Phakopsora pachyrhizi
| Phakopsora pachyrhizi | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Phylum: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Urediniomycetes |
| Subclass: | Incertae sedis |
| Order: | Uredinales |
| Family: | Phakopsoraceae |
| Genus: | Phakopsora |
| Species: | P. pachyrhizi |
| Binomial name | |
| Phakopsora pachyrhizi Syd. & P. Syd., (1914) | |
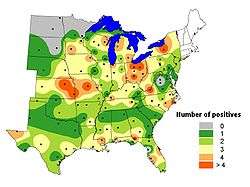 | |
| Contour map showing numbers of NADP sites testing positive for P. pachyrhizi in center and East of USA in 2006. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Malupa sojae | |
Phakopsora pachyrhizi is a plant pathogen. It causes Asian soybean rust.
Symptoms
The disease froms tan to dark-brown or reddish-brown lesions with one to many prominent, globe-like orifices.[1] Urediniospores form from these pores.[2] Lesions initially are small, turning from gray to tan or brown as they increase in size. The lesions are most abundant on the bottom surface of leaves but can also form on petioles, pods, and stems.
Risk factors
Uredospores are wind-blown and are produced abundantly on the infected tissue of soybeans or other legume hosts.[1]
Control
The disease is often controlled using the fungicides oxycarboxin, triforine, or triclopyr.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 Shanmugasundaram, S.; Yeh, C.C.; Hartman, G.L.; Talekar, N.S. (1991). Vegetable Soybean Research Needs for Production and Quality Improvement (PDF). Taipei: Asian Vegetable Research and Development Center. pp. 86–87. ISBN 9789290580478. Retrieved 6 February 2016.
- ↑ Sinclair, James Burton; Backman, P. A. (1989). Compendium of Soybean Diseases (3rd ed.). St Paul, MN: APS Press. ISBN 9780890540930.