Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Council
| Legislative Council of Jammu and Kashmir | |
|---|---|
| 6th Assembly | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
Chairman | |
Deputy Chairman | |
Leader of House |
Naeem Akhtar (PDP) |
Leader of Opposition |
Shri Ali Mohammad Dar, JKNC |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 36 |
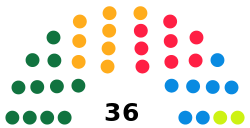 | |
Political groups |
PDP: 11 seats BJP: 8 seats NC: 8 seats INC: 7 seats Vacant: 2 seats |
| Meeting place | |
| Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Council | |
| Website | |
| http://jklegislativecouncil.nic.in | |
The Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Council (also known as the Jammu and Kashmir Vidhan Parishad) is the upper house of the legislature of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir; the lower house is the Legislative Assembly of Jammu and Kashmir. The Jammu and Kashmir State Legislature consists of the Governor, Legislative Assembly and Legislative Council.[1]
History
The first legislature of the kingdom that is now the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir was established by the government of the Maharaja of Kashmir Hari Singh in 1934.[2] In 1957, according to the Legislative Councils Act by the Parliament of India and a new constitution was adopted by the constituent assembly, a bicameral legislature system was founded.[1][2]
Membership and tenure
Largely governed by the Indian Constitution and acts of the Indian Parliament, the eligibility criteria for membership of the Legislative Council is:[3]
- The person must be a citizen of India.
- The person must be at least 30 years of age.
- Must possess the qualifications stipulated by any act of Parliament.
- The person must not hold any office of profit in the Union or state government(s), other than a ministerial position. If he does, he must resign from it upon election
- The person cannot be member any Vidhan Sabha, the Lok Sabha, or the Rajya Sabha
- Must be of sound mind and physical health, as determined by a court.
Members of the Legislative Councils serve a fixed six-year term.[3] One-third of the membership retires every two years, but members are eligible for re-election. Unlike the lower house, the composition of the council is not determined by direct popular vote. As per law, the council's membership cannot exceed 40 seats; currently the Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Council is composed of 36 seats, as per section 50 of the state constitution.[3][4]
Composition of Legislative Council
Legislative Council shall consist of thirty-six members, chosen in the manner provided in this section.
- Eleven members shall be elected by the members of the Legislative Assembly from amongst persons who are residents of the Province of Kashmir such that of the members so elected, at least one shall be a resident of Tehsil Leh and at least one shall be a resident of Tehsil Kargil.
- Eleven members shall be elected by the members of the Legislative Assembly from amongst persons who are residents of the Province of Jammu such that of the members so elected, at least one shall be a resident of Doda District and at least one shall be a resident of Poonch District.
- One member each shall be elected from the members of municipal council, town area committees and notified area committees in the Province of Kashmir and Jammu resptively (1(K) + 1(J) =Total two)
- Two members each shall be elected by the members of the Panchayats and such other local bodies in the Province of Kashmir and Jammu respectively (2(K) + 2(J) =Total four)
- Eight members shall be nominated by the Governor, not more than three of whom shall be persons belonging to any of the socially or economically backward classes in the State, and the others shall be persons having special knowledge or practical experience in respect of matters such as literature, science, art, co-operative movement and social service.
Functions
The Legislative Council serves two sessions - budget and monsoon.[5] However, it can be convened at any time by the state governor. It lacks many of the powers and responsibilities that are bestowed to the Legislative Assembly.[3] While any form of legislation save those concerning financial appropriations may originate in the council, the lower house is the source of most legislation, which upon passage is forward for approval by the Legislative Council.[3] In addition, it is required to decide an appropriations bill sent from the Legislative Assembly within 14 days.[3][4] Legislation not concerning appropriations has to be decided upon within three months.[3][4] Whether a bill is an Ordinary Bill or a Money bill, is decided by the Speaker of the Vidhan Sabha. However, the Vidhan Parishad does enjoy some amount of power.
- It is not subject to dissolution. It is a permanent House.
- It is highly specialised and professional
- It can send bills back for reconsiderations, with or without recommendations
- it can delay bills for a maximum of six months (two considerations), by which time the Vidhan Sabha may withdraw the bill
Current members
| SNo | NAME OF MEMBER | Constituency | Party Position | Term Commences | Retirement | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hussain Shri Master Noor | Assembly - Jammu | J&KNC | 20-04-2011 | 19-04-2017 | |
| 2 | Sharma Shri Jugal Kishore | Assembly - Jammu | INC | 26-03-2012 | 19-04-2017 | |
| 3 | Blowria Smt. Rani Gargi | Assembly - Jammu | INC | 17-03-2013 | 16-03-2019 | |
| 4 | Firdoos Ahmad Tak | Assembly - Jammu | PDP | 03-03-2015 | 16-03-2019 | |
| 5 | Sharma Shri Yash Pal | Assembly - Jammu | PDP | 17-03-2013 | 16-03-2019 | |
| 6 | Surinder Kumar Choudhary | Assembly - Jammu | PDP | 17-03-2015 | 16-03-2021 | |
| 7 | Charanjeet Singh | Assembly - Jammu | BJP | 17-03-2015 | 16-03-2021 | |
| 8 | Vibod Gupta | Assembly - Jammu | BJP | 17-03-2015 | 16-03-2021 | |
| 9 | Sajad Ahmad Kichloo | Assembly - Jammu | J&KNC | 17-03-2015 | 16-03-2021 | |
| 10 | Gupta Shri Naresh Kumar | Assembly - Jammu (Doda) | INC | 17-03-2013 | 16-03-2019 | |
| 11 | Mir Shri Jehangir Hussain | Assembly - Jammu (Poonch) | INC | 20-04-2011 | 19-04-2017 | |
| 12 | Yasir Reshi | Assembly - Kashmir | PDP | 03-03-2015 | 19-04-2017 | |
| 13 | Singh Sardar Dharam Bir | Assembly - Kashmir | J&KNC | 20-04-2011 | 19-04-2017 | |
| 14 | Veeri Dr. S Bashir Ahmad | Assembly - Kashmir | J&KNC | 20-04-2011 | 19-04-2017 | |
| 15 | Andrabi Syed Naeem Akhtar | Assembly - Kashmir | PDP | 17-03-2013 | 16-03-2019 | Minister for Education |
| 16 | Sofi Yousuf | Assembly - Kashmir | BJP | 03-03-2015 | 16-03-2019 | |
| 17 | Ganai Shri Showkat Hussain | Assembly - Kashmir | J&KNC | 17-03-2013 | 16-03-2019 | |
| 18 | Parrey Shri Mohammad Muzaffar | Assembly - Kashmir | INC | 17-03-2013 | 16-03-2019 | |
| 19 | Qaiser Jamshed Lone | Assembly - Kashmir | J&KNC | 17-03-2015 | 16-03-2021 | |
| 20 | Javed Ahmad | Assembly - Kashmir | PDP | 17-03-2015 | 16-03-2021 | |
| 21 | Anayat Ali | Assembly - Kashmir (Kargil) | PDP | 17-03-2015 | 16-03-2021 | |
| 22 | Chering Dorjay | Assembly - Kashmir (Ladakh) | BJP | 17-03-2015 | 16-03-2021 | Minister for Cooperatives |
| 23 | Vacant | Local Bodies - Jammu | from 16-10-2011 caused due to retirement of S. Arvinder
Singh. | |||
| 24 | Vacant | Local Bodies - Kashmir | from 28-12-2008 caused due to election of Shri Nizam-ud-din
Bhat as MLA. | |||
| 25 | Bhagat Shri Sham Lal | Panchayat - Jammu | INC | 07-12-2012 | 06-12-2018 | |
| 26 | Ganai Dr.(Ms.) Shehnaz | Panchayat - Jammu | J&KNC | 07-12-2012 | 06-12-2018 | |
| 27 | Dar Shri Ali Mohammad | Panchayat - Kashmir | J&KNC | 07-12-2012 | 06-12-2018 | |
| 28 | Monga Shri Ghulam Nabi | Panchayat - Kashmir | INC | 07-12-2012 | 06-12-2018 | |
| 29 | Zafar Iqbal Manhas | Nominated | PDP | 09-04-2015 | 08-04-2021 | |
| 30 | Ashok Khajuria | Nominated | BJP | 09-04-2015 | 08-04-2021 | |
| 31 | Vikramaditya Singh | Nominated | PDP | 09-04-2015 | 08-04-2021 | |
| 32 | Ramesh Arora | Nominated | BJP | 09-04-2015 | 08-04-2021 | |
| 33 | Saif-ud-din Bhat | Nominated | PDP | 09-04-2015 | 08-04-2021 | |
| 34 | Ajatshatru Singh | Nominated | BJP | 09-04-2015 | 08-04-2021 | |
| 35 | Mohammad Khursheed Alam | Nominated | PDP | 09-04-2015 | 08-04-2021 | |
| 36 | Surinder Mohan Ambardar | Nominated | BJP | 09-04-2015 | 08-04-2021 |
Party-wise strength of Members in J&K Legislative Council
- Jammu and Kashmir People’s Democratic Party—11
- Bhartiya Janata Party—08
- Jammu and Kashmir National Conference—08
- Indian National Congress—07
- Vacancies:- 2 seats (Local Bodies).
Total Strength—36
Office bearers
The Legislative Council is headed by a Chairman and Deputy Chairman chosen by members of the councils. The "Leader of the House" is the leader of the party (or coalition) holding the most number of seats in the council. The "Leader of the Opposition" represents the second-largest party or coalition. The present office-bearers are:[5]
- Chairman:Haji Inayat Ali (PDP)
- Deputy Chairman:Jahangir Hussain Mir INC
- Leader of the House: Naeem Akhtar (PDP)
- Leader of the Opposition: Ali Mohammad Dar JKNC
- Secretary: Abdul Majid Bhat
References
- 1 2 "Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Council". National Informatics Centre. Retrieved 31 August 2010.
- 1 2 "Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly". National Informatics Centre. Retrieved 29 August 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 J.C. Johari (2004). Indian Polity: A Concise Study of the Indian Constitution, Government and Politics. Lotus Press. pp. 127–30. ISBN 978-81-89093-68-6.
- 1 2 3 Pooja Narang (1999). Encyclopedaedic Dictionary of Business Organization. Sarup & Sons. pp. 485–95. ISBN 978-81-7625-059-7.
- 1 2 "Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Council". National Informatics Centre. Retrieved 31 August 2010.