Octreotide scan
| Octreotide scan | |
|---|---|
| Diagnostics | |
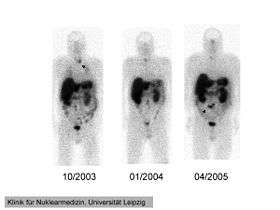 111In-pentetreotide scintigraphy of the 41-year-old man with ectopic Cushing' syndrome caused by a neuroendocrine carcinoma of the mesentery. Radiotracer accumulation in the left thyroid in 10/2003 (arrow). The mesenterial neuroendocrine tumor became clearly visible in 4/2005 (arrow). | |
| ICD-9-CM | 92.18 |
| OPS-301 code | 3-70c |
An octreotide scan or octreoscan is a type of scintigraphy used to find carcinoid, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, and to localize sarcoidosis. Octreotide, a drug similar to somatostatin, is radiolabeled with indium-111,[1] and is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. The radioactive octreotide attaches to tumor cells that have receptors for somatostatin. A radiation-measuring device detects the radioactive octreotide, and makes pictures showing where the tumor cells are in the body.
It is also called somatostatin receptor scintigraphy and SRS.
Octreotide scanning is reported to have a sensitivity between 75% and 100% for detecting pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ medicinenet.com > Carcinoid Syndrome (cont.) By Dennis Lee and Jay Marks. Retrieved Mars 2011
- ↑ Kwekkeboom, DJ; Krenning, EP (April 2002). "Somatostatin receptor imaging.". Seminars in nuclear medicine. 32 (2): 84–91. doi:10.1053/snuc.2002.31022. PMID 11965603.
External links
- Octreotide scan entry in the public domain NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the U.S. National Cancer Institute document "Dictionary of Cancer Terms".
This article incorporates public domain material from the U.S. National Cancer Institute document "Dictionary of Cancer Terms".