PKN3 (gene)
| PKN3 | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | PKN3, UTDP4-1, protein kinase N3 | ||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 2388285 HomoloGene: 50980 GeneCards: PKN3 | ||||||||||||||||
| Genetically Related Diseases | |||||||||||||||||
| obesity[1] | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||||||
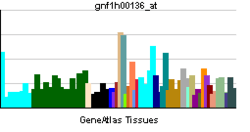 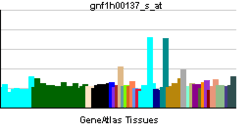 | |||||||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl | |||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 9: 128.7 – 128.72 Mb | Chr 2: 30.08 – 30.09 Mb | |||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [2] | [3] | |||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
PKN3 is a protein kinase C-related molecule and thought to be an effector mediating malignant cell growth downstream of activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K).[4] It is thought that chronic activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/PTEN signal transduction pathway contributes to metastatic cell growth and that PKN3 may mediate that growth.1
PKN3 is required for invasive prostate cell growth as assessed by 3D cell culture assays and in an orthotopic mouse tumor model by inducible expression of short hairpin RNA (shRNA). PKN3 may represent a target for therapeutic intervention in cancers that lack tumor suppressor PTEN function or depend on chronic activation of PI3K.
Interactions
PKN3 (gene) has been shown to interact with ARHGAP26.[5]
References
- ↑ "Diseases that are genetically associated with PKN3 view/edit references on wikidata".
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: PKN3 protein kinase N3".
- ↑ Shibata, H; Oishi K; Yamagiwa A; Matsumoto M; Mukai H; Ono Y (Jul 2001). "PKNbeta interacts with the SH3 domains of Graf and a novel Graf related protein, Graf2, which are GTPase activating proteins for Rho family". J. Biochem. Japan. 130 (1): 23–31. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a002958. ISSN 0021-924X. PMID 11432776.
Further reading
- Wissing J, Jänsch L, Nimtz M, et al. (2007). "Proteomics analysis of protein kinases by target class-selective prefractionation and tandem mass spectrometry". Mol. Cell Proteomics. 6 (3): 537–47. doi:10.1074/mcp.T600062-MCP200. PMID 17192257.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334.
. PMID 15489334. - Leenders F, Möpert K, Schmiedeknecht A, et al. (2005). "PKN3 is required for malignant prostate cell growth downstream of activated PI 3-kinase". EMBO J. 23 (16): 3303–13. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600345. PMC 514518
 . PMID 15282551.
. PMID 15282551. - Humphray SJ, Oliver K, Hunt AR, et al. (2004). "DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 9". Nature. 429 (6990): 369–74. doi:10.1038/nature02465. PMC 2734081
 . PMID 15164053.
. PMID 15164053. - Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932. - Shibata H, Oishi K, Yamagiwa A, et al. (2001). "PKNbeta interacts with the SH3 domains of Graf and a novel Graf related protein, Graf2, which are GTPase activating proteins for Rho family". J. Biochem. 130 (1): 23–31. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a002958. PMID 11432776.
- Oishi K, Takahashi M, Mukai H, et al. (2001). "PKN regulates phospholipase D1 through direct interaction". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (21): 18096–101. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010646200. PMID 11259428.
- Oishi K, Mukai H, Shibata H, et al. (1999). "Identification and characterization of PKNbeta, a novel isoform of protein kinase PKN: expression and arachidonic acid dependency are different from those of PKNalpha". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 261 (3): 808–14. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1116. PMID 10441506.