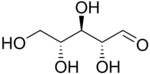
Ribose
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4S,5R)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-2,3,4-triol | |||
| Other names
D-Ribose | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 50-69-1 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | aldehydo form D-(−)-Ribose: Interactive image | ||
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1159662 | ||
| ChemSpider | 4470639 aldehydo form D-(−)-Ribose | ||
| DrugBank | DB01936 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.055 | ||
| EC Number | 200-059-4 | ||
| PubChem | 5779 5311110 aldehydo form D-(−)-Ribose | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties[1][2] | |||
| C5H10O5 | |||
| Molar mass | 150.13 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | white solid | ||
| Melting point | 95 °C (203 °F; 368 K) | ||
| 100 g/1 L (25 °C (77 °F)) | |||
| Chiral rotation ([α]D) |
−21.5° (H2O) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related aldopentoses |
Arabinose Xylose Lyxose | ||
| Related compounds |
Deoxyribose | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Ribose is a carbohydrate with the formula C5H10O5; specifically, it is a pentose monosaccharide (simple sugar) with linear form H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H, which has all the hydroxyl groups on the same side in the Fischer projection.
The term may refer to either of two enantiomers. The term usually indicates D-ribose, which occurs widely in nature and is discussed here. Its synthetic mirror image, L-ribose, is not found in nature.
D-Ribose was first reported in 1891 by Emil Fischer. It is a C'-2 carbon epimer of the sugar D-arabinose (both isomers of which are named for their source, gum arabic) and ribose itself is named as a partial rearrangement of letters in the word 'arabinose'.[3]
The ribose β-D-ribofuranose forms part of the backbone of RNA. It is related to deoxyribose, which is found in DNA. Phosphorylated derivatives of ribose such as ATP and NADH play central roles in metabolism. cAMP and cGMP, formed from ATP and GTP, serve as secondary messengers in some signalling pathways.
Structure
Ribose is an aldopentose (a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms) that, in its open chain form, has an aldehyde functional group at one end. In the conventional numbering scheme for monosaccharides, the carbon atoms are numbered from C1' (in the aldehyde group) to C5'. The deoxyribose derivative found in DNA differs from ribose by having a hydrogen atom in place of the hydroxyl group at C2'. This hydroxyl group performs a function in RNA splicing.
Like many monosaccharides, ribose exists in an equilibrium among 5 forms—the linear form H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4–H and either of the two ring forms: alpha- or beta-ribofuranose (“C3'-endo”), with a five-membered ring, and alpha- or beta-ribopyranose (“C2'-endo”), with a six-membered ring. The beta-ribopyranose form predominates in aqueous solution.[4]
The “D-” in the name D-ribose refers to the stereochemistry of the chiral carbon atom farthest away from the aldehyde group (C4'). In D-ribose, as in all D-sugars, this carbon atom has the same configuration as in D-glyceraldehyde.
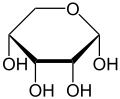 α-D-Ribopyranose
α-D-Ribopyranose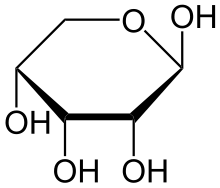 β-D-Ribopyranose
β-D-Ribopyranose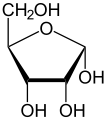 α-D-Ribofuranose
α-D-Ribofuranose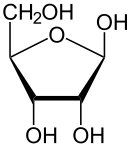 β-D-Ribofuranose
β-D-Ribofuranose
Relative abundance of different forms of ribose in solution: β-D-ribopyranose (59%), α-D-ribopyranose (20%), β-D-ribofuranose (13%), α-D-ribofuranose (7%) and open chain (0.1%).[5]
Phosphorylation
In biology, D-ribose must be phosphorylated by the cell before it can be used. Ribokinase catalyzes this reaction by converting D-ribose to D-ribose 5-phosphate. Once converted, D-ribose-5-phosphate is available for the manufacturing of the amino acids tryptophan and histidine, or for use in the pentose phosphate pathway. The absorption of D-ribose is 88–100% in the small intestines (up to 200 mg/kg/h).[6]
References
- ↑ The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals (11th ed.), Merck, 1989, ISBN 091191028X, 8205
- ↑ Weast, Robert C., ed. (1981). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (62nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. C-506. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8.
- ↑ Nechamkin, Howard (December 1958). "Some interesting etymological derivations of chemical terminology". Science Education. 42 (5): 463–474. doi:10.1002/sce.3730420523.
- ↑ Angyal, S. J. (March 1969). "The Composition and Conformation of Sugars in Solution". Angewandte Chemie. 8 (3): 157–166. doi:10.1002/anie.196901571. Retrieved 5 June 2012.
- ↑ Drew, Kenneth N.; Zajicek, Jaroslav; Bondo, Gail; Bose, Bidisha; Serianni, Anthony S. (February 1998). "13C-labeled aldopentoses: detection and quantitation of cyclic and acyclic forms by heteronuclear 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy". Carbohydrate Research. 307 (3-4): 199–209. doi:10.1016/S0008-6215(98)00040-8. Retrieved 11 December 2014.
- ↑ "Herbal Remedies, Supplements A-Z Index". PDRHealth. Archived from the original on 11 October 2008.