Allkaruen
| Allkaruen Temporal range: Early Jurassic - Middle Jurassic, 182–168 Ma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Skeletal elements | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | †Pterosauria |
| Clade: | †Breviquartossa |
| Genus: | †Allkaruen Codorniú et al., 2016[1] |
| Species: | †A. koi |
| Binomial name | |
| Allkaruen koi Codorniú et al., 2016[1] | |
Allkaruen (meaning "ancient brain") is a genus of rhamphorhynchoid pterosaur from the Early-to-Middle Jurassic Cañadon Asfalto Formation in Argentina.[1] It contains a single species, A. koi.
Description
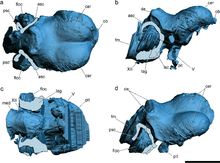
As demonstrated by a CT scan, the braincase of Allkaruen exhibits a unique set of traits that are intermediate between more basal pterosaurs such as Rhamphorhynchus and more derived pterodactyloid pterosaurs such as Anhanguera. These traits are the position of the anterior semicircular canal of the inner ear,[2] the relative orientations of the occiput and occipital condyle, the relative positions of the lateral margins of the flocculus and cerebral hemispheres, and the ratio between the length of the brain and the height of the hindbrain.[1] In addition, the relative orientations of the frontal bone and lateral semicircular canal are more similar to Rhamphorhynchus than Anhanguera, while the optic lobes are positioned lower than the forebrain as in pterodactyloids.[1][2] This unique combination of characters indicates that the anatomy of the braincase in pterodactyloids evolved through mosaic evolution.
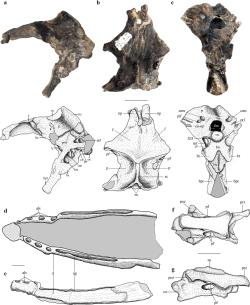
The parietals of Allkaruen were long, being 60% of the length of the frontals; the frontals themselves were broad, flat, and extensively pneumatized. The lower jaw was about 3.5 times the length of the section of the skull that is preserved, and it is curved upwards at its tip. The dentary bore four or five tooth sockets in its front half, and in the latter half they were replaced by a groove; this combination is unique among pterosaurs.[1]
Allkaruen was a small pterosaur. The holotype specimen would have been an adult, since its skull was entirely fused.[1]
Discovery and naming
The holotype of Allkauren consists of a braincase (MPEF-PV 3613), a mandible (MPEF-PV 3609), and a cervical vertebra (MPEF-PV 3615); a similar cervical vertebra (MPEF-PV 3616) was also referred to the genus.[1] These elements were in 2000 discovered in the Cañadón Asfalto Formation, Cerro Cóndor, Chubut, Argentina, for which dates ranging from the Toarcian to earliest Bathonian have been proposed.[3] Other elements, mostly disarticulated and consisting of a number of limb bones as well as another mandible, were also discovered at the site.[1][4]
The name Allkaruen is Tehuelche in origin, being derived from all ("brain") and karuen ("ancient"). The specific name, koi, originates from the Tehuelche word for "lake", in reference to the fact that the type locality would have been a saline lake.[1][5]
Classification
In 2016, two phylogenetic analyses were conducted based on the dataset from the description of Darwinopterus in order to determine the phylogenetic position of Allkaruen.[6] One analysis was restricted to the holotype braincase, while the other included the holotype mandible and cervical vertebrae as well. Allkaruen was consistently recovered as the sister taxon of the Monofenestrata; the consensus of the 360 most parsimonious trees is shown below.[1]
| Breviquartossa |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Codorniú, L.; Carabajal, A.P.; Pol, D.; Unwin, D.; Rauhut, O.W.M (2016). "A Jurassic pterosaur from Patagonia and the origin of the pterodactyloid neurocranium". PeerJ. 4: e2311. doi:10.7717/peerj.2311.
- 1 2 Witmer, L.M.; Chatterjee, S.; Franzosa, J.; Rowe, T. (2003). "Neuroanatomy of flying reptiles and implications for flight, posture and behaviour". Nature. 425: 950–953. doi:10.1038/nature02048.
- ↑ Cúneoa, R.; Ramezani, J.; Scasso, R.; Pol, D.; Escapa, I.; Zavattieri, A.M.; Bowring, S.A. (2013). "High-precision U–Pb geochronology and a new chronostratigraphy for the Cañadón Asfalto Basin, Chubut, central Patagonia: Implications for terrestrial faunal and floral evolution in Jurassic". Gondwana Research. 24 (3-4): 1267–1275. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2013.01.010.
- ↑ Codorniú, L.; Rauhut, O.W.M.; Pol, D. (2010). "Osteological features of Middle Jurassic pterosaurs from Patagonia (Argentina)". Acta Geoscientica Sinica. 31 (suppl. 1): 12–13.
- ↑ Cabaleri, N.G.; Armella, C.; Silva Nieto, D.G. (2005). "Saline paleolake of the Cañadón Asfalto Formation (Middle-Upper Jurassic), Cerro Cóndor, Chubut province (Patagonia), Argentina". Facies. 51 (1): 350–364. doi:10.1007/s10347-004-0042-5.
- ↑ Lu, J.; Unwin, D.M.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Ji, Q. (2010) [2009]. "Evidence for modular evolution in a long-tailed pterosaur with a pterodactyloid skull". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 277: 383–389. doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.1603.