979, 35, 2329.
- ↑ "Battery claims greater capacity than lithium ion". Electronics Weekly. Retrieved 2005-09-16.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/21/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
