Salicylanilide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Hydroxy-N-phenylbenzamide | |
| Other names
2-Hydroxybenzanilide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 87-17-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 6610 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.571 |
| PubChem | 6872 |
| UNII | LHP8NEY345 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H11NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 213.24 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline solid |
| Melting point | 136 to 138 °C (277 to 280 °F; 409 to 411 K) |
| Hazards | |
| EU classification (DSD) |
Xi |
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S36/37/39 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Salicylanilide is a chemical compound which is the amide of salicylic acid and aniline. It is classified as both a salicylamide and an anilide.[2]
Derivatives of salicylanilide have a variety of pharmacological uses. Chlorinated derivatives including niclosamide, oxyclozanide, and rafoxanide are used as anthelmintics, especially as flukicides. Brominated derivatives including dibromsalan, metabromsalan, and tribromsalan are used as disinfectants with antibacterial and antifungal activities.

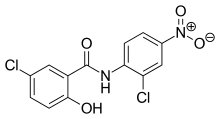 Niclosamide
Niclosamide Oxyclozanide
Oxyclozanide Rafoxanide
Rafoxanide
Uses
Salicylanilides may be used as antiseptics.
References
- ↑ Salicylanilide at chemicalland21.com
- ↑ Salicylanilides at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/3/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.