Angiokeratoma
| Angiokeratoma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | oncology, dermatology |
| ICD-10 | D23 (ILDS D23.L74) |
| ICD-O | M9141/0 |
| DiseasesDB | 31444 |
| eMedicine | article/1056046 |
| MeSH | D000794 |
Angiokeratoma is a benign cutaneous lesion of capillaries, resulting in small marks of red to blue color and characterized by hyperkeratosis. Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum refers to Fabry's disease,[1] but this is usually considered a distinct condition.
Classification
Angiokeratoma may be classified as:
- Angiokeratoma of Mibelli (also known as "Mibelli's angiokeratoma,"[2] "Telangiectatic warts"[3]) consists of 1- to 5-mm red vascular papules, the surfaces of which become hyperkeratotic in the course of time.[3]:589 The disease is named after Italian dermatologist Vittorio Mibelli (1860-1910).[4]
- Angiokeratoma of Fordyce (also known as "Angiokeratoma of the scrotum and vulva," though not to be confused with Fordyce's spots)[3] is a skin condition characterized by red to blue papules on the scrotum or vulva.
- Solitary angiokeratoma is a small, bluish-black, warty papule that occurs predominantly on the lower extremities.[3]:590
- Verrucous vascular malformation (also known as "Angiokeratoma circumscriptum naeviforme") is a malformation of dermal and subcutaneous capillaries and veins, a congenital vascular malformation, which, over time, a verrucous component appears.[3]:584
Signs and symptoms
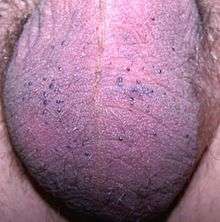
Presentation includes telangiectasia, acanthosis, and hyperkeratosis.[5]
Presentation can be solitary or systemic.[6]
Diagnosis
Due to the rarity of different types of vascular conditions, angiokeratomas may be misdiagnosed. A biopsy of the lesion can produce a more accurate diagnosis.
Pathophysiology
Histology
Angiokeratomas characteristically have large dilated blood vessels in the superficial dermis and hyperkeratosis (overlying the dilated vessels).
-

Scrotal angiokeratoma; visible large dilated blood vessels and hyperkeratosis
-
Scrotal angiokeratoma (Fordyce type); multiple papules made by dilatated capillaries
-
Scrotal angiokeratoma (Fordyce type); dilated cavernous capillaries, acanthosis
-
Scrotal angiokeratoma (Mibelli type); blood vessels close to the epidermis
-
Angiokeratoma (Mibelli type)
Complications
In some instances nodular angiokeratomas can produce necrotic tissue and valleys that can harbor fungal, bacterial and viral infections. Infections can include staphylococcus. If the lesion becomes painful, begins draining fluids or pus, or begins to smell, consult a physician. In these instance a doctor may recommend excision and grafting.
Treatment
Outpatient treatments such as interventional radiology, lasers, and physical therapy are employed to reduce the severity of the vascular lesions. However, in some cases lasers have caused a reaction in the tissue causing it to expand and become exposed to infection. Excision and grafting may be necessary to remove the lesion. Recovery time on such an operation ranges from 3 to 12 weeks depending on location of the graft, healing time and the possibility of complications.
See also
- Fabry disease (i.e. angiokeratoma corporis diffusum)
- Angiokeratoma of Mibelli
- List of cutaneous conditions
References
- ↑ Trickett R, Dowd H (October 2006). "Angiokeratoma of the scrotum: a case of scrotal bleeding". Emerg Med J. 23 (10): e57. doi:10.1136/emj.2006.038745. PMC 2579622
 . PMID 16988295.
. PMID 16988295. - ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- 1 2 3 4 5 James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ↑ Mibelli's disease II @ Who Named It
- ↑ "angiokeratoma" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ Sion-Vardy N, Manor E, Puterman M, Bodner L (January 2008). "Solitary angiokeratoma of the tongue" (PDF). Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 13 (1): E12–4. PMID 18167473.