Aridity index
An aridity index (AI) is a numerical indicator of the degree of dryness of the climate at a given location. A number of aridity indices have been proposed (see below); these indicators serve to identify, locate or delimit regions that suffer from a deficit of available water, a condition that can severely affect the effective use of the land for such activities as agriculture or stock-farming.
Historical background and indices
At the turn of the 20th century, Wladimir Köppen and Rudolf Geiger developed the concept of a climate classification where arid regions were defined as those places where the annual rainfall accumulation (in centimetres) is less than 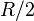 , where:
, where:
-
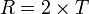 if rainfall occurs mainly in the cold season,
if rainfall occurs mainly in the cold season, -
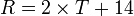 if rainfall is evenly distributed throughout the year, and
if rainfall is evenly distributed throughout the year, and -
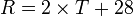 if rainfall occurs mainly in the hot season.
if rainfall occurs mainly in the hot season.
where 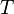 is the mean annual temperature in Celsius.
is the mean annual temperature in Celsius.
This was one of the first attempts at defining an aridity index, one that reflects the effects of the thermal regime and the amount and distribution of precipitation in determining the native vegetation possible in an area. It recognizes the significance of temperature in allowing colder places such as northern Canada to be seen as humid with the same level of precipitation as some tropical deserts because of lower levels of potential evapotranspiration in colder places. In the subtropics, the allowance for the distribution of rainfall between warm and cold seasons recognizes that winter rainfall is more effective for plant growth that can flourish in the winter and go dormant in the summer than the same amount of summer rainfall during a warm-to-hot season. Thus a place like Athens, Greece that gets most of its rainfall in winter can be considered to have a humid climate (as attested in lush foliage) with roughly the same amount of rainfall that imposes semi-desert conditions in Midland, Texas, where rainfall largely occurs in the summer.
In 1948, C. W. Thornthwaite proposed an AI defined as:
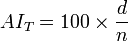
where the water deficiency 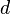 is calculated as the sum of the monthly differences between precipitation and potential evapotranspiration for those months when the normal precipitation is less than the normal evapotranspiration; and where
is calculated as the sum of the monthly differences between precipitation and potential evapotranspiration for those months when the normal precipitation is less than the normal evapotranspiration; and where 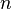 stands for the sum of monthly values of potential evapotranspiration for the deficient months (after Huschke, 1959). This AI was later used by Meigs (1961) to delineate the arid zones of the world in the context of the UNESCO Arid Zone Research programme.
stands for the sum of monthly values of potential evapotranspiration for the deficient months (after Huschke, 1959). This AI was later used by Meigs (1961) to delineate the arid zones of the world in the context of the UNESCO Arid Zone Research programme.
In the preparations leading to the UN Conference on Desertification (UNCOD), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) issued a dryness map based on a different aridity index, proposed originally by Mikhail Ivanovich Budyko (1958) and defined as follows:
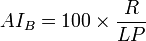
where 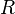 is the mean annual net radiation (also known as the net radiation balance),
is the mean annual net radiation (also known as the net radiation balance), 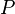 is the mean annual precipitation, and
is the mean annual precipitation, and 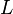 is the latent heat of vaporization for water. Note that this index is dimensionless and that the variables
is the latent heat of vaporization for water. Note that this index is dimensionless and that the variables 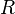 ,
, 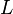 and
and 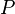 can be expressed in any system of units that is self-consistent.
can be expressed in any system of units that is self-consistent.
More recently, the UNEP has adopted yet another index of aridity, defined as:
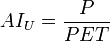
where 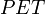 is the potential evapotranspiration and
is the potential evapotranspiration and 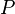 is the average annual precipitation (UNEP, 1992). Here also,
is the average annual precipitation (UNEP, 1992). Here also, 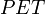 and
and 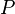 must be expressed in the same units, e.g., in millimetres. In this latter case, the boundaries that define various degrees of aridity and the approximate areas involved are as follows:
must be expressed in the same units, e.g., in millimetres. In this latter case, the boundaries that define various degrees of aridity and the approximate areas involved are as follows:
| Classification | Aridity Index | Global land area |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperarid | AI < 0.05 | 7.5% |
| Arid | 0.05 < AI < 0.20 | 12.1% |
| Semi-arid | 0.20 < AI < 0.50 | 17.7% |
| Dry subhumid | 0.50 < AI < 0.65 | 9.9% |
See also
References
- Budyko, M. I. (1958) The Heat Balance of the Earth's Surface, trs. Nina A. Stepanova, US Department of Commerce, Washington, D.D., 259 p.
- Huschke, Ralph E. (1959) Glossary of Meteorology, American Meteorological Society, Boston, Second printing-1970.
- McIntosh, D. H. (1972) Meteorological Glossary, Her Majesty's Stationery Office, Met. O. 842, A.P. 897, 319 p.
- Meigs, P. (1961) 'Map of arid zone', in L. D. Stamp (Editor) A History of Land Use in Arid Regions, UNESCO Arid Zone Research, Publication XVII, Paris, 388 p.
- UNCOD Secretariat (1977) Desertification: Its causes and consequences, Pergamon Press, 448 p.
- UNEP (1992) World Atlas of Desertification.