Plan 1919
Plan 1919 was a military strategy drawn up by J.F.C. Fuller in 1918 during World War I. His plan criticised the practice of physically destroying the enemy, and instead called for tanks to rapidly advance into the enemy's rear area to destroy supply bases and lines of communication, which would also be bombed. He suggested a lightning thrust toward the command center of the German Army:
- ... every available bombing machine should concentrate on the various supply and road centres. The signal communication should not be destroyed, for it is important that the confusion resulting from the dual attack carried out by the Medium D tanks and aeroplanes should be circulated by the enemy. Bad news confuses, confusion stimulates panic .... (then) a carefully mounted tank, infantry and artillery attack should be launched, the objective of which is the zone of the enemy's guns: namely the secondary tactical zone some 10,000 yeards deep.[1]
- so does an army depend for its power on the will of its Commander and his Staff: cut that will off and the army will be paralyzed. He proposed using Medium D tanks to disorganise the enemy’s Command in rear of the entrenched zone.[2]
The Allied advance and German retreat across France and Belgium in 1918 had begun to show some of the pace and aspects that would mark later mechanized warfare; British tanks played an increasing role, and German rear-guard defenses focused on stopping their advance. Although never implemented, Plan 1919 would have carried these trends forward earlier, and can be said to have formed the basis for later blitzkrieg tactics and the Soviet theories of Deep Battle and Deep Operations
Background
By 1918, the German, French and British armies had been through years of trench warfare and were getting close to the breaking point. Both sides realized that a new form of warfare was needed for the successful conclusion of the war. Tanks, although used unsuccessfully at the Battles of the Somme and Passchendaele, were used in the Battle of Cambrai and demonstrated their usefulness. Although the main objective was not achieved and the German artillery made short work of them after the initial shock wore off, they inspired military theorists to try to incorporate them properly.
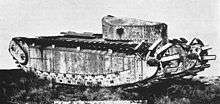
In the spring of 1918, J.F.C. Fuller submitted a study titled "The tactics of the attack as affected by the speed and circuit of the Medium D tank",[3] a bold new plan involving tanks and air support that aimed to target the German leadership and supply lines, as opposed to the then current tactic of grinding away at the main forces.
Fuller's plan had three elements. The first was a fast attack by medium tanks and aircraft against the German headquarters, removing its ability to control their forces. Then the main assault by heavy tanks, infantry and artillery would make break the German lines. Finally cavalry, light tanks and infantry mounted on trucks would follow the retreating Germans preventing them from reforming or counterattacking.[4]
His plan was to be used as the blueprint for the spring offensive the next year and was titled Plan 1919. The German surrender that November precluded the implementation of the plan, but it was studied extensively by the Germans and used as the model for their Blitzkrieg attacks during the next war (Fuller).[5] Plan 1919, although never carried out, laid the “groundwork” for numerous upgrades in military equipment, technology, and tactics of modern warfare .
Fuller's ideas were largely in line with papers put forward by other members of the Tank Corps such as by Capper and Elles' paper "The future of tank operations and production requirements" which envisaged tank forces of several thousand light, medium and heavy tanks and the means and time it would take to produce them and deploy them to the front.[6]
The Plan
Fuller, in his Military History of the Western World states, "There are two ways of destroying an organization: 1. by wearing it down, 2. by rendering it inoperative. In war the first comprises the killing, wounding, capturing and disarming of the enemy's soldiers- body warfare. The second, the rendering inoperative of his power of command- brain warfare. To take a single man as an example: the first method may be compared to a succession of slight wounds which will eventually cause him to bleed to death; the second- a shot through the brain."
To accomplish this "shot through the brain" Fuller's plan required generals to penetrate the enemy’s defenses using tanks and targeting his chain of supply; so that in the ensuing confusion the enemy leadership could then be eliminated decisively. The goal of this was “the destruction of the enemy’s policy” (Reid) . This would be accomplished by armored units penetrating the enemy lines and causing havoc in the rear areas, with the ultimate aim of eliminating the enemy leadership. The Plan emphasized the intended use of aircraft in the support role, along with motorized infantry to conduct operations in terrain unsuited to tanks. This mobile form of operations utilizing tanks and aircraft was a huge departure from the established infantry tactics of the day.
Detractors point out the flaws in Fuller’s plan. It is a strong point that the tank required by the plan had not been fielded yet, and that war weary Britain could not afford the manpower and materials needed to implement it (Palazzo) , and as was demonstrated at Cambrai, the German artillery was deadly against the current British tanks without accompanying artillery support.
A new 40 ton tank design Mark VIII tank – based on the earlier British heavy tanks – was under construction in late 1918 with an ambitious production scheme of up to 4,500 tanks. Hundreds of these would be used in the spearhead and once these had broken through the German lines, the faster medium tanks would have "raced through" to disrupt the enemy rear. Aircraft would have been used to resupply the tanks and keep the breakthrough moving. (Ellis)
The British had a "trench fighter" design in production with orders for 1,400 aircraft. The Sopwith Salamander was armoured so that it could strafe and bomb the enemy trenches and artillery with less risk.
Plan 1919's effect
Plan 1919, although never carried out, laid the “groundwork” for upgrades in military equipment, technology, and tactics of modern warfare. The Americans designed a new tank based on the British Medium “D” tank, as described by Fuller in his Plan 1919, to be able to execute the new mobile form of warfare (Hofmann) . The Germans modeled their blitzkrieg style of modern warfare, in the subsequent world war, upon Fuller’s Plan 1919. This style of warfare emphasized the use of armored units and close air support, to make quick attacks designed to penetrate the enemy’s front lines and cause confusion (Fuller) . This type of warfare is still used today, as demonstrated by the American forces in Operation Iraqi Freedom, when they first occupied Iraq.
Fuller's Theory
Fuller’s theory of having the tanks, aircraft, and numerous other warfare tactics prescribed in Plan 1919 was that a mobile battlefield would provide more protection against losses to friendly forces. Fewer soldiers therefore put at risk on the battlefield, implied fewer troops to command, therefore making it easier for the commander to lead troops . More effective battles could then be fought with fewer casualties. Warfare could then become more organized. Superior firepower, and air power would increase the combat effectiveness of attacking command and communication centers .
Fuller drew up the plans for Plan 1919 with many beliefs and hopes for the future of armies in Europe and around the world . He believed that Plan 1919 was the groundwork for numerous innovations in the armed forces . The new armies would consist of highly trained and proficient individuals that would be professional in the way they acted and the way they led on the battlefield . Fuller also believed that with time, military technologies would become more advanced and more proficient in their performed operations . This meant that technologies would thus become more deadly and more effective at destroying the enemy, allowing more pinpoint strikes and minimizing collateral damage .
The Chemical Plan
Fuller's plan was not the only option on the table for 1919. As Albert Palazzo points out in his paper "Plan 1919– The Other One", the chemical warfare planners had big plans for the next year's offensive . He points out they were fielding a new gas called DM, which penetrated the German masks(47) . The technology for this new gas was much closer to fruition than the tank required by Fuller's plan . In addition, Winston Churchill, as Minister of Munitions, had already called for the production of gas agents to be increased by five times the current production(46) .
The chemical advocates therefore did not have to contend with technology issues. They were utilizing a proven method of warfare. Their plan only called for increasing the extent of chemical warfare. Palazzo also points out they intended to use airplanes as delivery systems for the chemical agents and envisioned the gas being used to target command centres (45).
In many respects then, the gas advocates plan seems to have offered much the same possibility for success, with little of the implementation difficulties of Fuller's plan. The armistice however made their plans unnecessary also. In history's light however, this plan remains obscure due to the nature of chemical warfare. As Palazzo put it, "few weapons have inspired such universal revulsion" (39).
References
Notes
Bibliography
- Fuller, J.F.C. A Military History of the Western World Vol 3. New York: Funk & Wagnalls, 1956.
- Fuller, J.F.C. Memoirs of an Unconventional Soldier pages 282–283 & 318–341. London: Ivor Nicholson and Watson, 1936.
- Reid, Brian Holden. "J.F.C. Fuller's Theory of Mechanized Warfare". The Journal of Strategic Studies 1.3 (1978):295–312
- Palazzo, Albert. "Plan 1919 – The Other One". The Journal of the Society For Army Historical Research 77 (1999):39–50.
- Hofmann, George. "The Demise of the US Tank Corps and Medium Tank Development Program". Military Affairs 37-1 (Feb. 1973):20–25
- Johnson, Robert. “Plan 1919”. Chandelle: A Journal of Aviation History 2.1 March 1997. October 2007
- Armour in Profile No 19: Tank Mark VIII "The International", Ellis and Chamberlain (1967) Profile Publications