Dry Mesa Quarry

The Dry Mesa Dinosaur Quarry is situated in southwestern Colorado, United States, near the town of Delta. Its geology forms a part of the Morrison Formation and has famously yielded a great diversity of animal remains from the Jurassic Period, among them Ceratosaurus, Supersaurus, and Torvosaurus. The quarry is found within the Uncompahgre National Forest.
History
In 1971, a large theropod phalanx (Torvosaurus tanneri) was discovered at Dry Mesa by Daniel and Vivian Jones of Delta, Colorado. The find was reported to James A. Jensen of Brigham Young University (BYU) who commenced quarrying operations in 1972. Under the direction of the BYU Earth Science Museum, the quarry has been excavated for 13 field seasons. Approximately 4000 bones have been collected, making it one of the most prolific dinosaur producing accumulations in the Morrison Formation. Thirty vertebrate genera are represented in the quarry including dinosaurs, a pterosaur, crocodile, turtle, lungfish, and a prototherian mammal. Twenty-three genera of dinosaurs have been found in the quarry distinguishing it as the most diverse Jurassic dinosaur assemblage. The quarry is especially recognized for its large sauropods, among which Supersaurus vivianae and "Ultrasaurus" mcintoshi are the most celebrated finds (Richmond and Morris, 1999).
Geology
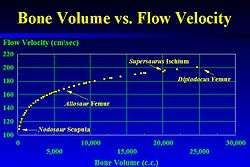
The Dry Mesa Dinosaur Quarry of western Colorado yields one of the most diverse Upper Jurassic vertebrate assemblages in the world. This fossil assemblage was deposited within a poorly sorted sandstone bed that is stratigraphically situated in the lower portion of the upper Brushy Basin Member of the Morrison Formation. The bone accumulation, consisting of thousands of bones, was the consequence of two cataclysmic events, a drought, and flash flood. In the Dry Mesa area, a severe drought resulted in the mass mortality of dinosaurs and other vertebrates. These animals were attracted to a remnant water hole of the dry Lake T'oo'dichi' lake bed where they died of starvation and dehydration. This mass mortality produced a considerable accumulation of disarticulated vertebrate remains. Subsequently, a short-lived flash flood traversed the dry lake beds. The quarry sandstone bed is a 2 meter thick, 121 meter wide, very poorly sorted pebble-rich sublitharenite. The channel sandstone shows abundant trough cross-stratification and a possible antidune bedform composed of gravel and sand which indicates flow velocities as high as 200 cm/s (5 miles/hour). Measured bone volumes can be equated to flow velocities. These calculated bone volume velocities are in agreement with flow velocities determined from grain size and bedforms. The river flow direction, based upon bedform orientations and bone elongation statistics, was to the east-northeast. Geologic and taphonomic characteristics indicate a short transport distance for the bone accumulation (Richmond and Morris, 1999).
Paleofauna
References
- Richmond, D.R. and Morris, T.H., 1999, Stratigraphy and cataclysmic deposition of the Dry Mesa Dinosaur Quarry, Mesa County, Colorado, in Carpenter, K., Kirkland, J., and Chure, D., eds., The Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation: An Interdisciplinary Study, Modern Geology v. 22, no. 1-4, pp. 121–143.
- Morris, T.H., Richmond, D.R., and Grimshaw, S.C., 1996, Orientation of dinosaur bones in riverine environments: Insights into sedimentary dynamics and taphonomy, in Morales, M., ed., The Continental Jurassic: Symposium Volume, Museum of Northern Arizona Bulletin 60, pp. 521–530.
- Richmond, D.R., 1994, Brigham Young University Thesis: Stratigraphy, sedimentology and microfacies analysis of the Dry Mesa Dinosaur Quarry, Mesa County, Colorado, 101 p.