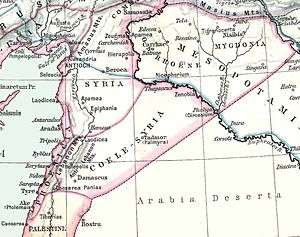
Syrian tetrapolis
The Syrian tetrapolis consisted of the cities Antioch, Seleucia Pieria, Apamea, and Laodicea in Syria.[1][2]
Tetrapolis of Seleuceia
The region known as 'Seleucis of Syria' was administered by a Tetrapolis of the four largest cities founded by Seleucus Nicator;[3][4]
- Antioch Epidaphne —from the name of his father and the largest city.
- Laodiceia —from his mother.
- Apameia —from his wife Apama.
- Seleuceia in Pieria —eponym of the founder.
Upper Syria
Further information: Syria (region) and Geography of Syria

Map of the Orontes River. White lines are country borders, river names are italic on a blue background, current cities or major towns have white backgrounds, orange background for other places of significance.
Under the Macedonian kings, Upper Syria (Syria Superior) was divided into four parts (tetrarchies) which were named after their capitals;[5]
- Antioch
- Apamea
- Laodicea ad Libanum (now Latakia)
- Seleuceia (indeterminate location)[6]
- Seleukeia Near Belos
- Seleukeia In Pieria/Seleukeia On the Bay of Issos
- Seleucia at the Zeugma
- Seleucia ad Pyramum
- Seleucia ad Calycadnum
Under the Romans, the province was divided into nine districts :
- Cassiotis
- Apamene, capital Apamea in Syria
- Chalcidice
- Seleucis
- Pieria
- Commagene
- Cyrrhestice
- Chalybonitis
- Palmyrene.
References
- ↑ Mikhail Ivanovitch Rostovtzev (1926). The Social and economic history of the Roman empire, Volume 2 (Paperback ed.). Biblo-Moser. p. 244. ISBN 0-8196-2164-1.
- ↑ Encyclopædia Britannica, 11th ed., s.v. 'Seleucia'.
- ↑ Strabo (1889). The geography of Strabo. Bell. p. 161.
p. 161 at Google Books
- ↑ "Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854) William Smith, LLD, Ed.". Perseus. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography, illustrated by numerous engravings on wood. William Smith, LLD. London. Walton and Maberly, Upper Gower Street and Ivy Lane, Paternoster Row; John Murray, Albemarle Street. 1854.
- ↑ Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (Great Britain) (1842). Penny cyclopaedia of the Society for the diffusion of useful knowledge. C. Knight. pp. 476–.
Antient Divisions of Syria. –Under the Macedonian kings Syria was divided into four parts (tetrarchies), which were named after their capitals, Antioch, Seleuceia, Apamea, and Laodicea. Both the Greeks and the Romans called the northern portion of Syria, that is the whole country with the exception of Coele-Syria, Phoenice, and Palestine, by the name of Upper Syria (???, Syria Superior), to distinguish it from Coele Syria (???, that is, the Hollow Syria), which was the name given to the valley between the ridges of Libanus and Anti Libanus. Under the Romans the province was divided into nine districts: Cassiotis, Apamene, Chalcidice, Seleucis, Pieria, Commagene, Cyrrhestice, Chalybonitis, Palmyrene.(Image of p. 476 at Google Books)
- ↑ Cohen, Getzel M. (3 October 2006). The Hellenistic Settlements in Syria, the Red Sea Basin, and North Africa. Berkeley : University of California Press. p. 401. ISBN 978-0-520-93102-2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/13/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.