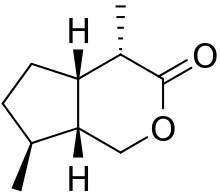
Iridomyrmecin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(4S,4aS,7S,7aR)-4,7-dimethylhexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-3(1H)-one | |
| Other names
Iridomyrmexin | |
| Identifiers | |
| 485-43-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 390867 |
| PubChem | 442427 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H16O2 | |
| Molar mass | 168.24 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Iridomyrmecin is a defensive chemical, classified as an iridoid, isolated from ants of the genus Iridomyrmex.[1] Iridomyrmecin is also found in a variety of plants including Actinidia polygama.[2]
References
- ↑ Cavill, G. W. K.; Ford, D. L.; Locksley, H. D. (1956). "The chemistry of ants. I. Terpenoid constituents of some Australian Iridomyrmex species". Australian Journal of Chemistry. 9 (2): 288–293. doi:10.1071/CH9560288.
- ↑ Sakan, Takeo; Isoe, Sachihiko; Hyeon, Suong Be; Katsumura, Ryuichi; Maeda, Takashi; Wolinsky, Joseph; Dickerson, Dorsey; Slabaugh, Michael; Nelson, David (1965). "Exact nature of matatabilactone and the terpenes of Nepeta cataria". Tetrahedron Letters. 46: 4097–4102. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)99572-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/1/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.