Tukang Besi language
| Tukang Besi | |
|---|---|
| Native to | Indonesia |
| Region | Sulawesi, Tukang Besi Archipelago |
Native speakers | 250,000 (1995)[1] |
|
Austronesian
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 |
Either: khc – Tukang Besi North bhq – Tukang Besi South |
| Glottolog |
tuka1247[2] |
Tukang Besi is an Austronesian language spoken in the Tukangbesi Islands in southeast Sulawesi in Indonesia by a quarter million speakers.
Phonology
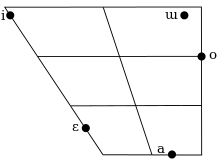
The vowel phonemes of Tukang Besi
The northern dialect of Tukang Besi has 25 consonant phonemes and a basic 5-vowel system.[3] It features stress which is usually on the second-to-last syllable. The language has two implosive consonants, which are uncommon in the world's languages. The coronal plosives and /s/ have prenasalized counterparts which act as separate phonemes.
| Bilabial | Dental/ Alveolar |
Velar | Glottal | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||||
| Plosive | plain | p | b | t̪ | (d̪) | k | ɡ | ʔ |
| prenasalized | mp | mb | n̪t̪ | n̪d̪ | ŋk | ŋɡ | ||
| Implosive | ɓ | ɗ̪ | ||||||
| Fricative | plain | β | s | (z) | h | |||
| prenasalized | n̪s̪ | |||||||
| Trill | r | |||||||
| Lateral | l̪ | |||||||
/b/ only appears in loanwords, but it contrasts with /ɓ/. [d] and [z] are not phonemic and appear only as allophones of /dʒ/ which appears only in loanwords.
References
- ↑ Tukang Besi North at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
Tukang Besi South at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) - ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Tukang Besi". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Donohue, Mark (1999). "Tukang Besi". Handbook of the International Phonetic Association. Cambridge University Press. pp. 151–53. ISBN 0-521-65236-7.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/1/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.