Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line
| Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
|
A Tokyo Metro 03 series EMU on the Hibiya Line | |||
| Overview | |||
| Native name | 東京地下鉄日比谷線 | ||
| Type | Rapid transit | ||
| Locale | Tokyo | ||
| Termini |
Naka-Meguro Kita-Senju | ||
| Stations | 21 | ||
| Daily ridership | 1,073,900 (201)[1] | ||
| Operation | |||
| Opened | March 28, 1961 | ||
| Owner | Tokyo Metro | ||
| Depot(s) | Senju, Takenotsuka | ||
| Rolling stock | Tokyo Metro 03 series, Tobu 20000 series | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 20.3 km (12.6 mi) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) | ||
| Electrification | 1,500 V DC overhead catenary | ||
| Operating speed | 80 km/h (50 mph) | ||
| |||
The Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line (東京地下鉄日比谷線 Tōkyō Chikatetsu Hibiya-sen) is a subway line in Tokyo, Japan, owned and operated by the Tokyo subway operator Tokyo Metro. The line was named after the district of Hibiya, under which it passes.
Overview

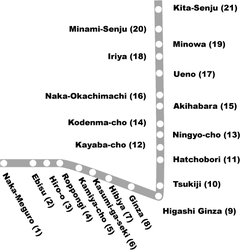
The Hibiya Line runs between Naka-Meguro in Meguro and Kita-Senju in Adachi. The line's path is somewhat similar to that of the Ginza Line; however, the Hibiya Line was designed to serve a number of important districts, such as Ebisu, Roppongi, Tsukiji, Kayabachō and Senju, which were not on an existing line.
The Hibiya Line is connected to the Tobu Skytree Line at Kita-Senju, and through services operate between Naka-Meguro and Tōbu-Dōbutsu-Kōen on the Tobu Skytree Line, and onward to Minami-Kurihashi on the Tobu Nikko Line.[2] Some peak-hour services terminate at Takenotsuka, Kita-Koshigaya or Kita-Kasukabe on the Tobu Skytree Line.[2]
Prior to 16 March 2013, when through-running began between the Tokyo Metro Fukutoshin Line and the Tokyu Toyoko Line, Hibiya Line trains also inter-ran via the Tokyu Toyoko Line to Kikuna.[3]
According to the Tokyo Metropolitan Bureau of Transportation, as of June 2009 the Hibiya Line is the eighth most crowded subway line in Tokyo, running at 164% capacity between Minowa and Iriya stations.[4]
On maps, diagrams and signboards, the line is shown using the color "silver", and its stations are numbered with the prefix "H".
Station list
All stations are located in Tokyo.
Planned stations
A new, as-yet unnamed, station is scheduled to be built between Kamiyachō and Kasumigaseki, provisionally opening in 2020 to serve the 2020 Summer Olympics, and full opening by fiscal 2022.[5] Situated 800 m south of Kasumigaseki and 500 m north of Kamiyacho, it will be located on the west side of the Toranomon Hills commercial and residential complex which opened in June 2014, and will provide connections with a new bus and bus rapid transit terminal also planned ahead of the 2020 Olympics.[5]
Rolling stock
- Tokyo Metro 03 series (42 8-car sets, since 1988)
- Tobu 20000 series (since 1988)
New 7-car Tokyo Metro 13000 series and Tobu 70000 series EMUs are scheduled to be phased in on Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line and Tobu Skytree Line through services between fiscal 2016 and 2019, replacing the Tokyo Metro 03 and Tobu 20000 series fleets. The new trains will have 20 m long cars with four pairs of doors per side.[6]
 Tokyo Metro 03 series
Tokyo Metro 03 series Tobu 20000 series
Tobu 20000 series
Past
- TRTA 3000 series (from 1961 until July 1994)
- Tobu 2000 series (from 1962 until 1993)
- Tokyu 7000 series (original) (from 1964 until 1991)
- Tokyu 1000 series (from 1991 until 2013)
 TRTA 3000 series in 1988
TRTA 3000 series in 1988 Tobu 2000 series
Tobu 2000 series- Tokyu 7000 series
 Tokyu 1000 series
Tokyu 1000 series
History
The Hibiya Line was the fourth subway line built in Tokyo after the Ginza Line, Marunouchi Line, and Toei Asakusa Line.
Its basic plan was drawn up by a Ministry of Transportation committee in 1957. Called "Line 2" at the time, it was designed to connect Naka-Meguro in southwest Tokyo with Kita-Koshigaya in the northeast. The full northeastern extension of the line was never built, as the Tobu Railway upgraded to quadruple track within the same corridor to meet capacity demands.
Work began in 1959, with the first section opening in March 1961. The line opened in stages: the northern section, between Kita-Senju and Ningyōchō, was operational in May 1962; the southern section, between Naka-Meguro and Kasumigaseki, opened in March 1964. The final segment, bridging Higashi-Ginza and Kasumigaseki, opened on August 29, 1964, just weeks before the opening ceremony for the 1964 Summer Olympics. This was something of a coup for the Teito Rapid Transit Authority (the predecessor of today's Tokyo Metro), as the Toei Asakusa Line, which was also to be completed in time for the Olympics, had fallen behind schedule and remained under construction for the duration of the Games.
The Hibiya Line was one of the lines targeted in the 1995 Aum sarin gas attack.
On March 8, 2000, five people were killed and 63 were injured when a derailed Hibiya Line train was sideswiped by a second train near Naka-Meguro Station.[7]
References
- ↑ Tokyo Metro station ridership in 2010 Train Media (sourced from Tokyo Metro) Retrieved May 28, 2012.
- 1 2 Tobu Timetable, 16 March 2013, p.177-188
- ↑ The 地下鉄 [The Subway]. Japan: Sansuisha. 2004. p. 27. ISBN 4-06-366218-7.
- ↑ Metropolis, "Commute", June 12, 2009, p. 07. Capacity is defined as all passengers having a seat or a strap or door railing to hold on to.
- 1 2 日比谷線に新駅設置、東京メトロ [Tokyo Metro to build new station on Hibiya Line]. Tetsudo.com (in Japanese). Japan: Asahi Interactive, Inc. 15 October 2014. Retrieved 15 October 2014.
- ↑ Failure Knowledge Database 日比谷線の列車脱線衝突 Retrieved on 11 March 2009 (Japanese)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tokyo Metro Hibiya Line. |