Idolomantis diabolica
| Devil's flower mantis Idolomantis diabolica | |
|---|---|
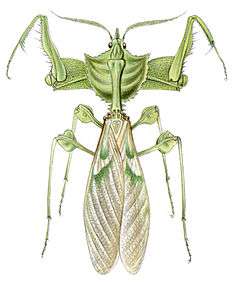 | |
| Idolomantis diabolica adult male (dorsal) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Mantodea |
| Family: | Empusidae |
| Subfamily: | Blepharodinae |
| Genus: | Idolomantis Uvarov, 1940 |
| Species: | I. diabolica |
| Binomial name | |
| Idolomantis diabolica (Saussure, 1869) | |
| Synonyms[1][2] | |
| |
Idolomantis diabolica, commonly known as the devil's flower mantis or giant devil's flower mantis, is one of the largest species of praying mantis, possibly the largest that mimics flowers. It is the only species classified under the genus Idolomantis.[3]
Description

Idolomantis diabolica is a large mantis of the family Empusidae. Females grow to be about 13 centimetres (about 5 inches) in length and males to about 10 centimetres (about 4 inches).[4] They are native to Ethiopia, Kenya, Malawi, Somalia, Tanzania, South Sudan and Uganda. Its threat display is magnificently colored, with red, white, blue, purple and black.[5]
Anatomy
The anatomical structure of Idolomantis diabolica is almost identical to species of the mantodea order, however, the morphology of each species varies according to the native habitat.
Head
The head of Idolomantis diabolica contains three vital components: compound eyes, antennas, and mandibles. The compound eyes, composed of thousands of individual photoreceptor cells, facilitates sight. The photoreceptor units, for instance, allows the insect to capture a perceptual span of 180 degrees.[6] This allows Idolomantis diabolica to identify prey and predators without hindering its vulnerability. The antennae, a pair of long and thin bristles, serve as the insect's sensory perception. Projecting outwards, the antennae can detect much in the surrounding environment such as chemicals, movement, and odors. The male antennae are more developed than those of the females and are feather-like. This allows them to track down females by analysing the pheromones released by the females. These pheromones notify the males that the females are ready to reproduce.[7] The mandibles, denoted as the "jaws" of an insect, act as a food processor. For example, the mandibles can be used to "tear, puncture, or grind" food.[8]
Thorax
The thorax constitutes a large portion of the insect's body. In fact, it is composed of three sections: the "prothorax, mesothorax, and metathorax".[9] Each section "contains one pair of legs, however, the wings are found only on the mesothoracic and metathoracic segments."[7]
Abdomen
Reproductive organs, respiratory organs, and other organ systems occupy the abdomen region of the insect. Sclerites reside above the abdomen region to prevent puncture or fracture to the internal organs.
Behaviour
Defensive behaviour
In the event of being confronted by a predator, Idolomantis diabolica initiates a deimatic display in an attempt "to scare off or momentarily distract a predator".[10] Its front legs, specifically the femur, are raised to expose the conspicuous patterns depicted on the bottom of the thorax and abdomen. Similarly, the wings display a combination of vibrant colours. Observational analysis of Idolomantis diabolica in captive settings revealed an additional tactic of shifting its wings left to right to startle and confuse predators.[11]
Predatory behaviour
In the presence of prey, Idolomantis diabolica, impersonating a flower, remains motionless. The objective is to seduce the insect into its striking zone. In this zone, Idolomantis diabolica utilizes the tibia portion of its leg to grasp and maintain a strong grip on the prey. The mandibles are then "wielded as formidable weapons" to decapitate and devour the prey.[8] The dietary preference of Idolomantis diabolica is exclusive to airborne insects, specifically "flies, moths, butterflies and beetles".[12]
Reproduction
Copulation
Before reproducing, mature females display dimorphic features in an attempt to attract males. Females lower the "tip of their abdomen and raising the wings slightly to expose more of the uppermost side of the abdomen, thus releasing pheromone to attract a mate".[12] However, sexual cannibalism is prominent among pairs of Idolomantis diabolica that remain in captivity. Due to its precautions nature, intrusive environments conjure up aggressive behaviour. For example, a female, in the process of copulating, adopts predatorial instincts which often conclude with the female devouring the head of the male.[6]
Nymphs
Females deposit eggs in an ootheca constructed to withstand approximately ten to fifty nymphs.[12] The incubation period varies according to temperature and humidity, however, observational analysis reveals an average duration of fifty days is required for hatching.[13] Upon entering the instar stage, the developmental period of an insect, the nymphs feed on small insects such as houseflies and fruit flies. In addition, "males will develop into adults after about 7 moultings, while females develop after 8 moultings".[12] The average lifespan of Idolomantis diabolica varies according to the habitat, however, the average lifespan is twelve months.[6]
Pet Industry
Due to its beauty and dramatic displays, Idolomantis diabolica is considered a prestigious pet. Consumers, specifically in the western hemisphere, purchase thousands on a yearly basis.
See also
References
- ↑ "Idolomantis diabolica (Saussure, 1869)". Mantodea Species File (Version 1.0/4.0). Retrieved March 3, 2012.
- ↑ William Forsell Kirby (1904). A Synonymic Catalogue of Orthoptera. Volume 1. Orthoptera Euplexoptera, Cursoria, et Gressoria (Forficulid , Hemimerid , Blattid , Mantid , Phasmid ) (PDF). p. 316.
- ↑ "Idolomantis Uvarov, 1940". Mantodea Species File (Version 1.0/4.0). Retrieved March 3, 2012.
- ↑ http://www.swissmantis.ch/articles.php?lng=de&pg=90
- ↑ "Idolomantis diabolica (Devils flower mantis) Caresheet". InsectStore. Retrieved March 3, 2012.
- 1 2 3 Laman, Tim. "Praying Mantis". National Geographic. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- 1 2 "Insect Morphology". University of Sydney. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- 1 2 Schmidt, Chris. "Morphological and Functional Diversity of Ant Mandibles". Tree of Life. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- ↑ "Insect Morphology". University of Syndey. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- ↑ "Devils Flower Mantis". Keeping Insects. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- ↑ "Devils Flower Mantis". Keeping insects. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 "Giant Devils Flower Mantis" (PDF). Louisville Zoo. Retrieved 1 April 2014.
- ↑ Saw, Yen. "Giant Devil Flower Mantis Log". USA Mantis. Retrieved 2 April 2014.