Western Satraps
| Western Satraps (Ariaca) | ||||||||||
| Possibly vassals of Kushan Empire | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
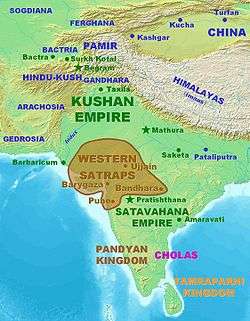 Approximate territory of the Western Kshatrapas (35–405). | ||||||||||
| Capital | Ujjain Barygaza | |||||||||
| Languages | Pali (Kharoshthi script) Sanskrit, Prakrit (Brahmi script) Possibly Greek (Greek alphabet) | |||||||||
| Religion | Hinduism, Buddhism | |||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | |||||||||
| Satrap, King | ||||||||||
| • | c. 35 | Abhiraka | ||||||||
| • | 388–395 | Rudrasimha III | ||||||||
| Historical era | Antiquity | |||||||||
| • | Established | 35 | ||||||||
| • | Disestablished | 405 | ||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Today part of | | |||||||||
The Western Satraps, Western Kshatrapas, or Kshaharatas (35–405) were Saka rulers of the western and central part of India (Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh states).
They were contemporaneous with the Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent and were possibly their overlords, and the Satavahana (Andhra) who ruled in Central India. They are called "Western" in contrast to the "Northern" Indo-Scythian satraps who ruled in the area of Mathura, such as Rajuvula, and his successors under the Kushans, the "Great Satrap" Kharapallana and the "Satrap" Vanaspara.[1] Although they called themselves "Satraps" on their coins, leading to their modern designation of "Western Satraps", Ptolemy in his 2nd century "Geographia" still called them "Indo-Scythians".[2] The power of the Saka rulers started to decline in the 2nd century CE after the Saka rulers were defeated by the south Indian Emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni of the Satavahana dynasty.[3] Later the Saka kingdom was completely destroyed by Chandragupta II of the Gupta Empire in the 4th century CE.[4]
Altogether, there were 27 independent Western Satrap rulers during a period of about 350 years. The word Kshatrapa stands for satrap, itself descended from Old Persian and which means viceroy or governor of a province.
History
First expansion: Kshaharata dynasty (1st century CE)
The Western Satraps are thought to have started with the rather short-lived Kshaharata dynasty (also called Chaharada, Khaharata or Khakharata depending on sources).[5] The term Kshaharata is also known from the 6 CE Taxila copper plate inscription, in which it qualifies the Indo-Scythian ruler Liaka Kusulaka. The Nasik inscription of the 19th year of Sri Pulamavi also mentions the Khakharatavasa, or Kshaharata race.[6]
The earliest Kshaharata for whom there is evidence is Abhiraka, whose rare coins are known. He was succeeded by Bhumaka, father of Nahapana, who only used on his coins the title of Satrap, and not that of Raja or Raño (king). Bhumaka was the father of the great ruler Nahapana, according to one of the latter's coins. His coins bear Buddhist symbols, such as the eight-spoked wheel (dharmachakra), or the lion seated on a capital, a representation of a pillar of Ashoka.
Nahapana succeeded to him, and became a very powerful ruler. He occupied portions of the Satavahana empire in western and central India. Nahapana held sway over Malwa, Southern Gujarat, and Northern Konkan, from Bharuch to Sopara and the Nasik and Poona districts.[7] His son-in-law, the Saka Ushavadata (married to his daughter Dakshamitra), is known from inscriptions in Nasik and Karle to have been viceroy of Nahapana, ruling over the southern part of his territory.[8]
Nahapana is mentioned in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea under the name Nambanus,[9] as ruler of the area around Barigaza:
41. "Beyond the gulf of Baraca is that of Barygaza and the coast of the country of Ariaca, which is the beginning of the Kingdom of Nambanus and of all India. That part of it lying inland and adjoining Scythia is called Abiria, but the coast is called Syrastrene. It is a fertile country, yielding wheat and rice and sesame oil and clarified butter, cotton and the Indian cloths made therefrom, of the coarser sorts. Very many cattle are pastured there, and the men are of great stature and black in color. The metropolis of this country is Minnagara, from which much cotton cloth is brought down to Barygaza."— Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, Chap. 41 [10]
Under the Western Satraps, Barigaza was one of the main centers of Roman trade with India. The Periplus describes the many goods exchanged:
49. There are imported into this market-town (Barigaza), wine, Italian preferred, also Laodicean and Arabian; copper, tin, and lead; coral and topaz; thin clothing and inferior sorts of all kinds; bright-colored girdles a cubit wide; storax, sweet clover, flint glass, realgar, antimony, gold and silver coin, on which there is a profit when exchanged for the money of the country; and ointment, but not very costly and not much. And for the King there are brought into those places very costly vessels of silver, singing boys, beautiful maidens for the harem, fine wines, thin clothing of the finest weaves, and the choicest ointments. There are exported from these places spikenard, costus, bdellium, ivory, agate and carnelian, lycium, cotton cloth of all kinds, silk cloth, mallow cloth, yarn, long pepper and such other things as are brought here from the various market-towns. Those bound for this market-town from Egypt make the voyage favorably about the month of July, that is Epiphi."— Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, Chapter 48.[11]
Goods were also brought down in quantity from Ujjain, the capital of the Western Satraps:
48. Inland from this place and to the east, is the city called Ozene, formerly a royal capital; from this place are brought down all things needed for the welfare of the country about Barygaza, and many things for our trade : agate and carnelian, Indian muslins and mallow cloth, and much ordinary cloth.— Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, Chapter 48.[11]
Some ships were also fitted out from Barigaza, to export goods westward across the Indian ocean:
"Ships are also customarily fitted out from the places across this sea, from Ariaca and Barygaza, bringing to these far-side market-towns the products of their own places; wheat, rice, clarified butter, sesame oil, cotton cloth, (the monache and the sagmatogene), and girdles, and honey from the reed called sacchari. Some make the voyage especially to these market-towns, and others exchange their cargoes while sailing along the coast."— Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, Chapter 14.[11]
Nahapana also established the silver coinage of the Kshatrapas.
Nahapana and Ushavadata were ultimately defeated by the powerful Satavahana king Gautamiputra Satakarni. Gautramiputra drove the Sakas from Malwa and Western Maharashtra, forcing Nahapana west to Gujarat. Gautamiputra restruck many of Nahapana's coins.

Kardamaka dynasty, family of Castana (1st–4th century)
A new dynasty, called the Bhadramukhas or Kardamaka dynasty, was established by the "Satrap" Castana. The date of Castana is not certain, but many believe his reign started in the year 78 CE, thus making him the founder of the Saka era.[12] This is consistent with the fact that his descendants (who we know used the Saka era on their coins and inscriptions) would use the date of their founder as their era. Castana was satrap of Ujjain during that period. A statue found in Mathura together with statues of the Kushan king Kanishka and Vima Taktu, and bearing the name "Shastana" is often attributed to Castana himself, and suggests Castana may have been a feudatory of the Kushans. Conversely, the Rabatak inscription also claims Kushan dominion over Western Satrap territory (by mentioning Kushan control over the capital Ujjain), during the reign of Kanishka (c. 127–150 CE).
Territory under Chastana
The territory of the Western Satraps at the time of Chastana is described extensively by the geographer Ptolemy in his "Geographia", where he qualifies them as "Indo-Scythians". He describes this territory as starting from Patalene in the West, to Ujjain in the east ("Ozena-Regia Tiastani", "Ozene, capital of king Chastana"), and beyond Barigaza in the south.
Moreover the region which is next to the western part of India, is called Indoscythia. A part of this region around the (Indus) river mouth is Patalena, above which is Abiria. That which is about the mouth of the Indus and the Canthicolpus bay is called Syrastrena. (...) In the island formed by this river are the cities Pantala, Barbaria. (...) The Larica region of Indoscythia is located eastward from the swamp near the sea, in which on the west of the Namadus river is the interior city of Barygaza emporium. On the east side of the river (...) Ozena-Regia Tiastani (...) Minnagara".— Ptolemy Geographia, Book Seven, Chapter I
Victory against the Satavahanas: Rudradaman I
Around 130 CE, Rudradaman I, grandson of Chastana, took the title "Mahakshatrapa" ("Great Satrap"), and defended his kingdom from the Satavahanas. The conflict between Rudradaman and Satavahanas became so gruelling, that in order to contain the conflict, a matrimonial relationship was concluded by giving Rudradaman's daughter to the Satavahana king Vashishtiputra Satakarni.
The Satavahanas and the Western Satraps remained at war however, and Rudradaman I defeated the Satavahanas twice in these conflicts, only sparing the life of Vashishtiputra Satakarni due to their family alliance:
"Rudradaman (...) who obtained good report because he, in spite of having twice in fair fight completely defeated Satakarni, the lord of Dakshinapatha, on account of the nearness of their connection did not destroy him."— Junagadh rock inscription [13]
Rudradaman regained all the previous territories held by Nahapana, except for the southern areas of Poona and Nasik:
"Rudradaman (...) who is the lord of the whole of eastern and western Akaravanti (Akara: East Malwa and Avanti: West Malwa), the Anupa country, Anarta, Surashtra, Svabhra (northern Gujarat), Maru (Marwar), Kachchha (Cutch), Sindhu-Sauvira (Sindh and Multan districts), Kukura (Eastern Rajputana), Aparanta ("Western Border" – Northern Konkan), Nishada (an aboriginal tribe, Malwa and parts of Central India) and other territories gained by his own valour, the towns, marts and rural parts of which are never troubled by robbers, snakes, wild beasts, diseases and the like, where all subjects are attached to him, (and) where through his might the objects of [religion], wealth and pleasure [are duly attained]".
Recently discovered pillar inscriptions describe the presence of a Western Satrap named Rupiamma in the Bhandara district of the area of Vidarbha, in the extreme northeastern area of Maharashtra, where he erected the pillars.[15]
Rudradarman is known for his sponsoring of the arts. He is known to have written poetry in the purest of Sanskrit, and made it his court language. His name is forever attached to the inscription by Sudharshini lake.
He had at his court a Greek writer named Yavanesvara ("Lord of the Greeks"), who translated from Greek to Sanskrit the Yavanajataka ("Saying of the Greeks"), an astrological treatise and India's earliest Sanskrit work in horoscopy.[16]
Defeat against the Satavahanas: Yajna Sri Satakarni
The south Indian ruler Yajna Sri Satakarni of the Satavahana dynasty defeated the Western Satraps in the late 2nd century CE, which led to a decline in the power of the ruling dynasty.
Rudrasena II (256–278)
The Kshatrapa dynasty seems to have reached a high level of prosperity under the rule of Rudrasena II (256–278), 19th ruler of Kshatrapa.
The last Kshatrapa ruler of the Chastana family was Visvasena (Vishwasen), brother and successor to Bhartrdaman and son of Rudrasena II. A new family took over, started by the rule of Rudrasimha II, son of Lord (Svami) Jivadaman.
Defeat by the Guptas (c. 400)
A new family took control under Rudrasimha III. A fragment from the Natya-darpana mentions that the Gupta king Ramagupta, the elder brother of Chandragupta II, decided to expand his kingdom by attacking the Western Satraps in Gujarat.
The campaign soon took a turn for the worse and the Gupta army was trapped. The Saka king, Rudrasimha III, demanded that Ramagupta hand over his wife Dhruvadevi in exchange for peace. To avoid the ignominy the Guptas decide to send Madhavasena, a courtesan and a beloved of Chandragupta, disguised as the queen. However, Chandragupta changes the plan and himself goes to the Saka King disguised as the queen. He then kills Rudrasimha and later his own brother, Ramagupta. Dhruvadevi is then married to Chandragupta.
The Western Satraps were eventually conquered by emperor Chandragupta II. This brought an end to the rule of the Sakas on the subcontinent.
Coinage
The Kshatrapas have a very rich and interesting coinage. It was based on the coinage of the earlier Indo-Greek Kings, with Greek or pseudo-Greek legend and stylized profiles of royal busts on the obverse. The reverse of the coins however is original and typically depict a thunderbolt and an arrow, and later, a chaitya or three-arched hill and river symbol with a crescent and the sun, within a legend in Brahmi. These coins are very informative, since they record the name of the King, of his father, and the date of issue, and have helped clarify the early history of India.
 Coin of Bhumaka (?–119). Obv:Arrow, pellet, and thunderbolt. Kharoshthi inscription Chaharasada Chatrapasa Bhumakasa: "Ksaharata Satrap Bhumaka". Rev: Capital of a pillar with seated lion with upraised paw, and wheel (dharmachakra). Brahmi inscription: Kshaharatasa Kshatrapasa Bhumakasa. |
 Coin of Nahapana (119–124). British Museum. |
 Coin of the Western Satrap Chastana (c. 130 CE). Obv: King in profile. The legend typically reads "PANNIΩ IATPAΠAC CIASTANCA" (corrupted Greek script), transliteration of the Prakrit Raño Kshatrapasa Castana: "King and Satrap Castana". Rev: Chaitya with moon, star and river. Brahmi legend Rajno Mahakshatrapasa Ghsamotikaputrasa Casthanasa: "King and Great Satrap Chastana, son of Zamotika. |
 Silver coin of Rudradaman I (130–150). Obv: Bust of Rudradaman, with corrupted Greek legend "OVONIΛOOCVΛCHΛNO". Rev: Three-arched hill or Chaitya with river, crescent and sun. Brahmi legend: Rajno Ksatrapasa Jayadamasaputrasa Rajno Mahaksatrapasa Rudradamasa: "King and Great Satrap Rudradaman, son of King and Satrap Jayadaman" 16mm, 2.0 grams. |
 Coin of the Western Kshatrapa ruler Rudrasimha I (178–197).
Obv: Bust of Rudrasimha, with corrupted Greek legend "..OHIIOIH.." (Indo-Greek style).
Rev: Three-arched hill or Chaitya, with river, crescent and sun, within Prakrit legend in Brahmi script:Rajno Mahaksatrapasa Rudradamnaputrasa Rajna Mahaksatrapasa Rudrasihasa "King and Great Satrap Rudrasimha, son of King and Great Satrap Rudradaman". |
 Coin of Rudrasena I (200–222). |
 Coin of the last Western Satrap ruler Rudrasimha III (388–395). |
 The Guptas imitated Western Satrap coins for their silver coinage. Here, a coin of the Gupta king Kumaragupta I (414–455) (Western territories). |
Regnal dates
From the reign of Rudrasimha I, the date of minting of each coin, reckoned in the Saka era, is usually written on the obverse behind the king's head in Brahmi numerals, allowing for a quite precise datation of the rule of each king.[17] This is a rather uncommon case in Indian numismatics. Some, such as the numismat R.C Senior considered that these dates might correspond to the much earlier Azes era instead.
Also the father of each king is systematically mentioned in the reverse legends, which allows to reconstruct the regnal succession.
Languages
Kharoshthi, a script in use in more northern territories (area of Gandhara), is employed together with the Brahmi script and the Greek script on the first coins of the Western Satraps, but is finally abandoned from the time of Chastana.[18] From that time, only the Brahmi script would remain, together with the pseudo-Greek script on the facing, to write the Prakrit language employed by the Western satraps. Occasionally, the legends are in Sanskrit instead.
The coins of Nahapana bears the Greek script legend "PANNIΩ IAHAPATAC NAHAΠANAC", transliteration of the Prakrit "Raño Kshaharatasa Nahapanasa": "In the reign of Kshaharata Nahapana". The coins of Castana also have a readable legend "PANNIΩ IATPAΠAC CIASTANCA", transliteration of the Prakrit "Raño Kshatrapasa Castana": "In the reign of the Satrap Castana". After these two rulers, the legend in Greek script becomes denaturated, and seems to lose all signification, only retaining an esthetic value. By the 4th century, the coins of Rudrasimha II exhibit the following type of meaningless legend in corrupted Greek script: "...ΛIOΛVICIVIIIΛ...".[19]
Influences
The coins of the Kshatrapas were also very influential and imitated by neighbouring or later dynasties, such as the Satavahanas, and the Guptas. Silver coins of the Gupta kings Chandragupta II and his son Kumaragupta I adopted the Western Satrap design (itself derived from the Indo-Greeks) with bust of the ruler and pseudo-Greek inscription on the obverse, and a royal eagle (Garuda, the dynastic symbol of the Guptas) replacing the chaitya hill with star and crescent on the reverse.[20]
The Western Satrap coin design was also adopted by the subsequent dynasty of the Traikutakas (388–456).
Monuments
Sudarshan Lake of Satrap period is mentioned in major rock edicts of Junagadh but no trace of it remains. Six inscription-stones called Lashtis of 1st century were recovered from hillock near Andhau village in Khavda region of Kutch and were moved to Kutch Museum in Bhuj. They are earliest dated monuments of Satrap period and were erected in the time of Rudradaman I.[21]
Possible vassalage to the Kushans
It is still unclear whether the Western Satraps were independent rulers or vassals of the Kushans. The continued use of the word "Satrap" on their coin would suggest a recognized subjection to a higher ruler, possibly the Kushan emperor.[22]
Also, a statue of Chastana was found in Mathura at the Temple of Mat together with the famous statues of Vima Kadphises and Kanishka. This also would suggest at least alliance and friendship, if not vassalage. Finally Kanishka claims in the Rabatak inscription that his power extends to Ujjain, the classical capital of the Western Satrap realm. This combined with the presence of the Chastana statue side-by-side with Kanishka would also suggest Kushan alliance with the Western Satraps.
Finally, "Northern" Indo-Scythian satraps who ruled in the area of Mathura, the "Great Satrap" Kharapallana and the "Satrap" Vanaspara, are known from an inscription in Sarnath to have been feudatories of the Kushans.[1]
Generally the orientation taken by modern scholarship is that the Western Satraps were vassals of the Kushan, at least in the early period until Rudradaman I conquered the Yaudheyas who are usually thought themselves as Kushan vassals. The question is not considered as perfectly settled.
Main rulers
Kshaharata dynasty
Bhadramukhas or Kardamaka dynasty
Family of Chastana:
- Chastana (c. 78-130), son of Zamotika

- Jayadaman, son of Chastana
- Rudradaman I (c. 130–150), son of Jayadaman

- Damajadasri I (170–175)
- Jivadaman (175, d. 199)

- Rudrasimha I (175–188, d. 197)

- Isvaradatta (188–191)
- Rudrasimha I (restored) (191–197)

- Jivadaman (restored) (197–199)

- Rudrasena I (200–222)

- Samghadaman (222–223)
- Damasena (223–232)
- Damajadasri II (232–239) with
- Viradaman (234–238)
- Yasodaman I (239)
- Vijayasena (239–250)
- Damajadasri III (251–255)
- Rudrasena II (255–277)
- Visvasimha (277–282)
- Bhartrdaman (282–295)
- Visvasena (293–304)
Family of Rudrasimha II:
- Rudrasimha II, son of Lord (Svami) Jivadaman (304–348) with
- Yasodaman II (317–332)
- Rudradaman II (332–348)
- Rudrasena III (348–380)
- Simhasena (380–384(5?)
- Rudrasena IV (382–388)
- Rudrasimha III (388–395)

See also
| Middle kingdoms of India | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timeline and cultural period |
Northwestern India | Indo-Gangetic Plain | Central India | Southern India | ||
| Western Gangetic Plain | Northern India (Central Gangetic Plain) |
Northeastern India | ||||
| IRON AGE | ||||||
| Culture | Late Vedic Period | Late Vedic Period (Brahmin ideology)[lower-alpha 1] |
Late Vedic Period (Kshatriya/Shramanic culture)[lower-alpha 2] |
Pre-history | ||
| 6th century BC | Gandhara | Kuru-Panchala | Magadha | Adivasi (tribes) | ||
| Culture | Persian-Greek influences | "Second Urbanisation" Rise of Shramana movements |
Pre-history | |||
| 5th century BC | (Persian rule) | Shishunaga dynasty | Adivasi (tribes) | |||
| 4th century BC | (Greek conquests) | |||||
| HISTORICAL AGE | ||||||
| Culture | Spread of Buddhism | Pre-history | Sangam period (300 BC – 200 AD) | |||
| 3rd century BC | Maurya Empire | Early Cholas 46 other small kingdoms in Ancient Thamizhagam | ||||
| Culture | Preclassical Hinduism[lower-alpha 3] - "Hindu Synthesis"[lower-alpha 4] (ca. 200 BC - 300 AD)[lower-alpha 5][lower-alpha 6] Epics - Puranas - Ramayana - Mahabharata - Bhagavad Gita - Brahma Sutras - Smarta Tradition Mahayana Buddhism |
Sangam period (continued) | ||||
| 2nd century BC | Indo-Greek Kingdom | Shunga Empire | Adivasi (tribes) | Early Cholas 46 other small kingdoms in Ancient Thamizhagam | ||
| 1st century BC | Yona | Maha-Meghavahana Dynasty | ||||
| 1st century AD | Kuninda Kingdom | |||||
| 2nd century | Pahlava | Varman dynasty | ||||
| 3rd century | Kushan Empire | Western Satraps | Kamarupa kingdom | Kalabhra dynasty | ||
| Culture | "Golden Age of Hinduism"(ca. AD 320-650)[lower-alpha 7] Puranas Co-existence of Hinduism and Buddhism | |||||
| 4th century | Gupta Empire | Kalabhra dynasty | ||||
| 5th century | Maitraka | Adivasi (tribes) | Kalabhra dynasty | |||
| 6th century | Badami Chalukyas | |||||
| Culture | Late-Classical Hinduism (ca. AD 650-1100)[lower-alpha 8] Advaita Vedanta - Tantra Decline of Buddhism in India | |||||
| 7th century | Indo-Sassanids | Vakataka dynasty Empire of Harsha |
Mlechchha dynasty | Adivasi (tribes) | Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | |
| 8th century | Kidarite Kingdom | Pandyan Kingdom | ||||
| 9th century | Indo-Hephthalites (Huna) | Gurjara-Pratihara | Rashtrakuta dynasty | |||
| 10th century | Pala dynasty | Kalyani Chalukyas | ||||
References and sources for table References Sources
| ||||||
Notes
- 1 2 Kharapallana and Vanaspara are known from an inscription discovered in Sarnath, and dated to the 3rd year of Kanishka, in which they were paying allegiance to the Kushanas. Source: "A Catalogue of the Indian Coins in the British Museum. Andhras etc." Rapson, p ciii
- ↑ Ptolemy, "Geographia", Chap 7
- ↑ World history from early times to A D 2000 by B .V. Rao: p.97
- ↑ Ancient India by Ramesh Chandra Majumdar p. 234
- ↑ Rapson, p. CVII
- ↑ "Kharoshthi inscription, Taxila copper plate of Patika", Sten Konow, p25
- ↑ "The Satavahanas did not hold the western Deccan for long. They were gradually pushed out of the west by the Sakas (Western Khatrapas). The Kshaharata Nahapana's coins in the Nasik area indicate that the Western Kshatrapas controlled this region by the 1st century CE. By becoming master of wide regions including Malwa, Southern Gujarat, and Northern Konkan, from Broach to Sopara and the Nasik and Poona districts, Nahapana rose from the status of a mere Kshatrapa in the year 41 (58 AD) to that of Mahakshatrapa in the year 46 (63 AD)." in "History of the Andhras"
- ↑ "Catalogue of Indian coins of the British Museum. Andhras etc." Rapson. p. LVII
- ↑ "History of the Andhras", Durga Prasad Source
- ↑ Source
- 1 2 3 Source
- ↑ A. Jha and D. Rajgor: Studies in the Coinage of the Western Ksatraps, Nashik: Indian Institute of Research in Numismatic Studies, 1992, p. 7.
- 1 2 Source
- ↑ Rapson, "Indian coins of the British Museum" p.lx
- ↑ "Vidarbha also was under the rule of another Mahakshatrapa named Rupiamma, whose pillar inscription was recently discovered at Pavni in the Bhandara district [Mirashi, Studies in Indology, Vol. IV, p. 109 f.]. It records the erection of a chhaya-stambha or sculptured pillar at the place. The Satavahanas had, Therefore, to leave Western Maharashtra and Vidarbha. They seem to have repaired to their capital Pratishthana where they continued to abide waiting for a favourable opportunity to oust the Shaka invaders." Source
- ↑ Mc Evilley "The shape of ancient thought", p385 ("The Yavanajataka is the earliest surviving Sanskrit text in astrology, and constitute the basis of all later Indian developments in horoscopy", himself quoting David Pingree "The Yavanajataka of Sphujidhvaja" p5)
- ↑ Rapson CCVIII
- ↑ Rapson p. CIV
- ↑ Rapson, "A Catalogue of Indian coins in the British Museum. Andhras etc.", p.cxcii
- ↑ "Evidence of the conquest of Saurastra during the reign of Chandragupta II is to be seen in his rare silver coins which are more directly imitated from those of the Western Satraps... they retain some traces of the old inscriptions in Greek characters, while on the reverse, they substitute the Gupta type ... for the chaitya with crescent and star." in Rapson "A catalogue of Indian coins in the British Museum. The Andhras etc.", p.cli
- ↑ Hasmukh Dhirajlal Sankalia (1941). The Archaeology of Gujarat: Including Kathiawar. Natwarlal & Company. p. 46. Archived from the original on 2015.
- ↑ "The titles "Kshatrap" and "Mahakshatrapa" certainly show that the Western Kshatrapas were originally feudatories" in Rapson, "Coins of the British Museum", p.cv
In foot note number 13 on Rupiamma, I would like to point out that he wasn't from the Kshahartha family or the Kardamaka family of Chashtana. Some rulers used the title Mahakshtrapa without belonging to these dynasties. There is an article in Journal of Epigraphic Society of India Vol 18 by H.S. Thosar that will tell us the history of this Rupiamma. The pillar inscriptions merely mentions his name Mahakshtrapa Rupiamma with a low relief sculpture. There is no date or any other record. Rupiamma should not be included in the Western Satrap history.
References
- Rapson, "A Catalogue of Indian coins in the British Museum. Andhras etc."
- John Rosenfield, "The dynastic art of the Kushans", 1976
- Claudius Ptolemy, "The geography", Translated and edited by Edward Luther Stevenson, Dover Publications Inc., New York, ISBN 0-486-26896-9
External links
- History of the Andhras, Prasad 1988 With many references to Western Satrap rule
- Online catalogue of Western Kshatrapa coins
- Coins of the Western Kshatrapas
- The Kshatrapas in Nasik
- The Origins of the Indian Coinage Tradition at Academia.edu