OCA2
| OCA2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | ||||||
| Aliases | OCA2, BEY, BEY1, BEY2, BOCA, D15S12, EYCL, EYCL2, EYCL3, HCL3, P, PED, SHEP1, OCA2 melanosomal transmembrane protein | |||||
| External IDs | MGI: 97454 HomoloGene: 37281 GeneCards: OCA2 | |||||
| RNA expression pattern | ||||||
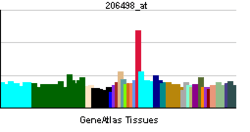 | ||||||
| More reference expression data | ||||||
| Orthologs | ||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | ||||
| Entrez | ||||||
| Ensembl |
|
|||||
| UniProt | ||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | ||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | ||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 15: 27.75 – 28.1 Mb | Chr 7: 56.24 – 56.54 Mb | ||||
| PubMed search | [1] | [2] | ||||
| Wikidata | ||||||
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
P protein, also known as melanocyte-specific transporter protein or pink-eyed dilution protein homolog, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the oculocutaneous albinism II (OCA2) gene.[3] The P protein is believed to be an integral membrane protein involved in small molecule transport, specifically tyrosine - a precursor of melanin. Certain mutations in OCA2 result in type 2 oculocutaneous albinism.[3] OCA2 encodes the human homologue of the mouse p (pink-eyed dilution) gene.
The human OCA2 gene is located on the long arm (q) of chromosome 15, specifically from base pair 28,000,020 to base pair 28,344,457 on chromosome 15.
Function
OCA2 provides instructions for making the protein called P protein which is located in melanocytes which are specialized cells that produce melanin. Melanin is responsible for giving color to the skin, hair, and eyes. Moreover, melanin is found in the light-sensitive tissue of the retina of the eye which plays a role in normal vision.
The exact function of protein P is unknown, but it has been found that it is essential for the normal coloring of skin, eyes, and hair; and likely involved in melanin production. This gene seems to be the main determinant of eye color depending on the amount of melanin production in the iris stroma (large amounts giving rise to brown eyes; little to no melanin giving rise to blue eyes).
Clinical significance
Mutations in the OCA2 gene cause a disruption in the normal production of melanin; therefore, causing vision problems and reductions in hair, skin, and eye color. Oculocutaneous albinism caused by mutations in the OCA2 gene is called oculocutaneous albinism type 2. The prevalence of OCA type 2 is estimated at 1/38,000-1/40,000 in most populations throughout the world, with a higher prevalence in the African population of 1/3,900-1/1,500.[4] Other diseases associated with the deletion of OCA2 gene are Angelman syndrome (light-colored hair and fair skin) and Prader-Willi syndrome (unusually light-colored hair and fair skin). With both these syndromes, the deletion often occurs in individuals with either syndrome.[5][6]
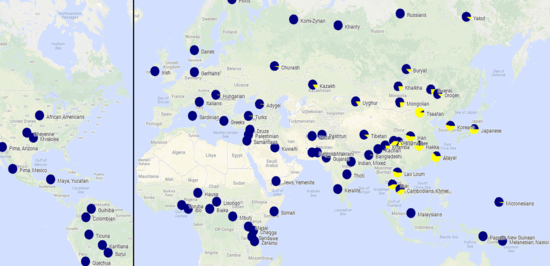
A mutation in the HERC2 gene adjacent to OCA2, affecting OCA2's expression in the human iris, is found common to nearly all people with blue eyes. It has been hypothesized that all blue-eyed humans share a single common ancestor with whom the mutation originated.[7][8][9]
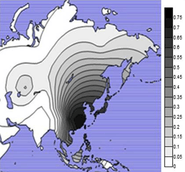
The His615Arg allele of OCA2 is involved in the light skin tone and the derived allele is restricted to East Asia with high frequencies, with highest frequencies in Eastern East Asia (49-63%), midrange frequencies in Southeast Asia, and the lowest frequencies in Western China and some Eastern European populations.[10][11]
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: OCA2 oculocutaneous albinism II (pink-eye dilution homolog, mouse)". Retrieved 2015-03-12.
- ↑ Hayashi, Masahiro; Suzuki, Tamio (April 2013). "Oculocutaneous albinism type 2". Orphanet. Retrieved 2014-11-09.
- ↑ "OCA2 - oculocutaneous albinism II". Genetics Home Reference - Your guide to understanding genetic conditions. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
- ↑ "Don't it make your brown eyes blue?". Understanding Genetics. Understanding Genetics. Retrieved 30 March 2013.
- ↑ Bryner J (2008-01-31). "Here's what made those brown eyes blue". Health News. MSNBC. Retrieved 2008-11-06.; Bryner J (2008-01-31). "One Common Ancestor Behind Blue Eyes". LiveScience. Imaginova Corp. Retrieved 2008-11-06.; "Blue-eyed humans have a single, common ancestor". News. University of Copenhagen. 2008-01-30. Retrieved 2008-11-06.
- ↑ Eiberg H, Troelsen J, Nielsen M, Mikkelsen A, Mengel-From J, Kjaer KW, Hansen L (2008). "Blue eye color in humans may be caused by a perfectly associated founder mutation in a regulatory element located within the HERC2 gene inhibiting OCA2 expression". Hum. Genet. 123 (2): 177–87. doi:10.1007/s00439-007-0460-x. PMID 18172690.
- ↑ Sturm RA, Duffy DL, Zhao ZZ, Leite FP, Stark MS, Hayward NK, Martin NG, Montgomery GW (2008). "A single SNP in an evolutionary conserved region within intron 86 of the HERC2 gene determines human blue-brown eye color". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82 (2): 424–31. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.11.005. PMC 2427173
 . PMID 18252222.
. PMID 18252222. - ↑ Donnelly MP, Paschou P, Grigorenko E, Gurwitz D, Barta C, Lu RB, Zhukova OV, Kim JJ, Siniscalco M, New M, Li H, Kajuna SL, Manolopoulos VG, Speed WC, Pakstis AJ, Kidd JR, Kidd KK (2012). "A global view of the OCA2-HERC2 region and pigmentation". Hum. Genet. 131 (5): 683–96. doi:10.1007/s00439-011-1110-x. PMC 3325407
 . PMID 22065085.
. PMID 22065085. - ↑ Edwards M, Bigham A, Tan J, Li S, Gozdzik A, Ross K, Jin L, Parra EJ (2010). "Association of the OCA2 polymorphism His615Arg with melanin content in east Asian populations: further evidence of convergent evolution of skin pigmentation". PLoS Genet. 6 (3): e1000867. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000867. PMC 2832666
 . PMID 20221248.
. PMID 20221248.
Further reading
- Oetting WS, King RA (1999). "Molecular basis of albinism: mutations and polymorphisms of pigmentation genes associated with albinism". Hum. Mutat. 13 (2): 99–115. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1999)13:2<99::AID-HUMU2>3.0.CO;2-C. PMID 10094567.
- Brilliant MH (2001). "The mouse p (pink-eyed dilution) and human P genes, oculocutaneous albinism type 2 (OCA2), and melanosomal pH". Pigment Cell Res. 14 (2): 86–93. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2001.140203.x. PMID 11310796.
- Ramsay M, Colman MA, Stevens G, Zwane E, Kromberg J, Farrall M, Jenkins T (1992). "The tyrosinase-positive oculocutaneous albinism locus maps to chromosome 15q11.2-q12". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 51 (4): 879–84. PMC 1682821
 . PMID 1415228.
. PMID 1415228. - Gardner JM, Nakatsu Y, Gondo Y, Lee S, Lyon MF, King RA, Brilliant MH (1992). "The mouse pink-eyed dilution gene: association with human Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes". Science. 257 (5073): 1121–4. doi:10.1126/science.257.5073.1121. PMID 1509264.
- Ludowese CJ, Thompson KJ, Sekhon GS, Pauli RM (1991). "Absence of predictable phenotypic expression in proximal 15q duplications". Clin. Genet. 40 (3): 194–201. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.1991.tb03076.x. PMID 1773534.
- Lee ST, Nicholls RD, Jong MT, Fukai K, Spritz RA (1995). "Organization and sequence of the human P gene and identification of a new family of transport proteins". Genomics. 26 (2): 354–63. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(95)80220-G. PMID 7601462.
- Spritz RA, Fukai K, Holmes SA, Luande J (1995). "Frequent intragenic deletion of the P gene in Tanzanian patients with type II oculocutaneous albinism (OCA2)". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 56 (6): 1320–3. PMC 1801108
 . PMID 7762554.
. PMID 7762554. - Lee ST, Nicholls RD, Schnur RE, Guida LC, Lu-Kuo J, Spinner NB, Zackai EH, Spritz RA (1994). "Diverse mutations of the P gene among African-Americans with type II (tyrosinase-positive) oculocutaneous albinism (OCA2)". Hum. Mol. Genet. 3 (11): 2047–51. PMID 7874125.
- Durham-Pierre D, Gardner JM, Nakatsu Y, King RA, Francke U, Ching A, Aquaron R, del Marmol V, Brilliant MH (1994). "African origin of an intragenic deletion of the human P gene in tyrosinase positive oculocutaneous albinism". Nat. Genet. 7 (2): 176–9. doi:10.1038/ng0694-176. PMID 7920637.
- Lee ST, Nicholls RD, Bundey S, Laxova R, Musarella M, Spritz RA (1994). "Mutations of the P gene in oculocutaneous albinism, ocular albinism, and Prader-Willi syndrome plus albinism". N. Engl. J. Med. 330 (8): 529–34. doi:10.1056/NEJM199402243300803. PMID 8302318.
- Rinchik EM, Bultman SJ, Horsthemke B, Lee ST, Strunk KM, Spritz RA, Avidano KM, Jong MT, Nicholls RD (1993). "A gene for the mouse pink-eyed dilution locus and for human type II oculocutaneous albinism". Nature. 361 (6407): 72–6. doi:10.1038/361072a0. PMID 8421497.
- Spritz RA, Lee ST, Fukai K, Brondum-Nielsen K, Chitayat D, Lipson MH, Musarella MA, Rosenmann A, Weleber RG (1997). "Novel mutations of the P gene in type II oculocutaneous albinism (OCA2)". Hum. Mutat. 10 (2): 175–7. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1997)10:2<175::AID-HUMU12>3.0.CO;2-X. PMID 9259203.
- Kerr R, Stevens G, Manga P, Salm S, John P, Haw T, Ramsay M (2000). "Identification of P gene mutations in individuals with oculocutaneous albinism in sub-Saharan Africa". Hum. Mutat. 15 (2): 166–72. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(200002)15:2<166::AID-HUMU5>3.0.CO;2-Z. PMID 10649493.
- Oetting WS, Gardner JM, Fryer JP, Ching A, Durham-Pierre D, King RA, Brilliant MH (1998). "Mutations of the human P gene associated with Type II oculocutaneous albinism (OCA2). Mutations in brief no. 205. Online". Hum. Mutat. 12 (6): 434. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1998)12:6<434::AID-HUMU16>3.0.CO;2-7. PMID 10671067.
- Passmore LA, Kaesmann-Kellner B, Weber BH (1999). "Novel and recurrent mutations in the tyrosinase gene and the P gene in the German albino population". Hum. Genet. 105 (3): 200–10. doi:10.1007/s004390051090. PMID 10987646.
- Manga P, Kromberg J, Turner A, Jenkins T, Ramsay M (2001). "In Southern Africa, brown oculocutaneous albinism (BOCA) maps to the OCA2 locus on chromosome 15q: P-gene mutations identified". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 68 (3): 782–7. doi:10.1086/318800. PMC 1274491
 . PMID 11179026.
. PMID 11179026. - Manga P, Orlow SJ (2001). "Inverse correlation between pink-eyed dilution protein expression and induction of melanogenesis by bafilomycin A1". Pigment Cell Res. 14 (5): 362–7. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2001.140508.x. PMID 11601658.
- Toyofuku K, Valencia JC, Kushimoto T, Costin GE, Virador VM, Vieira WD, Ferrans VJ, Hearing VJ (2002). "The etiology of oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) type II: the pink protein modulates the processing and transport of tyrosinase". Pigment Cell Res. 15 (3): 217–24. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2002.02007.x. PMID 12028586.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to OCA2. |