Léon Printemps
| Léon Printemps | |
|---|---|
 Portrait of Léon Printemps in 1924 | |
| Born |
Léon Printemps 26 May 1871 Paris, France |
| Died |
9 July 1945 (aged 74) Paris, France |
| Nationality |
|
| Education | École des Beaux-Arts de Paris |
| Known for | Portrait painter, Landscape painter |
Léon Printemps (26 May 1871 – 9 July 1945) was a French artist known best for his work as a portrait and landscape painter.
Biography
Léon Printemps was born in Paris to a family which originally hailed from Lille. From an early age he was attracted to painting.
His uncle, the sculptor Jules Printemps, a student of François Jouffroy at the École nationale des Beaux-Arts, supported his vocation and prepared him for the entrance examination to this school. He was admitted in 1892, joined the workshop of Gustave Moreau and regularly visited it until Moreau’s death in 1898. He also associated with such artists as Rouault, Matisse, Evenepoel, Albert Marquet, Edgar Maxence and Charles Milcendeau.
Around this period his work was largely part of the Symbolist movement and he experimented with a poetic or mythological vision and with the sensuality of the female nude.
Work
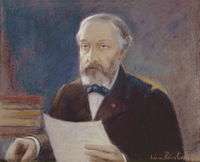
Portrait painter
He soon established his reputation as a portrait artist receiving commissions from such eminent personalities as Sully Prudhomme, the first recipient of the Nobel Prize in Literature, the Prince and Princess of Waldeck, Mr and Mrs Commettant, and Prince Yusupov, the assassin of Rasputin.
Léon Printemps married in 1903 and frequently painted his family in an intimate tone, particularly his daughter Lucile whose death at the age of 6 touched him profoundly, as well as his son René.
Landscape painter
Léon Printemps was a landscape painter his entire life. His desire to meet Flemish masters prompted him to travel to Belgium and the Netherlands at the end of the nineteenth century, returning home with various studies. Later in life his attraction to the beaches of Normandy, which were quite fashionable at the time, became more marked. After the First World War he started painting landscapes in Brittany and particularly the islands of the Vendée coast, the island of Noirmoutier, the island of Yeu, where he painted seascapes and portraits of fishermen and old farmers’ wives.
Flemish and Dutch influence
The appeal of the work of Flemish and Dutch masters during Printemps’ visits to the Louvre Museum inspired him to travel to Belgium and the Netherlands on several occasions with a desire to better understand the art of these great Flemish and Dutch masters. Several paintings, which were the outcome of his first visits to Belgium, were presented at the Salon des artistes français (1898 and 1905), the Salon artistique des PTT (1905) and in regional exhibitions, in Lille (1898) and in Nantes (1906).
In 1894 Printemps travelled to Belgium for the first time, presumably in the company of other students of Gustave Moreau, visiting Bruges, Ghent, Mechelen and Antwerp. Two years later he travelled to the Meuse Valley where he painted the Bayard Rock, a remarkable sight in Dinant. In 1897, he spent some time in the Netherlands visiting the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam. In 1898, he returned to Bruges and Mechelen. In 1929 and 1933 he also took his son René, who was also studying to become a painter at the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris, on a trip to explore these two cities.
Léon Printemps died on 9 July 1945, in his studio at 6 rue Furstenberg, where the Musée National Eugène Delacroix[1] is currently located.
Participation in Exhibitions – Awards and Merits
- Salon des artistes français, between 1893 and 1939. Honourable mention in 1900.
- Salon d’hiver, from 1907 until 1934.
- Salon des artistes de Paris.
- Exhibition of the Amis des arts de la Somme, in Amiens. Silver medal in 1896.
- Salon of the Union artistique du Nord, in Lille. Silver medal in 1896.
- Salon of the Rose-Croix, 1897.[2]
- Salon artistique des PTT.
- Exposition du Travail. Silver medal in 1899.
- Salon of the Société des Amis des arts de Nantes, from 1902 until 1908.
- Salon of the Cercle des Gobelins, from 1901 until 1903, 1913.
- International exhibition of the Palais des Beaux-Arts of Monte Carlo, 1903.
- World’s Fair in Paris Neuilly. Gold medal in 1900.
- World’s Fair in Seattle, Washington. Gold medal in 1909.
- Exhibition of the works of students of Gustave Moreau, Hessèle Gallery, 1910.
- Prix du souvenir – Guerre 1914-1918, 1924.
- Frattesi Award of the City of Paris, 1942.
Paintings in public collections
- Châlons-en-Champagne (Marne) : Municipal Museum – Parfum du soir – 1904. Donated by Baron Alphonse James de Rothschild.
- Châtenay-Malabry (Hauts de Seine) :
- Médiathèque : Portrait of Sully Prudhomme – 1902.
- House of Chateaubriand : La femme à la grille – 1898. - Cholet (Maine-et-Loire) : Museum of Art and History – L’Automne – 1900.[3]
- Clairoix (Oise) : Association Art, Histoire et Patrimoine de Clairoix : Church of Clairoix – Vallée de l’Aronde – 1910.
- Clermont (Oise) : Town hall – Bretonne d’Audierne – 1910.
- Compiègne (Oise) : Antoine Vivenel Museum – Au bois du rêve– 1899. Donated by Baron Alphonse James de Rothschild.
- Laffaux (Aisne) : Town Hall – Verdun – 1920.[4]
- Les Lucs-sur-Boulogne (Vendée) : Historial de la Vendée – 30 paintings (donated in 2013).[5]
- Lullin (Savoie) : Town Hall – Church – 1917.
- Noirmoutier (Vendée) :
- La Guérinière : Museum of Traditions of the Island – Paysage.
- L'Épine : Town Hall – Le marché de L'Épine – 1922.
- Noirmoutier-en-l’Île : Musée du Château – Poster of the National Railways – Trips to the Ocean Islands – 1928.
- Association des Amis de Noirmoutier – 25 paintings (donated in 2013).[5] - Paris : Fonds municipal d’art contemporain de la ville de Paris : Retour de pêche (Island of Yeu) – 1925.
- Quimper (Finistère) : Musée départemental Breton – 9 paintings (donated in 2015).[5]
- Riom (Puy-de-Dôme) : Musée F. Mandet – Le lierre enlaçant la fleur – 1903.
- Vauhallan (Essonne) : Syndicat d’initiative – L’église de Vauhallan – 1897.
- Versailles (Yvelines) : Musée Lambinet – La gare des matelots – 1918.
Retrospectives since 2000
- Paris, Town Hall of the seventh Arrondissement, March 2000.
- Island of Noirmoutier, Museum of the Traditions of the Island of Noirmoutier : La Guérinière, April – June 2000 ; L'Épine, July–August 2005.
- Châtenay-Malabry, exhibition on the occasion of the hundredth anniversary of the death of Sully Prudhomme, May 2007.
- Les Lucs-sur-Boulogne, participation in the exhibition « Des toiles et des voiles – L’île d’Yeu sous le regard des peintres »,
Historial de Vendée, 29 June – 23 September 2007. - Vauhallan, participation in the exhibition on the First World War, November 2008. Photos of some ten works.
- Île d’Yeu, participation in the exhibition on the artists of the La Meule Port, August 2009[6]
Bibliography
- Vincent Cristofoli, « Léon Printemps » in : Lettre aux Amis, Bulletin des Amis de l’île d’Yeu de Noirmoutier, 2000, n° 117, p. 3-7.
- Jean-François Henry, Marc-Adolphe Guégan, Poète de l’île d’Yeu, Town Hall of the Island of Yeu, 2009, 116 p.[6]
- Jacques Noireau, Léon Printemps – Catalogue raisonné, 2013 (printed in Belgium), 128 p. (ISBN 978-90-9027677-9)[7]
- Jacques Noireau, Léon Printemps, 2004, 82 p. (ISBN 2-9521233-0-6).[7]
- Caroline Mignot, Les élèves de Gustave Moreau au dernier Salon de la Rose-Croix (1897), Université Rennes II, September 2000. History of Art, Master's degree dissertation.
- Claire Printemps, Jacques Noireau, René Printemps, 2004, 69 p. (ISBN 2-9523305-0-6).[7]
- Patrick de Villepin, Le Bois de la Chaise – Le « petit Éden » de l’île de Noirmoutier, Vendée Patrimoine, 2009, Volume II.
- François Wiehn, Gérard Aubisse, Dictionnaire des peintres de Vendée, La Crèche, Geste Éditions, 2010, 434 p. (ISBN 978-2845617063).
- S.N. (collective work), L’île d’Yeu. Des peintres et des marins. 1850 à 1950, Paris, Éditions d’art Somogy, 2007, 460 p., 650 illustrations.
- S.N., « Sully Prudhomme par Léon Printemps, histoire d’un portrait » Article published in the Bulletin Municipal of May 2007 published by the municipality of Châtenay-Malabry following the donation by the family of the portrait of Sully Prudhomme.
Notes and references
- ↑ Musée National Eugène Delacroix website
- ↑ Cf. Caroline Mignot, op.cit., p. 119-120.
- ↑ This painting inspired two exhibitions : (a) Museum of Art and History of Narbonne : July–September 1996 ; (b) Museum of Fine Arts of Nice : 18 October 1996 – 19 January 1997. It is also included on page 52 of a catalogue of the Museum of Fine Arts in Nice, entitled : Vigne, Vins, Vignerons dans la peinture française, Les Presses de l’Imprimerie Escourbiac, Graulhet (Tarn), 1996.
- ↑ Donated by Jacques Noireau, the painter’s grandson, to the municipality of Laffaux and inauguration of the painting on 27 June 2009 during a conference at the Town Hall which focused on the First World War (CRID14-18).
- 1 2 3 Information obtained from the painter's family.
- 1 2 Léon Printemps was included in a section on five « artists from La Meule » (a port), which was published in the book on the poet Marc-Adolphe Guégan, edited by Jean-François Henry.
- 1 2 3 Catalogues still available from the editor.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Léon Printemps. |