Oncomelania hupensis
| Oncomelania hupensis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Oncomelania hupensis | |
| NE | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| (unranked): | clade Caenogastropoda clade Hypsogastropoda |
| Superfamily: | Rissooidea |
| Family: | Pomatiopsidae |
| Subfamily: | Pomatiopsinae |
| Genus: | Oncomelania |
| Species: | O. hupensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Oncomelania hupensis Gredler, 1881 | |
Oncomelania hupensis is a species of very small tropical freshwater snail, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Pomatiopsidae.
Distribution
Oncomelania hupensis has been found in China, and also in Japan, Philippines, and Indonesian island of Sulawesi.[1]
Description
Over the past a few decades, the taxonomy of Oncomelania hupensis has been a dispute due to the variation in morphological characters such as shell sculpture, operculum etc. Phenotypically, Oncomelania hupensis can be separated into ribbed- and smooth- shelled morphotypes. In China, the typical morphotype of Oncomelania hupensis is ribbed-shelled, and its distribution is restricted to Yangtze River basin. Smooth-shelled snails are also distributed in mainland China, but are considered as the same species and subspecies of Oncomelania hupensis.[1]
Oncomelania hupensis reported in other Far East countries are smooth-shelled, and have been considered either as subspecies of Oncomelania hupensis or independent species in this genus.[1]
 Photo of apertural view of a shell of Oncomelania hupensis hupensis. |
 Drawing of apertural view of a shell of Oncomelania hupensis nosophora. The scale is 1 mm. |
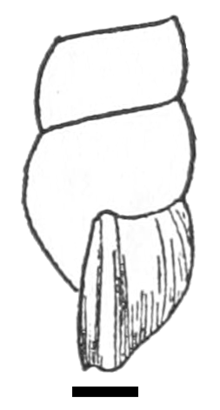 Drawing of lateral view of a part of a shell of Oncomelania hupensis nosophora. The scale is 1 mm. |
Subspecies

- Oncomelania hupensis chiui (Habe & Miyazaki, 1962) - in Taiwan[3]
- Oncomelania hupensis hupensis (Gredler, 1881) - in China.[3] It is the most widely distributed subspecies of Oncomelania hupensis and lives primarily at low altitude but a few populations live in hilly areas in the drainage area of the Yangtze River in mainland China. It has varix, no matter whether the shell is smooth or ribbed, but most populations have ribbed-shell. Oncomelania hupensis hupensis has the same shell growth allometry as Oncomelania hupensis robertsoni but has a longer shell on average.[1]
- Oncomelania hupensis formosana (Pilsbry & Hirase) - in Taiwan[3]
- Oncomelania hupensis guangxiensis (Liu, 1981)
- Oncomelania hupensis lindoesnsis (Davis & Carney, 1973) - in Sulawesi,[3] or as separates species Oncomelania lindoensis
- Oncomelania hupensis nosophora (Robson, 1915)[3] - it is Endangered (type I, CR+EN) taxon in Japan.[4]
- Oncomelania hupensis quadrasi (Möllendorff, 1895) - in Philippines[3]
- Oncomelania hupensis robertsoni (Bartsch, 1946) - It has a small, smooth shell but with no varix, is found in Sichuan and Yunnan provinces.[1]
- Oncomelania hupensis tangi (Bartsch, 1936) - It has a smooth shell but with thick varix, is found in Fujian province and Guangxi autonomous region, separated geographically from the Yangtze River, and extensive control measures have brought this subspecies to near extinction.[1]
There are 4 subspecies of Oncomelania hupensis in China: hupensis, robertsoni, tangi and guangxiensis.[5][6]
Genetic confirmation of thsese four Chinese subspecies: Based on shell form, biogeographical and allozyme data, Davis et al. (1995)[7] distinguished 3 subspecies of the Oncomelania hupensis in mainland China.[1] However, Zhou et al. (2008)[8] separated the Oncomelania hupensis guangxiensis out from Oncomelania hupensis tangi based on allozymes and amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP), which was verified recently by Li et al.[9] with internal transcribed spacer (ITS) and 16S fragments.
Genetics
It may also be possible that continuous control efforts, such as routine molluscicides in China, which have been used to control snails for about fifty years, might have imposed some effect on population genetics of these snails.[1]
The complete mitochondrial genome of Oncomelania hupensis has been released in 2010.[10]
Habitat

It is seasonally amphibious species which lives in lakes and on marshy ground.[11]
The habitats of Oncomelania hupensis in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River include lake/marshland regions and hill regions, both of which have extensive physical connections with the Yangtze River through channels or in low floodplains beside the Yangtze River. With frequent floodings of the Yangtze River, snails in these habitats can be dispersed and subsequently deposited widely in various localities. The accumulation of mixed sources of snails can then generate genetically diversified populations of snails, leading to the existence of various haplotypes.[1]
In Sichuan and Yunnan provinces in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, Oncomelania hupensis robertsoni are distributed in mountainous areas, and are not subjected to flood influence as much as in the middle and lower reaches of the river.[1] It is interesting to see that a relatively lower number of haplotypes were found in this region as compared with Oncomelania hupensis hupensis.[1] It appears likely that there has been certain degree of isolation for these mountainous populations.[1]
Parasites
This freshwater snail is significant medically, because it is an important vector of parasitic infection in the tropics and subtropics. It can serve as vectors for two serious human diseases: the schistosomiasis blood fluke parasite, and the paragonimus lung fluke parasites.
Oncomelania hupensis is the unique intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum,[6][12] which causes schistosomiasis endemic in the Far East, and especially in mainland China. Oncomelania hupensis largely determines the parasite's geographical range.[1]
See also
- Oncomelania hupensis quadrasi is synonymous with Oncomelania quadrasi (Davis, 1968). It is endemic in the Philippines.[13]
References
This article incorporates CC-BY-2.5 text from references.[1][2]
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Zhao Q. P., Jiang M. S., Littlewood D. T. J. & Nie P. (2010). "Distinct Genetic Diversity of Oncomelania hupensis, Intermediate Host of Schistosoma japonicum in Mainland China as Revealed by ITS Sequences". PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 4(3): e611. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000611.
- 1 2 Zhao Q. P., Jiang M. S., Littlewood D. T. J. & Nie P. (2010) "Distinct Genetic Diversity of Oncomelania hupensis, Intermediate Host of Schistosoma japonicum in Mainland China as Revealed by ITS Sequences". Ribbed-shelled Oncomelania hupensis hupensis (Gredler, 1881)". PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 4(3): e611. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000611.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Davis G. M. (1979). "The origin and evolution of the gastropod family Pomatiopsidae, with emphasis on the Mekong river Triculinae". Academy of natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Monograph 20: 1-120. ISBN 978-1-4223-1926-0. at Google Books.
- ↑ (Japanese) "カタヤマガイ". 日本のレッドデータ検索システム [Japanese Red List Data Book], accessed 17 July 2011.
- ↑ Zhou Yi-Biao, Zhao Gen-Ming & Jiang Qing-Wu. (2008). "Genetic Variability of Schistosoma japonicum (Katsorada, 1904) Intermediate Hosts Oncomelania hupensis (Gredler, 1881) (Gastropoda: Rissooidea)". Annales Zoologici 58(4): 881-889. 10.3161/000345408X396792.
- 1 2 Yi-Biao Zhou, Mei-Xia Yang, Gen-Ming Zhao, Jiang-Guo Wei & Qing-Wu Jiang. (2007). "Oncomelania hupensis (Gastropoda: Rissooidea), Intermediate Host Of Schistosoma japonicum In China: Genetics and Molecular Phylogeny Based On Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphisms". Malacologia 49(2): 367-382. doi:10.4002/0076-2997-49.2.367, abstract
- ↑ Davis G. M., Zhang Y., Guo Y. H. & Spolsky C. M. (1995). "Population genetics and systematic status of Oncomelania hupensis (Gastropoda: Pomatiopsidae) throughout China". Malacologia 37: 133–156.
- ↑ (Chinese) Zhou Y. B., Jiang Q. W., Zhao G. M. & Yuan H. C. (2007). "Subspecies differentiation of Oncomelania hupensis from mainland China". Chin J Schisto Control 19: 485–487.
- ↑ Li S. Z., Wang Y. X., Yang K., Liu Q., Wang Q., et al. (2009). "Landscape genetics: the correlation of spatial and genetic distances of Oncomelania hupensis, the intermediate host snail of Schistosoma japonicum in mainland China". Geospat Health 3: 221–231.
- ↑ Zhao Q. P., Zhang S. H., Deng Z. R., Jiang M. S. & Nie P. (2010). "Conservation and variation in mitochondrial genomes of gastropods Oncomelania hupensis and Tricula hortensis, intermediate host snails of Schistosoma in China". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 57(1): 215-226. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2010.05.026.
- 1 2 Kameda Y. & Kato M. (2011). "Terrestrial invasion of pomatiopsid gastropods in the heavy-snow region of the Japanese Archipelago". BMC Evolutionary Biology 11: 118. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-11-118.
- ↑ Lewis F. A., Liang Y., Raghavan N. & Knight M. (2008). "The NIH-NIAID Schistosomiasis Resource Center". PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2(7): e267. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000267.
- ↑ Garcia, R. G. (1972). "Tolerance of Oncomelania hupensis quadrasi to varying concentrations of dissolved oxygen and organic pollution". Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 47 (1): 59–70. PMC 2480802
 . PMID 4538906..
. PMID 4538906..
Further reading
- Shi, C. H., T. Wilke, G. M. Davis, M. Y. Xia & C. P. Qiu. 2002. Population genetics, microphylogeography, ecology and susceptibility to schistosome infection of Chinese Oncomelania hupensis hupensis (Gastropoda: Rissooidea: Pomatiopsidae) in the Miao River System. Malacologia 44:2333–347.
- Tang C.-T., Lu M.-K., Guo Y., Wang Y.-N., Peng J.-Y., Wu W.-B., Li W.-H., Weimer B. C. & Chen D. (2009). "Development of Larval Schistosoma japonicum Blocked in Oncomelania hupensis by Pre-Infection with Larval Exorchis Sp.". Journal of Parasitology 95(6): 1321-1325. doi:10.1645/GE-2055.1.
- Wilke, T., G. M. Davis, C. E. Chen, X. N. Zhou, X. P. Zeng, Y. Zhang & C. M. Spolsky. 2000. Oncomelania hupensis (Gastropoda: Rissooidea) in eastern China: molecular phylogeny, population structure, and ecology. Acta Tropica 77:215–227. abstract
- Wilke, T., G. M. Davis, D. C. Qiu & R. C. Speak. 2006. Extreme mitochondrial sequence diversity in the intermediate schistosomiasis host Oncomelania hupensis robertsoni: another case of ancestral polymorphism. Malacologia 48:1–2143–157.
- Yang, Guo-Jing1; Utzinger, Jürg; Sun, Le-Ping; Hong, Qing-Biao; Vounatsou, Penelope; Tanner, Marcel; Zhou, Xiao-Nong 2007.Effect of temperature on the development of Schistosoma japonicum within Oncomelania hupensis, and hibernation of O. hupensis. Parasitology Research, Volume 100, Number 4, March 2007, pp. 695–700(6). abstract
- Zhou, Y. B., Q. W. Jiang, G. M. Zhao & J. G. Wei. 2005. Analysis of morphological variation within Oncomelania hupensis population. Chinese Journal of Zoology 40:90–97.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Oncomelania hupensis. |
.jpg)