Juxtaglomerular cell
| Juxtaglomerular cell | |
|---|---|
|
Microscopic image of juxtaglomerular cells | |
|
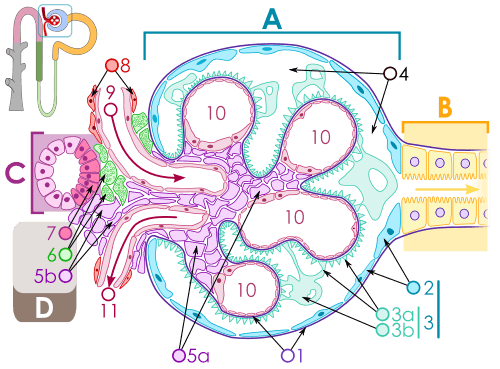
Drawing of renal corpuscle (juxtaglomerular cells (granular cells) are labeled as number 6. Macula densa cells are labeled 7, extra glomerular mesangium are labeled 5b. | |
The juxtaglomerular cells (JG cells, or granular cells) are cells in the kidney that synthesize, store, and secrete the enzyme renin. They are specialized smooth muscle cells mainly in the walls of the afferent arterioles, and some in the efferent arterioles, that deliver blood to the glomerulus. In synthesizing renin, they play a critical role in the renin-angiotensin system and thus in autoregulation of the kidney.
Juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin in response to a drop in pressure detected by stretch receptors in the vascular walls, or when stimulated by macula densa cells. Macula densa cells are located in the distal convoluted tubule, and stimulate juxtaglomerular cells to release renin when they detect a drop in sodium concentration in tubular fluid. Together, juxtaglomerular cells, extraglomerular mesangial cells and macula densa cells comprise the juxtaglomerular complex.
In appropriately stained tissue sections, juxtaglomerular cells are distinguished by their granulated cytoplasm.
The juxtaglomerular cell is a cell that is located near the glomerulus, hence its name.
Similar to cardiac tissue, juxtaglomerular cells harbor β1 adrenergic receptors. When stimulated by epinephrine or norepinephrine, these receptors induce the secretion of renin. These cells also respond directly to a decrease in systemic blood pressure which is manifested as a lower renal perfusion pressure.
See also
External links
- Histology image: 16010loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University