Telorchis
| Telorchis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Telorchis clemmydis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Trematoda |
| Order: | Plagiorchiida |
| Family: | Telorchiidae |
| Genus: | Telorchis[1] |
| Type species | |
| Telorchis clava | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Cercorchis, Paracercorchis, Protenes, some Distomum | |
Telorchis is a genus of trematode parasites found in many herps, comprising around 70 species.[2] This parasite is an indirect parasite, with a snail intermediate host and a reptile or amphibian definitive host. Typically found in the gastrointestinal tract of their definitive host, Telorchids attach to the wall of the intestinal tract with their oral sucker.
Morphology
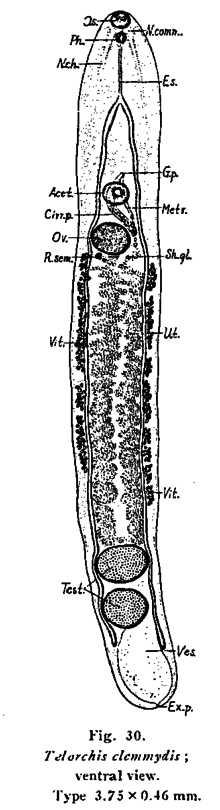
Description of Telorchis from Wharton 1940:[3] "Elongate, flat distomes with simple oral suckers. Oral and ventral suckers subequal. Pharynx present. Intestinal crura begin preacetabular and end near the posterior end of the body. Vitellaria lateral. Genital pore just anterior to the ventral sucker, usually somewhat to the left of the median line. Cirrus sac extends behind the acetabulum. Ovary posterior to or at the posterior level of cirrus sac. Uterus with descending and ascending coils, does not extend behind the testes. Metraterm anterior to ovary and usually about half as long as cirrus sac. Laurer's canal present. Testes in tandem at the posterior end."
Species
- Telorchis achavali[4]
- Telorchis aculeatus[5]
- Telorchis anacondae[6]
- Telorchis angustus[7]
- Telorchis assula[8]
- Telorchis attenuatus[9]
- Telorchis auridistomi[10]
- Telorchis bairdi[11]
- Telorchis bifurcus[12]
- Telorchis birabeni[13]
- Telorchis bonnerensis
- Telorchis bravoae[14]
- Telorchis caballeroi[15]
- Telorchis caudatus
- Telorchis chelopi[16]
- Telorchis clava[17]
- Telorchis clemmydis[18]
- Telorchis corti[5]
- Telorchis cryptobranchi
- Telorchis cyclemidis[19]
- Telorchis dhongokii[20]
- Telorchis diaphanus
- Telorchis diminutus[5]
- Telorchis dissentaneus[21]
- Telorchis dissimilis[22]
- Telorchis dollfusi
- Telrochis ercolani
- Telrochis erectus
- Telorchis gabesensis
- Telorchis geoclemmydis[18]
- Telorchis gorukhpuri
- Telorchis grocotti
- Telorchis guptai
- Telorchis guttati[16]
- Telorchis hagmanni
- Telorchis insculpti[16]
- Telorchis kinosterni
- Telorchis konoi
- Telorchis linstowi
- Telorchis leptus
- Telorchis lobosus[5]
- Telorchis medius[5]
- Telorchis megacotyle
- Telorchis membranaceus
- Telorchis necturi
- Telorchis nematoides
- Telorchis pallidus[16]
- Telorchis panamensis
- Telorchis parvus
- Telorchis patonianus
- Telorchis pellucidus
- Telorchis philippinensis
- Telorchis pleroticus[12]
- Telorchis poirieri
- Telorchis pseudoaculeatus
- Telorchis rapidulus
- Telorchis reelfooti
- Telorchis robustus[9]
- Telorchis ruszkowskii
- Telorchis scabrae
- Telorchis singularis
- Telorchis sirenis
- Telorchis solivagus
- Telorchis solivagus maroccanus
- Telorchis stenonura
- Telorchis stossichi[9]
- Telorchis stunkardi
- Telorchis texanus[11]
- Telorchis thamnophidis
References
- ↑ Luehe (1899). "Zur kenntnis einiger Distomen". Zoologischer Anzeiger. 22 (604): 524–539.
- ↑ Part 8 Trematoda and Trematode Diseases. 1968.
- ↑ Wharton, G. W. (1940). "The Genera Telorchis, Protenes, and Auridistomum (Trematoda: Reniferidae)". The Journal of Parasitology. 26 (6): 497–518. doi:10.2307/3272252. JSTOR 3272252.
- ↑ Mañé-Garzón & Holcman-Spector (1968). "Trematodos de las tortugas del Uruguay, VIII. Una nueva especie del género Telorchis (Lühe, 1900) del intestino de Pseudemys dorbigni (Dum. and Bib.)". Comunicaciones Zoologicas del Museo de Historia Natural de Montevideo. 9 (121): 1–4.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Stunkard, Horace (1915). "Notes on the Trematode Genus Telorchis with Descriptions of New Species". The Journal of Parasitology. JSTOR 3271020.
- ↑ MacCallum (1921). "Studies in helminthology. Pt. 1. Trematodes. Pt. 2. Cestodes. Pt. 3. Nematodes". Zoopathologica. 1: 141–284.
- ↑ Stafford (1900). "Some Undescribed Trematodes". Zool. Jahrb. Syst. 13: 399–414.
- ↑ Dujardin, Felix (1845). Histoire naturelle des helminthes ou vers intestinaux. Paris: Librairie Encyclopedique de Roret.
- 1 2 3 Goldberger (1911). "On some new parasitic trematode worms of the genus Telorchis". Hygiene Lab Bulletin. 71: 36–47.
- ↑ Byrd (1937). "The trematode parasites from a red-bellied watersnake, Farancia abacura". Parasitology. 29: 359–364. doi:10.1017/s0031182000024859.
- 1 2 Harwood (1932). "The helminths parasitic in the Amphibia and Reptilia of Houston, Texas, and vicinity". Proc. U. S. Nat. Mus. 81 (17): 1–71.
- 1 2 Braun (1899). "Weitere Mitteilungen uber endoparasitische Trematoden der Chelonien". Centralblatt für Bakteriologie und Parasitenkunde. 25: 714.
- ↑ Mañé-Garzón & Gil (1961). "Trematodos de las tortugas del Uruguay III. Una nueva especie del género Telorchis Lühe, 1900 (Trematoda Telorchidae)". Neotrópica. 7 (23): 38–43.
- ↑ Caballero & Zerecero (1960). "Tremátodos de las tortugas de México IX. Telorchis bravoae n. sp.". Anales del Instituto de Biologia, Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico.
- ↑ Herrera-Rosales (1951). "Tremátodos de los quelonios de México". Doctoral dissertation, BS Thesis, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México.
- 1 2 3 4 MacCallum (1919). "Notes on the genus Telorchis and other trematodes". Zoopathologica. 1: 88–89.
- ↑ Diesing (1850). Systema Helminthum, Vol. 1. Vienna.
- 1 2 Yamaguti (1933). "Studies on the helminth fauna of Japan, Part 1. Trematodes of birds, reptiles and mammals". Jap. J. Zool. 5: 72–74.
- ↑ Tubangui (1933). "Trematode parasites of Philippine vertebrates. vi. descriptions of new species and classification". Philipp. J. Sci. 52 (2): 157–97.
- ↑ Mehra, H. R., & Bokhari, M. A. (1932). "On new distomate trematodes of the subfamily Telorchiinae (family Lepodermatidae) with a systematic discussion of its genera". Allahabad Univ. Stud. 8: 47–62.
- ↑ Caballero, C. E. and Herrera-Rosales, E. (1947). "Trematodos de las tortugas de Mexico V. Descripcion de una nueva especie del genero Telorchis.". Anales Del Instituto de Biologia. 18: 159–164.
- ↑ Caballero, E. (1938). "Algunos tremátodos de reptiles de México". Anales del Instituto de Biologia de la Universidad Nacional de Mexico. 9: 103–120.