Pentagonal planar molecular geometry
| Pentagonal planar molecular geometry | |
|---|---|
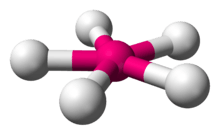 | |
| Examples | XeF5− |
| Steric number | 7 |
| Coordination number | 5 |
| Bond angle(s) | 72°, 144° |
| μ (Polarity) | 0 |
In chemistry, the pentagonal planar molecular geometry describes the shape of compounds where five atoms, groups of atoms, or ligands are arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of a pentagon.
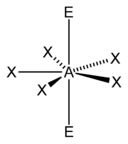
AX5E2
Examples
The only two pentagonal planar species known are the isoelectronic (nine valence electrons) ions XeF−
5 and IF2−
5.[1] Both are derived from the pentagonal bipyramid with two lone pairs occupying the apical positions and the five fluorine atoms all equatorial.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/5/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.