Vitellaria
| Vitellaria | |
|---|---|
| | |
| Shea Tree | |
| | |
| Shea nuts | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Sapotaceae |
| Genus: | Vitellaria C.F.Gaertn. |
| Species: | V. paradoxa |
| Binomial name | |
| Vitellaria paradoxa C.F.Gaertn. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Butyrospermum paradoxa | |
Vitellaria paradoxa (formerly Butyrospermum parkii), commonly known as shea tree, shi tree, /ˈʃiː/ or /ˈʃiː.ə/, or vitellaria, is a tree of the Sapotaceae family. It is the only species in genus Vitellaria,[1][2] and is indigenous to Africa. The shea fruit consists of a thin, tart, nutritious pulp that surrounds a relatively large, oil-rich seed from which shea butter is extracted.
The shea tree is a traditional African food plant. It has been claimed to have potential to improve nutrition, boost food supply in the "annual hungry season",[3] foster rural development, and support sustainable landcare.[4]
Description
The tree starts bearing its first fruit when it is 10 to 15 years old; full production is attained when the tree is about 20 to 30 years old. It then produces nuts for up to 200 years.
The fruits resemble large plums and take 4 to 6 months to ripen. The average yield is 15 to 20 kilograms of fresh fruit per tree, with optimum yields up to 45 kilograms. Each kilogram of fruit gives approximately 400 grams of dry seeds.
Composition
Shea butter fatty acid profiles
Shea butter is composed of five principal fatty acids: palmitic, stearic, oleic, linoleic, and arachidic (see Table below). About 85 to 90% of the fatty acid composition is stearic and oleic acids. The relative proportion of these two fatty acids affects shea butter consistency. The stearic acid gives it a solid consistency, while the oleic acid influences how soft or hard the shea butter is, depending on ambient temperature.
The proportions of stearic and oleic acids in the shea kernels and butter differ across the distribution range of the species. Ugandan shea butter has consistently high oleic acid content, and is liquid at warm ambient temperatures. It fractionizes into liquid and solid phases, and is the source of liquid shea oil. The fatty acid proportion of West African shea butter is much more variable than Ugandan shea butter, with an oleic content of 37 to 55%. Variability can be high even locally, and a tree that produces hard butter can grow with one that produces soft butter. Nuts are gathered from a wide area for local production, so shea butter consistency is determined by the average fatty acid profile of the population. Within West Africa, shea butter from the Mossi Plateau region of Burkina Faso has a higher average stearic acid content, and so is usually harder than shea butter from other West African regions.
| Fatty Acid | Mean | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16:0 Palmitic | 4.0 | 2.6 | 8.4 |
| 18:0 Stearic | 41.5 | 25.6 | 50.2 |
| 18:1 Oleic | 46.4 | 37.1 | 62.1 |
| 18:2 Linoleic | 6.6 | 0.6 | 10.8 |
| 20:0 Arachidic | 1.3 | 0.0 | 3.5 |
Shea butter phenolics
Phenolic compounds are known to have antioxidant properties. A recent study characterized and quantified the most important phenolic compounds in shea butter. This study identified 10 phenolic compounds, eight of which are catechins, a family of compounds being studied for their antioxidant properties. The phenolic profile is similar to that of green tea, and the total phenolic content of shea butter is comparable to virgin olive oil. Also, this study was performed on shea butter that had been extracted with hexane, and the authors note that traditional extraction methods may result in higher phenolic levels. Furthermore, they note that the catechin content alone of shea kernels is higher than the total phenolic content of ripe olives. This study also found that the overall concentration and relative percentages of different phenolic content in shea kernels varied from region to region. The authors hypothesized that the overall concentration of phenols in shea kernels is linked to the level of environmental stress that the trees endure.[5]
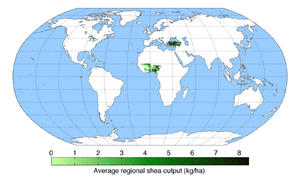
Distribution and habitat
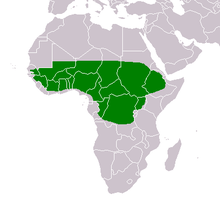
The shea tree grows naturally in the wild in the dry savannah belt of West Africa from Senegal in the west to Sudan in the east, and onto the foothills of the Ethiopian highlands. It occurs in 19 countries across the African continent, namely Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea Bissau, Ivory Coast, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Uganda, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Guinea.
A testa found at the site of the medieval village of Saouga is evidence of shea butter production by the 14th century.[6]
Uses
Shea butter has many uses and may or may not be refined. In the West it is mostly used for cosmetics as emollient. Throughout Africa it is used extensively for food, is a major source of dietary fat, and for medicinal purposes.
Etymology
The common name is shíyiri or shísu (lit. "shea tree") in the Bambara language of Mali. This is the origin of the English word, whose primary pronunciation is /ʃiː/ (rhyming with "tea"), although the pronunciation /ʃeɪ/ (rhyming with "day") is common and is listed second in major dictionaries. The tree is called ghariti in the Wolof language of Senegal, which is the origin of the French name of the tree and the butter, karité. In Hausa language the tree is called Kade or Kadanya. Indeed, the shea tree is so indispensable in Mole-Dagbang culinary and ethno-botanical practices that the Northern Ghanaian city of Tamale etymologically derives its name from the more traditional Dagomba name 'Tama-yile' (meaning 'Home of Shea nuts').
The tree was formerly classified in the genus Butyrospermum, meaning "butter seed". The species name parkii honors Scottish explorer Mungo Park, who learned of the tree while exploring Senegal. Park's Scottish origin is reflected in the English word shea, with a final -ea.
Vernacular names in Niger-Congo languages
| Language | Word | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Kusal | Ta'ama | shea nuts |
| Gonja | kakulugu | shea tree |
| Dagbani | tááŋ̀à | shea tree |
| Twi | ŋ̀kú | shea-butter |
| Igbo | òkwùma | shea-butter |
| Yoruba | ori | shea-butter |
| Nupe | èkó | shea-butter nut |
| Obiro | òkʷô | shea tree |
| Tinor | kɔ̃̀ɲɔ̃̀ | shea tree |
| Ake | kìkyɔ̃̀ | shea tree |
| Tarok | ìkíní | shea tree |
| Doori | kólá | shea tree |
| Bambara | ʃi | shea |
| Dagaare | Chuuma | shea nuts |
| Talensi | Ta-an | shea tree |
| Fon | Limou | |
| Ani | bushi burforno | shea butter |
| Marghi | Wur huma | shea tree |
| Zaar | Wangal | Shea |
Notes
- ↑ Vitellaria paradoxa. AgroForestry Tree Database. World Agroforestry Centre.
- ↑ Byakagaba, P., et al. (2011). Population structure and regeneration status of Vitellaria paradoxa (C.F.Gaertn.) under different land management regimes in Uganda. Agricultural Journal 6(1) 14-22.
- ↑ E.T. Masters; J.A. Yidana; P.N. Lovett. "Trade and sustainable forest management". FAO.org. Retrieved 2010-09-14.
- ↑ National Research Council (2006-10-27). "Shea". Lost Crops of Africa: Volume II: Vegetables. Lost Crops of Africa. 2. National Academies Press. ISBN 978-0-309-10333-6. Retrieved 2008-07-15.
- 1 2 Maranz, Steven; Wiesman, Zeev; Bisgaard, Johan; Bianchi, Giorgio (2004). "Germplasm resources of Vitellaria paradoxa based on variations in fat composition across the species distribution range". Agroforestry Systems (in cooperation with ICRAF). Kluwer Academic Publishers. 60 (1): 71–76. doi:10.1023/B:AGFO.0000009406.19593.90. (subscription required (help)).
- ↑
- Neumann, K., et al. 1998. Remains of woody plants from Saouga, a medieval west African village. Vegetation History and Archaeobotany, 7:57-77.
References
- Makerere University Institute of Environment and Natural Resources. 1998. Vitellaria paradoxa. In: IUCN 2012. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2012.2. Downloaded on 14 June 2013.
External links
- Vitellaria paradoxa. In: Brunken, U., et al. 2008. West African Plants — A Photo Guide. Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg, Frankfurt/Main.
