Aldol–Tishchenko reaction
The Aldol–Tishchenko reaction is a tandem reaction involving an aldol reaction and a Tishchenko reaction. In organic synthesis it is a method to convert aldehydes and ketones into 1,3-hydroxyl compounds. The reaction sequence in many examples starts from conversion of a ketone into an enolate by action of lithium diisopropylamide (LDA). The mono-ester diol is then converted into the diol by a hydrolysis step. With both the acetyl trimethylsilane[1] and propiophenone[2] as reactants, the diol is obtained as a pure diastereoisomer.
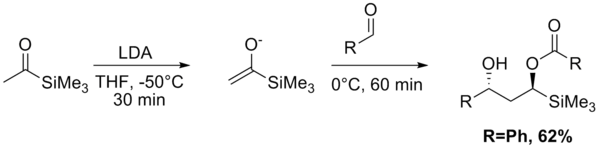
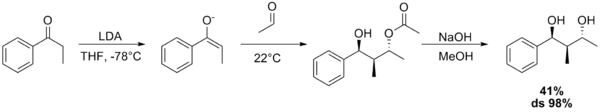
References
- ↑ Mitsunori Honda, Ryota Iwamoto, Yoshie Nogami and Masahito Segi (2005). "Stereoselective Tandem Aldol–Tishchenko Reaction with Acylsilanes". Chemistry Letters. 34 (4): 466. doi:10.1246/cl.2005.466.
- ↑ Paul M. Bodnar, Jared T. Shaw, and K. A. Woerpel (1997). "Tandem Aldol–Tishchenko Reactions of Lithium Enolates: A Highly Stereoselective Method for Diol and Triol Synthesis". J. Org. Chem. 62 (17): 5674–5675. doi:10.1021/jo971012e. Supporting information
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.