Tranz Metro
|
| |
| Overview | |
|---|---|
| Owner | KiwiRail |
| Locale | Wellington Region, New Zealand |
| Transit type | Suburban rail |
| Number of lines | 5 |
| Number of stations | 49 |
| Annual ridership | 11.6 million (2013-14)[1] |
| Headquarters | Wellington Railway Station, Wellington |
| Operation | |
| Began operation |
July 1938 (electric trains introduced in Wellington)[2] 1985 (CityRail created) 1995 (Renamed Tranz Metro) |
| Ended operation | 2 July 2016 (replaced by Transdev Wellington) |
| Number of vehicles | 166 |
| Technical | |
| System length | 154 km (96 mi) |
| Track gauge | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) |
| Electrification | 1,600V DC overhead catenary (95 km or 59 mi) |
Tranz Metro (formerly CityRail and before that Cityline), was a New Zealand public transport operator. Beginning as the New Zealand Railways Corporation's Cityline division as a result of restructuring in the 1980s, in its final form Tranz Metro was the operator of Metlink's suburban trains owned by the Greater Wellington Regional Council in the Wellington Region of New Zealand.
From 3 July 2016 Wellington's commuter rail services are operated by Transdev Wellington.[3]
History
Suburban passenger rail services in Auckland and Wellington were a part of the New Zealand Railways Department, while bus services were owned either by city corporations or the Railways. With the restructuring of the department into the New Zealand Railways Corporation in the early 1980s, suburban bus and rail services came under the Cityline brand as part of the Corporation's Rail Passenger Group. Further restructuring of the rail network came in the 1990s, and the suburban rail operations were renamed CityRail after they were transferred to New Zealand Rail Limited in 1991. That year the Auckland Regional Council bought the Auckland CityRail fleet and contracted New Zealand Rail to run it, extending the contract until 1993 and again for 10 years until 2003.[4]
In 1993 New Zealand Rail Limited was privatised, renamed Tranz Rail in 1995, with CityRail rebranded Tranz Metro. On 15 December 2000, as part of management changes at Tranz Rail, the company split Tranz Metro into wholly owned subsidiaries Tranz Metro Auckland Ltd[5] and Tranz Metro Wellington Ltd,[6] with the intention of selling them. Stagecoach New Zealand and Greater Wellington Regional Council (GWRC) announced their intention to bid for the Wellington company, but both were barred by the Commerce Commission from doing so. Tranz Rail did not bid for the Auckland contract when it expired in 2003. Australian-based Connex (later Veolia and now Transdev) won the contract, and took over from 23 August 2004.[7] Tranz Metro Wellington reverted to a business unit of Tranz Rail, with new contracts being signed with GWRC in 2006 for network access, rolling stock maintenance and service delivery. The contracts expire in 2016.[8]
In 2004 Toll Holdings of Australia bought a majority shareholding in Tranz Rail and renamed the company Toll NZ, and on 1 July 2008 it was bought (less the Tranz Link trucking and distribution arm) by the government and renamed KiwiRail. In October 2009 Cabinet agreed on a Metropolitan Rail Operating Model, which requires the operating contracts for metropolitan rail operations to be "contestable". This is in line with Auckland's rail contract.[9]
An agreement signed in July 2011 transferred ownership of KiwiRail's station buildings, excluding Wellington Railway Station, to the GWRC, along with the D/DM class and EM/ET units (the FP/FT units were already owned by GWRC). KiwiRail retains ownership of the tracks, platforms, electric traction and signalling systems.[10] The assets were valued at $107.5 million.[11] Ownership of the fleet transferred on 1 July 2011 to Greater Wellington Rail Ltd, formed by Greater Wellington Regional Council in 2006.[12]
In 2014, Transdev announced its intention to bid for the operations contract when it comes up for renewal in 2016.[3] The contact was awarded to the partnership between Transdev and Hyundai Rotem in December 2015, expected to commence in July 2016.[13]
Operations
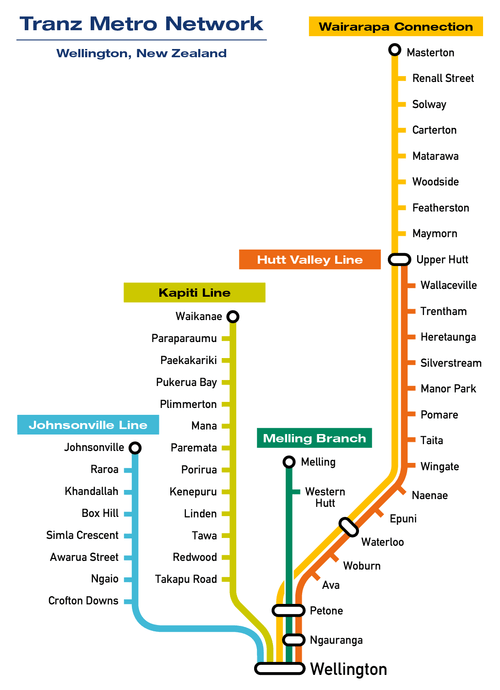
Metlink trains are operated under contract from GWRC, which subsidises the operation and owns station buildings and rolling stock. Typically 60% of that subsidy comes from central government through the NZ Transport Agency (formerly Land Transport New Zealand), which approves such funding after analysis of the economics and net benefits, the remainder coming from the GWRC. Public consultation in 2005-2006 resulted in some changes of emphasis in the new contract, which runs for ten years from June 2006.[14] The September 2006 fare rises and section changes were stated to part-pay for a major upgrade of trains and facilities over the next few years in conjunction with regional bus service improvements.
Rolling stock
Rolling stock as at 2 July 2016:
| Image | Class | Type | Number | Seats | Routes operated | Introduction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
FP class Matangi |
electric multiple unit | 75× 2-car sets | 149 | Kapiti Line Melling Line Hutt Valley Line Johnsonville Line |
2011–16 | |
| |
SW class | passenger carriage | 12× SW 3× SWG 3× SWS |
64 (SW) 37 (SWG/SWS) |
Wairarapa Connection | 2007 | |
 |
SE class | passenger carriage | 4× SE 1× SEG 1× SES |
64 (SE) 37 (SEG/SES) |
Wairarapa Line Kapiti Line (former) Hutt Valley Line (former) |
2008 (HVL and KPL, withdrawn 2011) 2013 (WRL) | |
| AG class | luggage van | 1 | - | Wairarapa Connection | 2007 | ||
 |
DFB class | diesel-electric locomotive | 5 | - | Wairarapa Connection | 2015 | |
Former rolling stock
| Image | Class | Type | Number | Seats | Routes operated | Introduction | Withdrawal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
EM/ET class Ganz Mavag |
electric multiple unit | 44× 2-car sets | 148 | Kapiti Line Melling Line Hutt Valley Line |
1981–82 | 2011–16 |
| |
DM/D class English Electric |
electric multiple unit | 49 | 132 | Hutt Valley Line | 1938–1954 | 1983–2012 |
 |
EO class | electric locomotive | 3 | - | Kapiti Line Hutt Valley Line |
2008 | 2011[15] |
 |
EW class | electric locomotive | 7 | - | Kapiti Line Melling Line Hutt Valley Line Johnsonville Line |
1952 | 1988 |
| |
NZR 56-foot carriage | passenger carriage | up to 56 | Kapiti Line Melling Line Hutt Valley Line Johnsonville Line Wairarapa Connection |
1937–1945 | 1988 (except Wairarapa and Capital Connection) 1998 (Capital Connection) 2007 (Wairarapa Connection) | |
 |
DC class | diesel-electric locomotive | 4 | - | Wairarapa Connection | 1978–80 | 2015 |
Upgrades
In 2008-2011 KiwiRail and GWRC undertook a major upgrade of the Metlink network, dubbed the Wellington Regional Rail Programme (WRPP). The $390 million program included:[16]
- The purchase of 48 two-car electric multiple units, the "Matangi" FP/FT class, to replace the aging DM/D class units and to increase capacity.
- Upgrading the electrification system, including refurbishing the overhead lines and masts and 12 new substations to increase electrical supply for the Matangi units.
- Upgrading the signalling system, including replacing control systems and signal wiring and hardening the track circuits from interference with the electrification.
- Upgrading platforms at several stations to accommodate Matangi units and longer train lengths.
- Upgrading the Johnsonville Line to accommodate both Ganz Mavag and Matangi units, by improving the loading gauge in the tunnels and under some bridges.
- Lengthening the three crossing loops on the Johnsonville Line to take longer trains.
- Double-tracking the Kapiti Line from Mackays Crossing through Paraparaumu to just south of Waikanae, to increase capacity. (The double track stops short of Waikanae Station to avoid the cost of building second bridges over State Highway 1 and the Waikanae River.)
- Electrifying the Kapiti Line from Paraparaumu to Waikanae.
- Adding additional stabling storage at Paekakariki and Waikanae for the Matangi and Ganz Mavag units.
- Installing a third, bi-directional, line into between Wellington Station and the Kapiti/Hutt Valley line junction to ease congestion at peak times.
Work started on the programme in 2008, and was largely completed in February 2011.[17]
Funding
In 2011/2012, Tranz Metro had annual operational expenses of $80.437m, and revenues of $80.442m. Most revenue (47% or $37.8m) comes from fares, 22% or $17.69m comes from Wellington Regional Council rates, and 30% or $24.13m from New Zealand Transport Agency public transport funding.[18]
See also
- Rail transport in New Zealand
- Public transport in the Wellington Region
- List of Wellington railway stations
- List of rapid transit systems
References
- ↑ "Wellington Metropolitan Rail 2013/14 Annual Report" (PDF). Greater Wellington Regional Council. 30 June 2014. Retrieved 24 July 2015.
- ↑ "Electric trains come to Wellington". New Zealand History online. 20 December 2012.
- 1 2 "Wellingtons trains to be run by French company Transdev after KiwiRail loses contract". The Dominion Post. 17 December 2015. Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- ↑ "Auckland Region Passenger Rail Service Report". Controller and Auditor-General of New Zealand. 4 November 2003.
- ↑ "Companies Office - Tranz Metro Auckland Limited". Companies Office. 15 December 2000. Retrieved 10 January 2012.
- ↑ "Companies Office - Tranz Metro Wellington Limited". Companies Office. 15 December 2000. Retrieved 10 January 2012.
- ↑ Matthew Dearney (23 August 2004). "New hand on lever of Auckland's trains". New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 9 January 2012.
- ↑ "Transdev Auckland eyes Kiwirail's Wellington contract". TVNZ. 20 June 2014.
- ↑ "Metropolitan Rail Operating Model". Ministry of Transport. October 2009.
- ↑ "$168m Wellington Rail Package Signed". The Dominion Post. 5 July 2011.
- ↑ "KiwiRail on track with 29% increase in operating surplus". KiwiRail. 29 August 2011. Retrieved 30 August 2011.
- ↑ "Capital gets $88 million rail upgrade". The Dominion Post. 10 March 2011. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ↑ TRANSDEV HYUNDAI ROTEM ANNOUNCED PREFERRED BIDDER TO OPERATE GREATER WELLINGTON RAIL NETWORK, Transdev Australasia, Retrieved 5 January 2016
- ↑ "Rail contract approved by Greater Wellington". Greater Wellington Regional Council. 29 June 2006.
- ↑ "Railfan". 18 (1). Triple M Publications. December 2011. ISSN 1173-2229.
- ↑ http://www.gw.govt.nz/story31646.cfm?
- ↑ Wellington Region Rail Programme (WRRP), Ontrack.
- ↑ "Wellington Regional Rail Annual Report 2011/2012" (PDF).