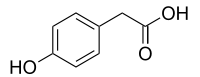
4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid | |
| Other names
p-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 156-38-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| 1448766 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:18101 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1772 |
| ChemSpider | 124 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.321 |
| EC Number | 205-851-3 |
| PubChem | 127 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 152.15 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Beige powder |
| Melting point | 150 °C (302 °F; 423 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid is a chemical compound found in olive oil[1] and beer.[2] In industry the chemical is an intermediate used to synthesize atenolol[3] and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid.[4]
Synthesis
4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid is obtained by reducing 4-hydroxymandelic acid with elemental phosphorus and iodine.[3]
References
- ↑ Papadopoulos, George; Boskou, Dimitrios (1991). "Antioxidant effect of natural phenols on olive oil". Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society. 68 (9): 669. doi:10.1007/BF02662292.
- ↑ Determination of free and bound phenolic acids in beer. M. Nardini and A. Ghiselli, Food Chemistry, January 2004, Volume 84, Issue 1, Pages 137–143, doi:10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00257-7
- 1 2 Mattioda, Georges; Christidis, Yani (2000). "Glyoxylic Acid". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry: pg. 2. doi:10.1002/14356007.a12_495. Retrieved 27 December 2013.
- ↑ Sutton, Peter; Whittall, John (2012). Practical Methods for Biocatalysis and Biotransformations 2. Chichester, West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. pp. 150–153. ISBN 9781119991397.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.