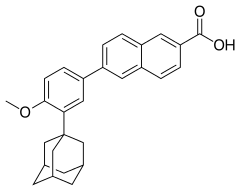
Adapalene
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Differin, Teva, Pimpal, Gallet, Adelene, Adeferin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a604001 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code | D10AD03 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Very low |
| Excretion | Biliary |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
106685-40-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 60164 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 5429 |
| DrugBank |
DB00210 |
| ChemSpider |
54244 |
| UNII |
1L4806J2QF |
| KEGG |
D01112 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:31174 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1265 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C28H28O3 |
| Molar mass | 412.52 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Adapalene is a third-generation topical retinoid primarily used in the treatment of mild-moderate acne, and is also used off-label to treat keratosis pilaris as well as other skin conditions.[1] It is effective against acne conditions where comedones are predominant.
Medical uses
It is used for the treatment of acne.[2]
Side effects
There is no evidence that the cream causes problems in the baby if used during pregnancy but this use has not been well studied.[2]
Interactions
Adapalene has been shown to enhance the efficacy of topical clindamycin, although adverse effects are also increased.[3] Application of adapalene gel to the skin 3–5 minutes before application of clindamycin enhances penetration of clindamycin into the skin, which may enhance the overall efficacy of the treatment as compared to clindamycin alone.[4]
Pharmacology
Unlike tretinoin (Retin-A), adapalene has also been shown to retain its efficacy when applied at the same time as benzoyl peroxide due to its more stable chemical structure.[5]
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption of adapalene through the skin is low. A study with six acne patients treated once daily for five days with two grams of adapalene cream applied to 1000 cm² of skin found no quantifiable amounts, or less than 0.35 ng/mL of the drug, in the patients' blood plasma.[6]
Mechanism of action
Unlike tretinoin, adapalene inhibits keratinocyte differentiation. This inhibition of keratinocyte differentiation and proliferation is responsible for adapalene’s comedolytic effect. It has both exfoliating and anti-inflammatory effects. In an in vivo study, adapalene’s ability to reduce comedo formation was demonstrated by a 50–60% reduction in comedo counts compared with vehicle.
History
Adapalene is a research product of Galderma Laboratories, France. Adapalene was approved in 1996 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in the treatment of acne.
Available forms

In the United States, adapalene is available under the brand name Differin' in three different preparations: 0.1% cream, 0.1% gel, and 0.3% gel.[7] The 0.1% gel is available as a generic made by Teva.[8][9] It is also available combined with benzoyl peroxide under the brand name Epiduo.[10] In Europe, only the 0.1% cream and 0.1% gel are available. Adapalene is currently marketed by Galderma under the trade names Differin in some countries, and Adaferin in India.[11] It is mostly available in 0.1% w/w gel form.
As of July 08, 2016, Galderma received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for Differin® Gel (adapalene gel 0.1%) as an over-the-counter (OTC) treatment for acne. [12]
References
- ↑ Rolewski S (2003). "Clinical review: topical retinoids". Dermatol Nurs. 15 (5): 447–50, 459–65. PMID 14619325.
- 1 2 "FDA approves Differin Gel 0.1% for over-the-counter use to treat acne". July 8, 2016. Retrieved 14 July 2016.
- ↑ Wolf JE, Kaplan D, Kraus SJ, et al. (2003). "Efficacy and tolerability of combined topical treatment of acne vulgaris with adapalene and clindamycin: a multicenter, randomized, investigator-blinded study". J Am Acad Dermatol. 49 (3 Suppl): S211–7. doi:10.1067/S0190-9622(03)01152-6. PMID 12963897.
- ↑ Jain GK, Ahmed FJ (2007). "Adapalene pretreatment increases follicular penetration of clindamycin: in vitro and in vivo studies". Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 73 (5): 326–9. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.34010. PMID 17921613.
- ↑ Martin B, Meunier C, Montels D, Watts O (October 1998). "Chemical stability of adapalene and tretinoin when combined with benzoyl peroxide in presence and in absence of visible light and ultraviolet radiation". Br J Dermatol. 139 Suppl 52: 8–11. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2133.1998.1390s2008.x. PMID 9990414.
- ↑ "DIFFERIN® (adapalene) Cream, 0.1% Label" (PDF). FDA. May 25, 2000. Retrieved 4 Oct 2011.
- ↑ About Differin Archived May 9, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Teva Introduces Adapalene Gel, 0.1%". PharmQD. 4 June 2010. Retrieved 30 Aug 2011.
- ↑ Webber, Keith (2 June 2010). "FDA Approval Letter" (PDF). Department of Health and Human Services. Retrieved 30 August 2011.
- ↑ http://www.webmd.com/news/20090106/fda-oks-new-acne-gel-epiduo
- ↑ http://www.drugsupdate.com/brand/generic/Adapalene/7099/none/2
- ↑ . FDA.gov http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm510362.htm. Missing or empty
|title=(help)
External links
- Adapalene General Information, Patient Information, Contraindications and Interactions
- Epiduo Prescribing Information