List of zones of Nepal
 |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Nepal |
| Constitution |
|
Legislature
|
|
Judiciary |
|
| Foreign relations |
|
Related topics |
As of 20 September 2015 Nepal is divided into 7 provinces. They are defined by schedule 4 of the new constitution, by grouping together the existing districts. Two districts however are split in two parts ending up in two different provinces.

The administrative subdivisions of Nepal (provinces and districts).
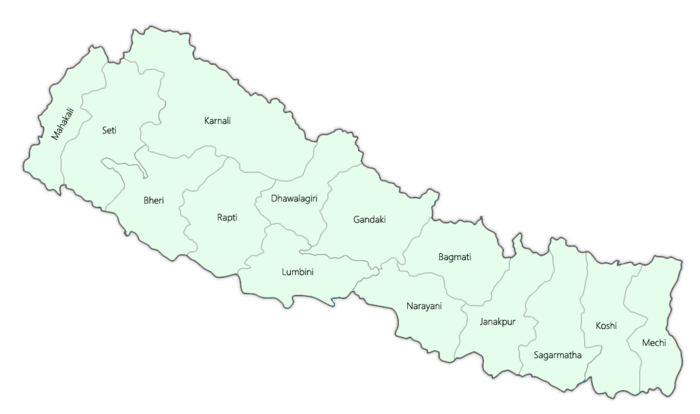
As of earlier model, Nepal was divided into 14 administrative zones (Nepali: अञ्चल; anchal) and 75 districts (Nepali: जिल्ला; jillā). The 14 administrative zones were grouped into five development regions (Nepali: विकास क्षेत्र; vikās kṣetra). Each district is headed by a Chief District Officer (CDO) and is responsible for maintaining law and order and coordinating the work of field agencies of the various government ministries.

From east to west:
- Eastern Development Region:
- Mechi Zone, named for the Mechi River
- Koshi Zone, named for the Kosi River
- Sagarmatha Zone, named for Sagarmatha (Mount Everest)
- Central Development Region:
- Janakpur Zone, named for its capital city
- Bagmati Zone, named for the Bagmati River
- Narayani Zone, named for the Narayani (lower Gandaki) River
- Western Development Region:
- Gandaki Zone, named for the Gandaki River
- Lumbini Zone, named for Lumbini, a pilgrimage site, birthplace of Gautama Buddha
- Dhaulagiri Zone, named for Dhaulagiri mountain
- Mid-Western Development Region:
- Rapti Zone, named for the West Rapti River
- Karnali Zone, named for the Karnali River
- Bheri Zone, named for the Bheri River
- Far-Western Development Region:
- Seti Zone, named for the Seti River
- Mahakali Zone, named after the Mahakali River
Clickable Map
See also
- Development Regions of Nepal
- List of districts of Nepal
- List of village development committees of Nepal
- ISO 3166-2:NP
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 12/5/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.