Minifloat
In computing, minifloats are floating point values represented with very few bits. Predictably, they are not well suited for general purpose numerical calculations. They are used for special purposes most often in computer graphics where iterations are small and precision has aesthetic effects. Additionally they are frequently encountered as a pedagogical tool in computer science courses to demonstrate the properties and structures of floating point arithmetic and IEEE 754 numbers.
Minifloats with 16 bits are half-precision numbers (opposed to single and double precision). There are also minifloats with 8 bits or even fewer.
Minifloats can be designed following the principles of the IEEE 754 standard. In this case they must obey the (not explicitly written) rules for the frontier between subnormal and normal numbers and they must have special patterns for infinity and NaN. Normalized numbers are stored with a biased exponent. The new revision of the standard, IEEE 754-2008, has 16-bit binary minifloats.
The Radeon R300 and R420 GPUs used an "fp24" floating-point format with 7 bits of exponent and 16 bits (+1 implicit) of mantissa.[1] "Full Precision" in Direct3D 9.0 is a proprietary 24-bit floating point format. Microsoft's D3D9 (Shader Model 2.0) graphics API initially supported both FP24 (as in ATI's R300 chip) and FP32 (as in Nvidia's NV30 chip) as "Full Precision" as well as FP16 as "Partial Precision" for vertex and pixel shader calculations performed by the graphics hardware.
In computer graphics minifloats are sometimes used to represent only integral values. If at the same time subnormal values should exist, the least subnormal number has to be 1. This statement can be used to calculate the bias value. The following example demonstrates the calculation as well as the underlying principles.
| Floating point precisions |
|---|
| IEEE 754 |
| Other |
Example
A minifloat in one byte (8 bit) with one sign bit, four exponent bits and three mantissa bits (in short a 1.4.3.−2 minifloat) should be used to represent integral values. All IEEE 754 principles should be valid. The only free value is the exponent bias, which will come out as −2. The unknown exponent is called for the moment x.
Numbers in a different base are marked as ...base. Example 1012 = 5. The bit patterns have spaces to visualize their parts.
Representation of zero
0 0000 000 = 0
Subnormal numbers
The mantissa is extended with 0.:
0 0000 001 = 0.0012 × 2x = 0.125 × 2x = 1 (least subnormal number) ... 0 0000 111 = 0.1112 × 2x = 0.875 × 2x = 7 (greatest subnormal number)
Normalized numbers
The mantissa is extended with 1.:
0 0001 000 = 1.0002 × 2x = 1 × 2x = 8 (least normalized number) 0 0001 001 = 1.0012 × 2x = 1.125 × 2x = 9 ... 0 0010 000 = 1.0002 × 2x+1 = 1 × 2x+1 = 16 0 0010 001 = 1.0012 × 2x+1 = 1.125 × 2x+1 = 18 ... 0 1110 000 = 1.0002 × 2x+13 = 1.000 × 2x+13 = 65536 0 1110 001 = 1.0012 × 2x+13 = 1.125 × 2x+13 = 73728 ... 0 1110 110 = 1.1102 × 2x+13 = 1.750 × 2x+13 = 114688 0 1110 111 = 1.1112 × 2x+13 = 1.875 × 2x+13 = 122880 (greatest normalized number)
Infinity
0 1111 000 = +infinity 1 1111 000 = −infinity
If the exponent field were not treated specially, the value would be
0 1111 000 = 1.0002 × 2x+14 = 217 = 131072
Not a Number
x 1111 yyy = NaN (if yyy ≠ 000)
Without the IEEE 754 special handling of the largest exponent, the greatest possible value would be
0 1111 111 = 1.1112 × 2x+14 = 1.875 * 217 = 245760
Value of the bias
If the least subnormal value (second line above) should be 1, the value of x has to be x = 3. Therefore the bias has to be −2, that is every stored exponent has to be decreased by −2 or has to be increased by 2, to get the numerical exponent.
All values
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 36 40 44 48 52 56 60
64 72 80 88 96 104 112 120 128 144 160 176 192 208 224 240
256 288 320 352 384 416 448 480 512 576 640 704 768 832 896 960
1024 1152 1280 1408 1536 1664 1792 1920 2048 2304 2560 2816 3072 3328 3584 3840
4096 4608 5120 5632 6144 6656 7168 7680 8192 9216 10240 11264 12288 13312 14336 15360
16384 18432 20480 22528 24576 26624 28672 30720 32768 36864 40960 45056 49152 53248 57344 61440
65536 73728 81920 90112 98304 106496 114688 122880 Inf NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
-0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 -10 -11 -12 -13 -14 -15
-16 -18 -20 -22 -24 -26 -28 -30 -32 -36 -40 -44 -48 -52 -56 -60
-64 -72 -80 -88 -96 -104 -112 -120 -128 -144 -160 -176 -192 -208 -224 -240
-256 -288 -320 -352 -384 -416 -448 -480 -512 -576 -640 -704 -768 -832 -896 -960
-1024 -1152 -1280 -1408 -1536 -1664 -1792 -1920 -2048 -2304 -2560 -2816 -3072 -3328 -3584 -3840
-4096 -4608 -5120 -5632 -6144 -6656 -7168 -7680 -8192 -9216 -10240 -11264 -12288 -13312 -14336 -15360
-16384 -18432 -20480 -22528 -24576 -26624 -28672 -30720 -32768 -36864 -40960 -45056 -49152 -53248 -57344 -61440
-65536 -73728 -81920 -90112 -98304 -106496 -114688 -122880 -Inf NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
Properties of this example
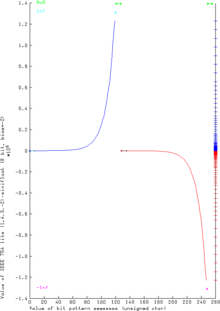
Integral minifloats in one byte have a greater range of ±122880 than twos complement integer with a range −128 to +127. The greater range is compensated by a poor precision, because there are only 4 mantissa bits, equivalent to slightly more than one decimal place. They also have greater range than half-precision minifloats with range ±65504, also compensated by lack of fractions and poor precision.
There are only 242 different values (if +0 and −0 are regarded as different), because 14 bit patterns represent NaN.
The values between 0 and 16 have the same bit pattern as minifloat or twos complement integer. The first pattern with a different value is 00010001, which is 18 as a minifloat and 17 as a twos complement integer.
This coincidence does not occur at all with negative values, because this minifloat is a signed-magnitude format.
The (vertical) real line on the right shows clearly the varying density of the floating point values - a property which is common to any floating point system. This varying density results in a curve similar to the exponential function.
Although the curve may appear smooth, this is not the case. The graph actually consists of distinct points, and these points lie on line segments with discrete slopes. The value of the exponent bits determines the absolute precision of the mantissa bits, and it is this precision that determines the slope of each linear segment.
Arithmetic
Addition

The graphic demonstrates the addition of even smaller (1.3.2.3)-minifloats with 6 bits. This floating point system follows the rules of IEEE 754 exactly. NaN as operand produces always NaN results. Inf − Inf and (−Inf) + Inf results in NaN too (green area). Inf can be augmented and decremented by finite values without change. Sums with finite operands can give an infinite result (i.e. 14.0+3.0 − +Inf as a result is the cyan area, −Inf is the magenta area). The range of the finite operands is filled with the curves x+y=c, where c is always one of the representable float values (blue and red for positive and negative results respectively).
Subtraction, multiplication and division
The other arithmetic operations can be illustrated similarly:
-

Subtraction
-

Multiplication
-
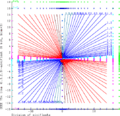
Division
See also
References
- ↑ Buck, Ian (2005-03-13), "Chapter 32. Taking the Plunge into GPU Computing", in Pharr, Matt, GPU Gems, ISBN 0-321-33559-7, retrieved 2011-02-20
- Munafo, Robert (15 May 2016). "Survey of Floating-Point Formats". Retrieved 8 August 2016.