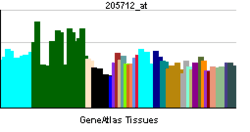
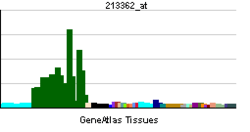
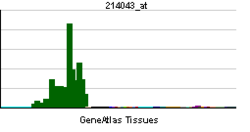
PTPRD
| View/Edit Human | |||
Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase delta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPRD gene.[3][4][5]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP contains an extracellular region, a single transmembrane segment and two tandem intracytoplasmic catalytic domains, thus represents a receptor-type PTP. The extracellular region of this protein is composed of three Ig-like and eight fibronectin type III-like domains. Studies of the similar genes in chick and fly suggest the role of this PTP is in promoting neurite growth, and regulating neurons axon guidance. Multiple tissue specific alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been reported.[5]
Clinical significance
Mutations in the PTPRD gene are associated with autism,[6] obsessive–compulsive disorder,[7] and breast cancer.[8]
Interactions
PTPRD has been shown to interact with PTPRS[9] and liprin-alpha-1.[10]
References
- ↑ "Diseases that are genetically associated with PTPRD view/edit references on wikidata".
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Pulido R, Krueger NX, Serra-Pagès C, Saito H, Streuli M (Apr 1995). "Molecular characterization of the human transmembrane protein-tyrosine phosphatase delta. Evidence for tissue-specific expression of alternative human transmembrane protein-tyrosine phosphatase delta isoforms". J Biol Chem. 270 (12): 6722–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.12.6722. PMID 7896816.
- ↑ Mizuno K, Hasegawa K, Katagiri T, Ogimoto M, Ichikawa T, Yakura H (Sep 1993). "MPTP delta, a putative murine homolog of HPTP delta, is expressed in specialized regions of the brain and in the B-cell lineage". Mol Cell Biol. 13 (9): 5513–23. PMC 360267
 . PMID 8355697.
. PMID 8355697. - 1 2 "Entrez Gene: PTPRD protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, D".
- ↑ Lei N, et al. (2010). "Autism Is Associated with Inherited Deletions in PTPRD and NCAM2". PAS 2010; Abstract 2320.1. Pediatric Academic Societies.
- ↑ "OCD: New Genetic Marker Reported". Retrieved 2015-08-16.
- ↑ "Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours". Nature. Nature Publishing Group. 490 (7418): 61–70. 2012. doi:10.1038/nature11412. PMC 3465532
 . PMID 23000897.
. PMID 23000897. - ↑ Wallace MJ, Fladd C, Batt J, Rotin D (May 1998). "The second catalytic domain of protein tyrosine phosphatase delta (PTP delta) binds to and inhibits the first catalytic domain of PTP sigma". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (5): 2608–16. PMC 110640
 . PMID 9566880.
. PMID 9566880. - ↑ Pulido R, Serra-Pagès C, Tang M, Streuli M (Dec 1995). "The LAR/PTP delta/PTP sigma subfamily of transmembrane protein-tyrosine-phosphatases: multiple human LAR, PTP delta, and PTP sigma isoforms are expressed in a tissue-specific manner and associate with the LAR-interacting protein LIP.1". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92 (25): 11686–90. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.25.11686. PMC 40467
 . PMID 8524829.
. PMID 8524829.
Further reading
- Krueger NX, Streuli M, Saito H (1990). "Structural diversity and evolution of human receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatases.". EMBO J. 9 (10): 3241–52. PMC 552056
 . PMID 2170109.
. PMID 2170109. - Schaapveld RQ, van den Maagdenberg AM, Schepens JT, Weghuis DO, Geurts van Kessel A, Wieringa B, Hendriks WJ (1995). "The mouse gene Ptprf encoding the leukocyte common antigen-related molecule LAR: cloning, characterization, and chromosomal localization.". Genomics. 27 (1): 124–30. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1014. PMID 7665159.
- Pulido R, Serra-Pagès C, Tang M, Streuli M (1996). "The LAR/PTP delta/PTP sigma subfamily of transmembrane protein-tyrosine-phosphatases: multiple human LAR, PTP delta, and PTP sigma isoforms are expressed in a tissue-specific manner and associate with the LAR-interacting protein LIP.1.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92 (25): 11686–90. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.25.11686. PMC 40467
 . PMID 8524829.
. PMID 8524829. - Wagner J, Gordon LA, Heng HH, Tremblay ML, Olsen AS (1997). "Physical mapping of receptor type protein tyrosine phosphatase sigma (PTPRS) to human chromosome 19p13.3.". Genomics. 38 (1): 76–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0594. PMID 8954782.
- Wallace MJ, Fladd C, Batt J, Rotin D (1998). "The second catalytic domain of protein tyrosine phosphatase delta (PTP delta) binds to and inhibits the first catalytic domain of PTP sigma.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (5): 2608–16. PMC 110640
 . PMID 9566880.
. PMID 9566880. - Serra-Pagès C, Medley QG, Tang M, Hart A, Streuli M (1998). "Liprins, a family of LAR transmembrane protein-tyrosine phosphatase-interacting proteins.". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (25): 15611–20. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.25.15611. PMID 9624153.
- Blanchetot C, den Hertog J (2000). "Multiple interactions between receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase (RPTP) alpha and membrane-distal protein-tyrosine phosphatase domains of various RPTPs.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (17): 12446–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.17.12446. PMID 10777529.
- Blanchetot C, Tertoolen LG, Overvoorde J, den Hertog J (2003). "Intra- and intermolecular interactions between intracellular domains of receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatases.". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (49): 47263–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M205810200. PMID 12376545.
- Woodings JA, Sharp SJ, Machesky LM (2003). "MIM-B, a putative metastasis suppressor protein, binds to actin and to protein tyrosine phosphatase delta.". Biochem. J. 371 (Pt 2): 463–71. doi:10.1042/BJ20021962. PMC 1223315
 . PMID 12570871.
. PMID 12570871. - Hillman RT, Green RE, Brenner SE (2005). "An unappreciated role for RNA surveillance.". Genome Biol. 5 (2): R8. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-2-r8. PMC 395752
 . PMID 14759258.
. PMID 14759258. - Sato M, Takahashi K, Nagayama K, Arai Y, Ito N, Okada M, Minna JD, Yokota J, Kohno T (2005). "Identification of chromosome arm 9p as the most frequent target of homozygous deletions in lung cancer.". Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 44 (4): 405–14. doi:10.1002/gcc.20253. PMID 16114034.
- Purdie KJ, Lambert SR, Teh MT, Chaplin T, Molloy G, Raghavan M, Kelsell DP, Leigh IM, Harwood CA, Proby CM, Young BD (2007). "Allelic imbalances and microdeletions affecting the PTPRD gene in cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas detected using single nucleotide polymorphism microarray analysis.". Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 46 (7): 661–9. doi:10.1002/gcc.20447. PMC 2426828
 . PMID 17420988.
. PMID 17420988.